Valve delay steam auto updates preserve bandwidth coronavirus – Valve delaying Steam auto-updates to preserve bandwidth during the coronavirus pandemic is a fascinating case study in balancing user experience with network resources. This article dives deep into the strategies Valve employed, examining the technical challenges, user impact, and alternative approaches.
The pandemic significantly increased the demand for bandwidth-intensive services like Steam. This article explores the various methods Valve used to mitigate these issues, considering the trade-offs between update speed and bandwidth conservation. We’ll analyze the impact on user experience, examine alternative update strategies, and discuss security considerations related to these bandwidth-saving measures.
Valve Delay Mechanisms
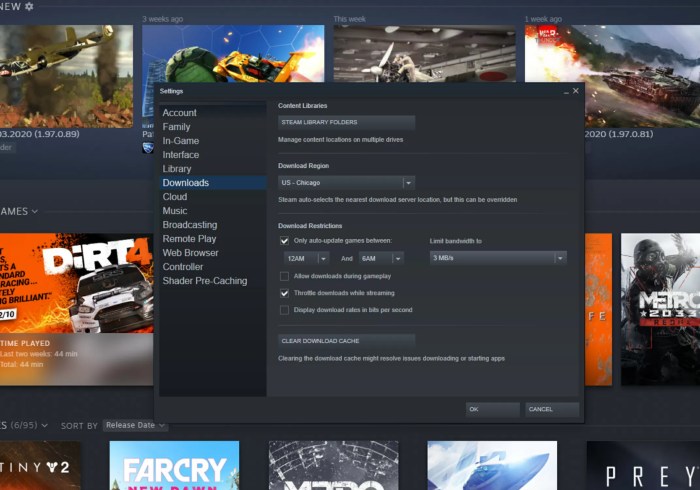
Valve’s Steam platform, crucial for game distribution and updates, faces the challenge of managing bandwidth usage and ensuring a smooth user experience. To address this, various strategies are employed to delay automatic updates, balancing these competing needs. This analysis delves into the methods Valve utilizes, the associated technical considerations, and the trade-offs involved in implementing these delays.Methods for Delaying Steam Auto-UpdatesValve employs a range of techniques to introduce delays in auto-updates, aiming to mitigate bandwidth strain on their servers and users.
These strategies are crucial for maintaining service reliability during periods of high traffic and ensuring a positive user experience.
Update Scheduling and Prioritization
Steam implements a sophisticated update scheduling system. Updates are often prioritized based on factors like file size, update frequency, and anticipated user demand. Smaller, less critical updates may be scheduled during off-peak hours or when server load is lower. This strategy aims to distribute the update traffic more evenly, minimizing potential bottlenecks and maximizing network efficiency. Furthermore, updates for specific games might be scheduled concurrently but staggered to reduce the overall impact on a single user’s bandwidth.
Bandwidth Throttling
This method involves limiting the rate at which update data is transferred. A dynamic throttling system can adjust the download speed based on factors like network conditions, user bandwidth, and server capacity. By reducing the data transfer rate, the system aims to prevent overloading the network infrastructure and maintain responsiveness during periods of high traffic. This technique can be particularly effective in reducing the impact on users with limited bandwidth, ensuring that updates do not consume excessive resources.
Update Chunking and Differential Updates
To reduce the total amount of data downloaded, Steam frequently employs techniques like update chunking. Large updates are divided into smaller segments, allowing users to download parts of the update asynchronously. Furthermore, differential updates identify the changes since the last version. This method significantly reduces the amount of data users need to download, saving bandwidth and time.
This approach is crucial for minimizing the impact of large updates on users’ bandwidth.
Network Congestion Avoidance
Steam implements strategies to identify and mitigate network congestion. This can involve detecting patterns of high traffic and adjusting update schedules or download speeds accordingly. The system might also use predictive models to anticipate network congestion and proactively reduce download speeds to prevent overloading the network. These measures ensure a stable and predictable user experience, even during periods of network strain.
Comparison of Delay Methods
| Delay Method | Impact on User Experience | Bandwidth Usage | Technical Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Update Scheduling | Generally positive, users may experience slight delays but reduced overall strain. | Moderate, dependent on schedule effectiveness. | Requires accurate traffic prediction and adaptability to dynamic conditions. |
| Bandwidth Throttling | Users might notice slower download speeds, but overall stability is enhanced. | Significantly reduced during peak periods. | Requires precise calculation of user bandwidth and server capacity. |
| Update Chunking/Differential Updates | Improved download speed and reduced latency, especially for large updates. | Substantially reduced data transfer. | Requires complex update management and efficient data handling. |
| Network Congestion Avoidance | Minimizes interruptions during periods of high network traffic. | Dynamically adjusts bandwidth usage. | Requires sophisticated algorithms to detect and predict congestion. |
Hierarchical Structure of Delay Techniques
The delay techniques used by Valve form a hierarchical structure, with different strategies interacting and complementing each other. At the highest level, the overarching goal is to minimize bandwidth consumption and ensure a positive user experience. Within this framework, scheduling, throttling, chunking, and congestion avoidance are deployed as individual strategies, each with a specific role in the overall process.
Bandwidth Preservation Strategies
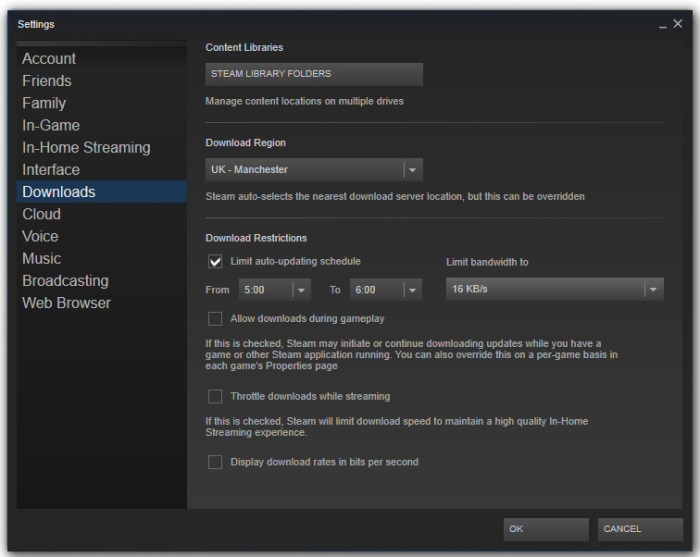
Steam’s auto-updates, crucial for maintaining a smooth gaming experience, often strain bandwidth, especially during periods of high user activity. This is amplified by the coronavirus pandemic, with increased internet usage and potentially limited bandwidth availability for many users. Efficient bandwidth preservation strategies are thus paramount to ensure a positive user experience. This blog post will explore various techniques employed by online services like Steam to optimize auto-update downloads and minimize bandwidth consumption.Optimizing bandwidth usage during Steam auto-updates is vital to maintain a positive user experience, especially in the context of increased internet usage during the pandemic.
Effective strategies, implemented on both the client and server sides, are crucial for minimizing the strain on users’ internet connections. This includes techniques for optimizing download processes, prioritizing downloads, and strategically managing server resources.
Steam’s valve delay auto-updates during the coronavirus pandemic were a real bandwidth-saving lifesaver. It’s amazing how much these seemingly small things can impact our online experiences, especially now. And speaking of performance, have you checked out the cutting-edge Chagall van den Berg performance sensors gloves motion tracking suit? chagall van den berg performance sensors gloves motion tracking suit It’s got advanced technology for capturing motion, and it’s certainly a cool addition to any athlete’s arsenal.
Luckily, these bandwidth-saving strategies from Steam are still a crucial factor in managing online resources, especially during peak times and when bandwidth is tight.
Strategies for Preserving Bandwidth
Efficient bandwidth management during auto-updates requires a multi-faceted approach. Prioritizing downloads and strategically controlling download speeds are essential to avoid overwhelming users’ connections. This includes techniques like throttling download rates during peak hours or using adaptive algorithms that adjust download speeds based on real-time network conditions.
- Download Throttling: Implementing download throttling mechanisms can help regulate the rate of data transfer, preventing sudden spikes in bandwidth consumption. This can be achieved by limiting the download speed to a pre-defined threshold, particularly during peak hours or times of high network congestion. This technique is widely used in online services to prevent overwhelming servers and maintain a smooth experience for all users.
For example, Netflix uses throttling to manage simultaneous streams and ensure a consistent experience for all subscribers.
- Adaptive Download Speed Control: Utilizing algorithms that dynamically adjust download speeds based on real-time network conditions is an effective strategy. These algorithms can analyze factors such as available bandwidth, latency, and network congestion to adjust the download speed accordingly. This ensures that the download rate remains manageable and avoids unnecessary strain on the user’s connection. For instance, many file-sharing services use adaptive algorithms to adjust download speeds in response to fluctuations in network traffic.
- Prioritization of Updates: Prioritizing the download of critical updates over non-essential ones can significantly reduce bandwidth usage. This technique involves categorizing updates based on their importance and urgency. Essential updates, such as security patches, are downloaded and installed first, while less critical updates can be deferred or scheduled for later download. This strategy is common in operating systems to prioritize critical system files over other data.
Techniques for Optimizing the Download Process
Several techniques are employed to optimize the download process and minimize bandwidth usage. These techniques involve various methods, from intelligent file splitting to efficient compression algorithms.
- File Chunking and Splitting: Dividing large update files into smaller chunks significantly improves the efficiency of the download process. If a download is interrupted, only the missing chunks need to be re-downloaded, thus minimizing wasted bandwidth. This is a common practice in many online file-sharing and streaming services to handle large files.
- Efficient Compression Algorithms: Using advanced compression algorithms can significantly reduce the size of update files, resulting in lower bandwidth usage. This involves employing sophisticated algorithms to compress data, thereby reducing the overall data volume. Modern compression techniques are employed by numerous online services, including cloud storage providers and video streaming platforms, to optimize file sizes.
- Multi-threading and Concurrent Downloads: Employing multi-threading and concurrent download mechanisms allows for downloading multiple files or parts of a file simultaneously. This can significantly speed up the download process, especially for large updates, while potentially requiring less bandwidth per unit of time.
Server-Side Optimization
Server-side optimization plays a crucial role in minimizing bandwidth usage during auto-updates. This includes strategies like content delivery networks (CDNs), efficient server configurations, and optimized file structures.
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): Utilizing Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) strategically positions servers geographically closer to users. This reduces latency and network traffic, thus optimizing the download process and minimizing bandwidth usage. CDNs are widely used by popular websites and streaming services to improve user experience.
- Optimized Server Configurations: Implementing optimized server configurations, including high-performance hardware and efficient software, ensures that the server can handle requests effectively and distribute updates efficiently. These measures ensure that the server resources can effectively manage download requests.
- Optimized File Structures: Optimizing file structures can lead to smaller file sizes and improved download speeds. This involves using optimized file formats and implementing efficient file organization strategies. By structuring files strategically, servers can minimize the time required to transfer data.
Trade-offs between Download Speed and Bandwidth Usage
Balancing download speed and bandwidth usage is a crucial aspect of bandwidth preservation. Different strategies have varying impacts on these two factors.
| Strategy | Download Speed | Bandwidth Usage | Trade-offs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Throttling | Lower | Lower | Reduced download speed for faster bandwidth usage. |
| Adaptive Download Speed Control | Variable | Lower (on average) | Adjusts to network conditions for optimal bandwidth usage. |
| File Chunking | Potentially higher | Lower (in case of interruptions) | Improved reliability in case of network disruptions. |
| Compression Algorithms | Variable | Lower | Smaller file size, but might impact download speed if compression is too aggressive. |
Impact of Coronavirus on Steam Auto-Updates: Valve Delay Steam Auto Updates Preserve Bandwidth Coronavirus
The coronavirus pandemic significantly altered digital lifestyles, dramatically increasing reliance on online services. This surge in online activity naturally impacted the demand for bandwidth-intensive services like Steam auto-updates, forcing platforms like Valve to adapt their strategies for maintaining service quality and user experience. The pandemic’s influence on user behavior and network conditions necessitated innovative approaches to update processes, requiring a more nuanced understanding of bandwidth management.Valve’s proactive measures in response to the increased bandwidth demands highlight the critical role of adapting to unforeseen circumstances in maintaining a robust online platform.
Adjustments to auto-update strategies, combined with user behavioral shifts and network conditions, are crucial to maintaining a reliable service. This period served as a critical case study in adapting to fluctuating demand, demonstrating the need for robust bandwidth-efficient update mechanisms.
Valve’s Steam auto-updates are a real lifesaver, especially during bandwidth-constrained times like the coronavirus pandemic. It’s a bit frustrating when updates take forever, but the delays often help preserve bandwidth. Speaking of frustrating, I was saddened to hear about the passing of Lloyd Morrisett, co-creator of Sesame Street, at 93 lloyd morrisett co creator of sesame street dies at 93.
Hopefully, Valve will continue to optimize their system to make auto-updates as efficient as possible during these times. Bandwidth conservation is key, after all.
Potential Impact on Demand for Bandwidth-Intensive Services
The pandemic led to a dramatic increase in the use of online gaming and entertainment platforms. Remote work and learning environments further amplified the demand for high-bandwidth services. This surge in online activity directly translated into heightened demand for Steam auto-updates, as users relied more heavily on these platforms for entertainment and social interaction. Increased numbers of users engaging with Steam’s content during lockdowns and remote work periods resulted in higher bandwidth consumption during these times.
Valve’s Adjustments to Auto-Update Strategies
Valve, recognizing the amplified demand, implemented several adjustments to their auto-update strategies. These included optimizing update schedules, prioritising update downloads during off-peak hours, and utilizing intelligent download algorithms. Valve also focused on creating more bandwidth-efficient update packages to reduce the overall download time. These measures aimed to mitigate the strain on network infrastructure and provide a more seamless user experience.
Changes in User Behavior and Network Conditions
User behavior shifted significantly. With lockdowns and remote work becoming the norm, peak usage times for Steam services altered, and users often faced varying network conditions. Some users experienced higher latency, limited bandwidth, or intermittent connectivity, demanding more flexible update protocols. Valve had to account for these dynamic changes in user behaviour and network conditions, which necessitated adjusting update timings and methods.
Examples of Bandwidth-Efficient Update Mechanisms
Valve’s approach involved utilizing a tiered update system, prioritizing critical updates, and introducing optional update settings for users. The platform also employed more granular control over update frequency and size, allowing users to tailor their update experience to their individual needs and bandwidth limitations. These methods ensured the platform remained responsive and accessible to all users, even during periods of high demand.
Challenges in Managing Bandwidth Usage
Managing bandwidth usage amid the pandemic’s impact presented several challenges. Predicting fluctuating demand, optimizing update schedules, and ensuring consistent service availability across various network conditions required careful planning and execution. Balancing the needs of millions of users with the demands of the network infrastructure was a significant hurdle. Furthermore, ensuring that updates did not negatively impact online gameplay or social interactions was another challenge.
User Experience and Delay Perception
Steam’s auto-updates, crucial for maintaining a smooth user experience, are significantly impacted by bandwidth limitations and external factors. Understanding how users perceive these delays is paramount for maintaining user satisfaction and loyalty. A well-designed approach to managing and communicating these delays directly affects the overall experience with the platform.
Factors Influencing User Satisfaction with Delayed Updates
User perception of delays is complex and influenced by several factors. Foremost among these is the duration of the delay itself. Longer delays generally lead to increased frustration, especially if users are experiencing other concurrent issues or need to access Steam immediately for gaming or other activities. The frequency of updates also plays a crucial role. Users accustomed to frequent updates might become more sensitive to delays than those who anticipate updates less often.
The impact of the delay on the user’s workflow and the perceived urgency of the update are also key factors. For instance, if a critical security patch is delayed, the user’s perception of the delay will be considerably more negative than if it’s a minor cosmetic update.
Comparing User Experiences with Different Delay Strategies
Different delay strategies can significantly impact user experience. For example, a strategy that prioritizes bandwidth preservation during peak hours might lead to longer update times but potentially reduce overall network congestion. This strategy can be more acceptable to users if they are aware of the rationale and provided with clear communication. On the other hand, a strategy that aims for rapid updates, even if it leads to higher bandwidth consumption, might be perceived as more convenient, especially if the updates are perceived as non-critical.
The key lies in balancing user needs with network efficiency and overall platform stability.
Methods for Effective Delay Communication
Effective communication is essential when managing update delays. Transparency about the reasons behind the delays is critical. Users appreciate knowing the cause of the delay, whether it’s due to high network traffic, maintenance procedures, or external factors. Clear and concise messaging about the expected duration of the delay is also essential. Providing estimated completion times or progress updates can alleviate user anxiety and frustration.
Users should also be informed about alternative actions, such as delaying the update or accessing the platform through different methods if necessary.
The Importance of Transparency in Managing Update Delays
Transparency in managing update delays is paramount for maintaining user trust and satisfaction. When users understand the rationale behind delays, they are more likely to accept them. Open communication about the strategies employed to mitigate delays and the impact on user experience fosters a sense of partnership between the platform provider and its users. This, in turn, strengthens the user-platform relationship and promotes long-term loyalty.
For example, a transparent explanation of how the platform prioritizes critical updates over less urgent ones can improve user comprehension and reduce frustration.
Alternative Update Strategies for Steam
Steam’s current auto-update system, while functional, has faced criticism regarding bandwidth consumption and user experience, particularly during periods of high internet traffic. Exploring alternative update strategies is crucial for optimizing the service and enhancing user satisfaction. These strategies must balance the need for efficient updates with the desire to minimize disruption to the user experience.Optimizing Steam’s update process necessitates considering various factors.
Bandwidth usage, user experience during updates, and the technical feasibility of implementing new strategies are all critical considerations. By examining alternative approaches, Steam can potentially mitigate bandwidth strain and improve the overall user experience, particularly during peak network demands or in regions with limited internet access.
Differential Updates
Differential updates are a common technique in software distribution, where only the changed portions of a file are downloaded, rather than the entire file. This significantly reduces download sizes and speeds up the update process.Steam could implement a differential update strategy by comparing the user’s existing game files to the updated version. Only the modified sections of the files would be downloaded.
This would be particularly effective for games with frequent patches or expansions. A notable example of this approach is seen in many modern operating systems, significantly reducing download sizes and improving update speeds.The primary benefit of differential updates is the substantial reduction in bandwidth usage. However, this approach might introduce some complexity in the update process, potentially requiring more intricate file management and comparison algorithms.
Valve’s delayed Steam auto-updates, designed to preserve bandwidth during the coronavirus pandemic, are a smart move. While I’m sure many people are enjoying trading their pokemon tcg pocket trade cards , the bandwidth savings are a definite win for everyone. It’s a thoughtful approach that hopefully continues to address bandwidth needs in the future, even without a global pandemic.
Furthermore, the size of the initial download may still be significant for new users or for large game installations.
Scheduled Updates
Scheduled updates allow users to define times when updates are downloaded, typically during off-peak hours. This approach can help manage bandwidth consumption and avoid disrupting users during peak times.Implementing scheduled updates requires user input and a clear notification system. Users can choose their preferred update time, and the system would automatically initiate the download process. This approach has the advantage of minimizing interference with the user’s active gameplay sessions.
However, this system might require a more sophisticated user interface for configuration. It also assumes that users are willing to schedule updates, which could potentially impact the frequency of updates. For example, a user may opt for a scheduled update during the night when they are not actively using the internet.
Prioritized Updates
Prioritizing updates based on factors like user activity, game popularity, or network conditions can be a useful strategy. For example, updates for less popular games could be scheduled during off-peak hours, while updates for frequently played games might be prioritized to minimize disruption.Implementing prioritized updates would require a system for tracking user activity and game popularity. This could potentially involve a combination of server-side and client-side algorithms.
The advantage is that updates for frequently played games are downloaded promptly, reducing disruption. A potential drawback is the complexity in developing an effective prioritization algorithm, as well as the possibility of bias or fairness issues. This approach could be beneficial for bandwidth management and user experience.
Client-Side Caching
Client-side caching involves storing frequently accessed or recently downloaded data on the user’s computer. This approach allows for faster access to the same data in subsequent updates.By incorporating caching, Steam could store frequently used game assets or recently downloaded update components. This can significantly improve the speed and efficiency of future updates. The primary benefit is faster subsequent updates.
However, this approach might require more storage space on the user’s computer, potentially impacting user storage needs.
Comparison Table
| Strategy | Complexity | User Experience | Technical Feasibility | Bandwidth Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Differential Updates | Medium | Slightly Lower | High | Low |
| Scheduled Updates | Low | High | High | Medium |
| Prioritized Updates | High | Medium | High | Medium |
| Client-Side Caching | Medium | High | Medium | Low |
Update Frequency and User Needs
Balancing the desire for frequent software improvements with the need to preserve bandwidth is a critical challenge for platform providers like Valve. Users expect up-to-date features and bug fixes, while excessive update traffic can strain network infrastructure and negatively impact user experience. This section delves into the interplay between update frequency and user needs, exploring trade-offs and potential solutions.The optimal update frequency strikes a delicate balance between delivering timely improvements and minimizing the burden on users’ internet connections.
This balance is influenced by factors like the size of the updates, the typical user’s bandwidth, and the urgency of the updates. Understanding these dynamics is key to developing a sustainable update strategy.
Analysis of Update Frequency and User Needs, Valve delay steam auto updates preserve bandwidth coronavirus
Different user groups have varying needs regarding update frequency. Power users, who often rely on the latest features and functionalities, may prefer frequent updates, even if it means higher bandwidth consumption. Conversely, casual users or those with limited bandwidth might prefer less frequent, larger updates to minimize their download time.
Trade-offs Between Frequent Updates and Bandwidth Preservation
Delivering frequent updates, while providing users with the latest features, often leads to higher bandwidth consumption. This increased traffic can negatively impact the user experience, particularly for those with limited bandwidth. Conversely, infrequent updates, while preserving bandwidth, might leave users with outdated software, potentially leading to compatibility issues or missing crucial bug fixes.
Examples of Different Update Frequencies
Various software providers employ different update strategies. Some, like Adobe, prioritize frequent, incremental updates to ensure features are current and bugs are promptly addressed. Others, like some game developers, might adopt a larger, less frequent update approach, especially if the software updates involve significant changes. This strategy is more appropriate for less frequent feature releases. This also allows for more thorough testing and quality assurance, which can reduce the frequency of subsequent updates.
Optimal Update Frequency
Identifying the optimal update frequency requires careful consideration of several factors. It involves analyzing user feedback, bandwidth limitations, and the rate of bug fixes or feature additions. Furthermore, the size of the updates is also critical. A smaller, more frequent update is generally better for users with limited bandwidth.
Model Illustrating the Interplay Between Update Frequency, Bandwidth, and User Satisfaction
The relationship between update frequency, bandwidth usage, and user satisfaction can be illustrated through a model. The model would feature three interconnected axes:
- Update Frequency: High frequency updates are associated with more frequent downloads and higher bandwidth usage, while lower frequency updates lead to less frequent downloads and lower bandwidth usage.
- Bandwidth Consumption: This axis reflects the amount of data transferred during updates. High frequency updates typically result in higher bandwidth consumption, while infrequent updates lead to lower bandwidth consumption.
- User Satisfaction: This axis represents user experience. A balance between frequent updates and bandwidth preservation is crucial for achieving high user satisfaction. Frequent updates provide access to new features and bug fixes, which enhances satisfaction. However, high bandwidth consumption can lead to dissatisfaction due to slow downloads and frustrating wait times.
The model would visually represent the interplay between these factors, showing how different update strategies can lead to varying levels of user satisfaction and bandwidth usage. It would highlight the ideal balance point where update frequency aligns with user needs and bandwidth capacity, maximizing user experience.
Security Considerations in Delayed Updates
Delayed Steam updates, while beneficial for bandwidth management, introduce a crucial security challenge. Maintaining the integrity of user systems becomes paramount, especially when updates addressing critical vulnerabilities are held back. The potential for exploitation during this period necessitates proactive measures to safeguard user accounts and data.
Security Implications of Delayed Updates
Delayed updates, even with the best intentions, can create a window of vulnerability for users. Malicious actors might exploit known vulnerabilities in older software versions before patches are applied. This is particularly concerning for critical systems like operating systems and applications with security-sensitive components. Such delays can potentially expose users to malware, phishing attempts, or other malicious activities.
A classic example is the rapid proliferation of exploits for older operating system versions after security vulnerabilities are discovered, before patches are widely deployed.
Importance of Maintaining System Integrity
System integrity is paramount during any update cycle, but especially during delayed update implementations. Maintaining a secure baseline for user systems involves robust security measures. These measures must be actively monitored and updated to address emerging threats. This ensures the systems remain protected against attacks that target known vulnerabilities in older versions. Failing to prioritize system integrity during delayed updates can lead to significant security breaches and data loss.
Potential Security Vulnerabilities Associated with Delayed Auto-Updates
Delayed auto-updates can introduce several potential security vulnerabilities. Unpatched vulnerabilities in applications or operating systems can be exploited by malicious actors, potentially allowing unauthorized access or data breaches. Furthermore, the prolonged exposure of outdated software versions to attack surfaces increases the risk of exploitation. For example, a user running a vulnerable version of a game client for an extended period might be targeted by exploits.
These risks are further compounded if user systems have not been configured for automatic updates.
Mitigation Strategies for Potential Risks
Several measures can be taken to mitigate the risks associated with delayed auto-updates. Regular vulnerability assessments of affected software components are crucial. Prioritizing timely patching of known vulnerabilities is essential. Educating users about the importance of timely updates and the risks of delayed updates is equally vital. Implementing strong access controls and user authentication measures will help limit the potential damage from unauthorized access.
Security Best Practices During Delayed Update Implementations
| Category | Best Practice | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Proactive Security Measures | Regular Vulnerability Assessments | Identify and address potential vulnerabilities in software components before they are exploited. |
| Proactive Patching | Apply security patches as soon as they become available, even if updates are delayed. | |
| Regular Security Audits | Regularly review system configurations and user access controls for security vulnerabilities. | |
| User Education | Communicate Risks and Importance of Updates | Inform users about the potential security risks of delayed updates and the importance of keeping software up-to-date. |
| System Configuration | Enable Automatic Updates (where possible) | Enable automatic updates to ensure software is updated as soon as patches are released. |
| Strong Access Controls | Implement strong access controls to limit the potential damage from unauthorized access. |
Final Review
In conclusion, Valve’s approach to delaying Steam auto-updates during the pandemic highlights the intricate relationship between user experience, bandwidth management, and evolving network conditions. While the strategies implemented helped preserve bandwidth, the impact on user experience warrants further consideration. The need for transparent communication and user-centered design remains crucial in future update management, particularly in times of high network strain.