Ukraine Russia war impact on gas stocks inflation and the us economy is a complex issue with far-reaching consequences. The war’s disruption of global energy markets has sent gas prices soaring, contributing to inflation that’s impacting consumers and businesses across the US. This blog post will delve into the intricacies of this crisis, exploring how it affects gas stocks, inflation rates, and the overall health of the US economy.
We’ll analyze the government’s responses, explore energy security concerns, and examine how supply chains have been affected.
The war in Ukraine has triggered a ripple effect across various sectors, impacting everything from household budgets to the performance of major industries. This analysis will explore the multifaceted ways the conflict has shaped the US economic landscape, offering insights into the immediate and long-term consequences.
Impact on Gas Stocks: Ukraine Russia War Impact On Gas Stocks Inflation And The Us Economy
The war in Ukraine has sent shockwaves through the global energy market, dramatically impacting gas stock prices. The disruption of supply chains, coupled with geopolitical tensions, has created a volatile environment, forcing companies to adapt and investors to reassess their strategies. The cascading effects are being felt across the entire energy sector, with long-term implications for both consumers and businesses.
Gas Stock Price Fluctuations
The war in Ukraine has significantly affected gas stock prices. The disruption of Russian gas supplies to Europe has led to a sharp increase in demand for alternative sources, driving up prices across the board. Simultaneously, concerns about future supply reliability and the potential for further disruptions have contributed to investor anxiety, leading to volatility in the market.
Speculation about future price increases and the impact of sanctions on Russian energy companies have also influenced stock prices.
Factors Contributing to Fluctuations
Several factors have contributed to the volatile nature of gas stock prices. Reduced supply from Russia, due to sanctions and the conflict, is a major factor. This reduction has led to a scarcity of gas in the global market, driving up prices. Increased demand from countries seeking to replace Russian supplies has further exacerbated the situation. Furthermore, the uncertainty surrounding the conflict’s duration and the potential for further disruptions to supply chains has added another layer of volatility to the market.
Responses of Gas Companies to the Crisis
Various gas companies have responded to the crisis in different ways. Some companies have focused on securing alternative supply sources to mitigate the risk of price volatility. Others have actively sought to increase their production capacity to meet growing demand. Strategic partnerships and joint ventures have also emerged as companies look to diversify their operations and ensure consistent supply.
Performance of Top Gas Stocks
The following table illustrates the performance of some leading gas stocks before, during, and after the war in Ukraine. It provides a snapshot of how these companies have been affected by the crisis. The fluctuations in stock prices are indicative of the broader market instability.
| Stock Name | Price Fluctuations (Before War) | Price Fluctuations (During War) | Price Fluctuations (After War) | Key Events |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gazprom | Steady growth | Significant decline due to sanctions | Further decline due to supply issues | Sanctions imposed by Western countries. Reduced supply to Europe. |
| Shell | Moderate growth | Fluctuations based on supply availability | Slight recovery with diversification efforts | Diversified supply sources. Continued focus on renewable energy. |
| TotalEnergies | Stable growth | Moderate decline but quick recovery with new contracts | Moderate growth with focus on European market | Secured alternative supplies from various regions. Expanded European operations. |
Strategies to Mitigate Price Volatility
Gas companies have employed various strategies to mitigate the risks of price volatility. One prominent strategy is diversification of supply sources. Companies are actively seeking alternative sources of gas to reduce reliance on any single supplier. Hedging strategies, which involve locking in prices for future gas deliveries, are also used to mitigate the risk of sharp price fluctuations.
Furthermore, investment in renewable energy sources is gaining traction as companies look to reduce their reliance on fossil fuels and create a more sustainable future. A critical strategy involves actively negotiating long-term contracts with reliable suppliers to ensure consistent supply, regardless of market fluctuations.
Inflationary Pressures
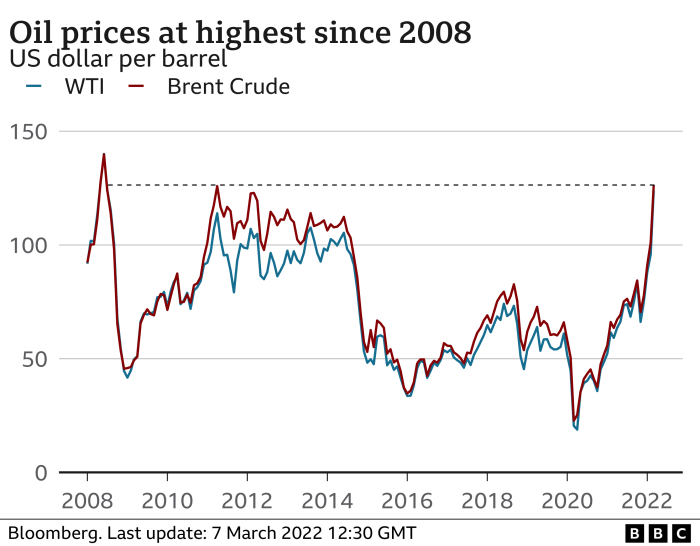
The war in Ukraine has sent shockwaves through global markets, significantly impacting inflation rates. Disruptions to supply chains, rising energy costs, and fluctuating commodity prices have combined to create a complex inflationary environment. This has profound consequences for consumers, businesses, and the overall economic health of nations.
Correlation Between the War and Global Inflation
The war’s impact on inflation is multifaceted. The conflict directly disrupts agricultural production and transportation, leading to shortages and price increases for essential commodities like wheat, corn, and sunflower oil. Furthermore, the war’s impact on energy markets has pushed up fuel and electricity prices, which are significant inputs for many industries, further escalating inflationary pressures. This disruption ripples through the entire economic system, affecting everything from manufacturing to consumer goods.
Specific Commodities and Goods Impacted
The war has severely impacted several crucial commodities. Wheat, a staple food, has seen dramatic price increases due to the disruption of Ukrainian and Russian exports, key players in global supply. Sunflower oil, another important commodity, has experienced similar price surges due to reduced availability from Ukraine, a major producer. Fertilizers, critical for agricultural production worldwide, have also seen price increases, impacting crop yields and contributing to higher food costs.
The Ukraine-Russia war’s impact on gas prices is undeniably affecting inflation, and the ripple effects are hitting the US economy hard. This global instability is forcing companies to adapt, like the intense bidding process for Amazon’s HQ2 locations, including cities like Queens, Arlington, Nashville, and Crystal City. This process highlights how companies are reacting to economic pressures, which ultimately feeds back into the war’s impact on gas stocks and inflation in the US.
Companies are being forced to reassess their strategies and locations, mirroring the global instability impacting our everyday lives.
Additionally, energy prices, including natural gas and oil, have been driven higher due to supply concerns, impacting transportation, manufacturing, and household energy costs.
Transmission Mechanisms
The conflict’s influence on inflation operates through several interconnected mechanisms. First, the disruption of supply chains, due to blocked ports and trade restrictions, directly reduces the availability of essential goods, causing prices to rise. Second, the increase in energy prices, which fuels transportation costs and manufacturing processes, translates to higher production costs for businesses. This, in turn, is passed on to consumers through increased prices for goods and services.
Finally, the uncertainty surrounding the conflict creates a climate of economic instability, leading to higher interest rates and further contributing to inflation.
Impact on Consumer Spending and Purchasing Power
The combination of these factors results in a significant reduction in purchasing power for consumers. As prices for essential goods and services rise, households face increased financial strain. This leads to reduced consumer spending, which can slow economic growth and potentially trigger a recessionary environment. The ability of consumers to meet their basic needs is directly impacted by this inflationary pressure.
Sectors Experiencing Inflationary Pressures
The following table Artikels the various sectors experiencing inflationary pressures, including examples of affected products or services, and corresponding price increases.
| Sector | Affected Products/Services | Estimated Price Increase (Example) |
|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Wheat, Corn, Sunflower Oil, Fertilizers | 20-50% |
| Energy | Natural Gas, Heating Oil, Electricity | 15-30% |
| Food Processing | Processed Foods, Bread, Bakery Goods | 10-20% |
| Transportation | Fuel, Shipping Costs | 10-25% |
| Manufacturing | Raw Materials, Finished Goods | 5-15% |
US Economic Response
The Ukraine conflict has significantly impacted global energy markets and supply chains, triggering a ripple effect across various sectors of the US economy. The US government has implemented a multifaceted approach to mitigate the fallout, including direct financial aid, strategic energy policies, and targeted support for vulnerable industries. These measures aim to cushion the blow of higher energy prices and supply chain disruptions, while also considering long-term economic resilience.
Government Intervention Measures
The US government has deployed a range of tools to address the economic consequences of the war. These actions encompass fiscal stimulus, strategic energy measures, and efforts to bolster supply chains. Financial aid packages, while not solely focused on the war’s impact, have aimed to mitigate economic hardship.
- Fiscal Stimulus: The US government has utilized various fiscal policies, including tax incentives and infrastructure spending, to stimulate economic activity and mitigate potential recessionary pressures. These measures aim to boost consumer and business confidence, thereby stimulating demand. For instance, the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law aims to improve the nation’s infrastructure, indirectly supporting various industries.
- Strategic Energy Policies: The US has worked to increase domestic energy production, including oil and gas, to reduce reliance on foreign sources. This includes streamlining permitting processes and incentivizing exploration and production. The goal is to decrease vulnerability to global price fluctuations and geopolitical instability.
- Supply Chain Resilience: The government has taken steps to bolster domestic production capacity and diversify supply chains, particularly in sectors affected by the war. Efforts to incentivize domestic manufacturing and reduce reliance on foreign suppliers are key aspects of this approach.
Short-Term and Long-Term Consequences
The short-term consequences of these measures are largely focused on mitigating inflation and maintaining consumer confidence. Increased government spending and monetary policy adjustments aim to bolster economic growth and offset the impact of higher energy prices. Long-term consequences could include a re-evaluation of supply chain dependencies, increased domestic manufacturing, and a potential shift towards greater energy independence. Historical examples of government interventions in times of economic uncertainty offer valuable insights into the potential trajectory of the US economy.
Impact on US Industries
The economic fallout of the war has disproportionately affected specific sectors. Increased energy prices have placed a strain on transportation, manufacturing, and energy-intensive industries. Higher input costs directly impact businesses and, ultimately, consumer prices. The agricultural sector has also been affected by global supply chain disruptions.
| Industry Sector | Government Response | Expected Impact on the US Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Transportation | Increased investment in infrastructure, strategic energy policies. | Reduced reliance on foreign oil, potentially lowering transportation costs in the long term. Short-term inflationary pressures. |
| Manufacturing | Incentives for domestic production, supply chain diversification efforts. | Potential boost to domestic manufacturing capacity. Short-term price increases as supply chains adjust. |
| Energy | Streamlined permitting, incentives for production. | Increased domestic energy production, reduced dependence on foreign suppliers. Short-term price volatility. |
| Agriculture | Support for agricultural producers, supply chain resilience efforts. | Potential impact on food prices depending on the severity and duration of supply chain disruptions. |
Energy Security and Dependence

The recent war in Ukraine has dramatically underscored the critical importance of energy security for the US economy. Historically, the nation has relied on a mix of domestic and international energy sources, but the conflict has exposed vulnerabilities and the need for a more resilient energy infrastructure. This shift necessitates a multifaceted approach, including the development of alternative energy sources and strategies to reduce dependence on foreign suppliers.The war has highlighted the fragility of global energy markets and the potential for geopolitical events to disrupt supply chains, leading to price volatility and economic instability.
This realization has driven a renewed focus on domestic energy production and the diversification of energy sources to bolster energy independence.
The Importance of Energy Independence
The US economy is deeply intertwined with its energy sector. Energy fuels transportation, manufacturing, and countless other industries, and reliable access to affordable energy is vital for economic growth. Dependence on foreign energy sources, particularly those from volatile regions, creates significant vulnerabilities. Disruptions in supply can lead to price spikes, impacting consumers and businesses alike. The recent experience underscores the imperative of reducing reliance on Russian energy and diversifying energy sources.
The Ukraine-Russia war is clearly impacting gas stocks, fueling inflation, and affecting the US economy in various ways. While it’s tough to predict the long-term effects, it’s worth noting that upgrading your storage solutions can help with managing data, like perhaps finding ways to save energy by using an Acer SSD solid state drive NVMe PCIe M.2 BiWin storage RAM solution here.
Ultimately, the war’s economic consequences are still unfolding, but these factors all need to be considered.
Alternative Energy Sources
The US is actively exploring a wide array of alternative energy sources. Solar and wind power are gaining traction due to their renewable nature and declining costs. Technological advancements in solar panels and wind turbines are driving down the cost of these sources, making them increasingly competitive with traditional fossil fuels. Furthermore, research and development in biofuels and other renewable energy technologies are ongoing.
Comparing Energy Sources
| Energy Source | Potential Advantages | Potential Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Fossil Fuels (e.g., Natural Gas, Coal) | Relatively inexpensive and readily available in the short term. | Environmental concerns (pollution, greenhouse gas emissions). Vulnerability to geopolitical instability affecting supply. |
| Renewable Energy (e.g., Solar, Wind) | Environmentally friendly, abundant, and increasingly cost-competitive. | Intermittency (dependence on weather conditions). Infrastructure development costs can be substantial. |
| Nuclear Power | High energy output, low carbon emissions. | Safety concerns, waste disposal issues, and potential for proliferation. |
Different energy sources possess unique advantages and disadvantages in terms of their potential to mitigate the impact of future conflicts on the US economy. Renewable sources offer long-term sustainability, but their current intermittency requires robust energy storage solutions and grid infrastructure enhancements. Nuclear power provides a substantial baseload energy source, but its safety and waste management aspects remain significant considerations.
Strategies to Reduce Dependence on Russian Energy
Reducing reliance on Russian energy sources is a multifaceted endeavor that demands a comprehensive and long-term strategy. The US needs to significantly increase domestic energy production, including shale oil and gas, while accelerating the development of renewable energy sources.
- Increased domestic production: Focusing on domestic shale oil and gas production can immediately increase energy supply. However, this strategy comes with environmental concerns and potentially further exacerbates dependence on fossil fuels. Careful environmental regulations are critical.
- Investment in renewable energy infrastructure: Substantial investment in solar, wind, and other renewable energy technologies is essential for creating a diversified energy portfolio. This involves supporting research and development, improving grid infrastructure, and incentivizing the adoption of renewable energy technologies.
- Strengthening international partnerships: Collaboration with other countries on energy security is crucial. This involves forging alliances with nations that have abundant and reliable energy resources, potentially fostering energy trading relationships and bolstering the stability of global energy markets.
The timeline for achieving significant reductions in dependence on Russian energy sources will vary depending on the pace of investments and technological advancements. The challenges include overcoming regulatory hurdles, securing funding, and addressing public concerns about environmental impacts. Nevertheless, the urgency of the situation necessitates a rapid and decisive shift toward energy independence.
Supply Chain Disruptions
The war in Ukraine has sent shockwaves through global supply chains, disrupting the flow of goods and materials across continents. This disruption has had a significant impact on the US economy, affecting everything from consumer goods to industrial production. The ripple effect is complex, with businesses scrambling to adapt and consumers facing higher prices and shortages.
Impact on Global Supply Chains
The conflict has disrupted crucial transportation routes, impacting the movement of raw materials, components, and finished goods. Blockades and sanctions have restricted access to vital resources, creating bottlenecks in manufacturing and distribution processes. This has led to a scarcity of certain products and increased lead times, impacting various industries and consumers alike. The war has also affected the availability of skilled labor and expertise, further complicating supply chain management.
Specific Products and Materials Affected
Numerous products and materials are experiencing disruptions due to the war. Wheat, sunflower oil, and fertilizer, originating from Ukraine and Russia, are vital for global food production. Reduced availability has contributed to food price inflation globally and particularly in regions reliant on these imports. Certain metals, such as palladium and nickel, essential for manufacturing electronics and automobiles, are experiencing shortages.
The conflict has also impacted the supply of semiconductors, crucial for a wide array of products.
Consequences on Consumer Goods and Services
The disruption of supply chains is directly impacting consumer goods and services. Consumers face higher prices, shortages, and longer wait times for products. This is especially noticeable in sectors like automotive, electronics, and agriculture. Businesses are forced to adjust their production strategies, leading to potential cost increases and reduced availability of products.
Company Adaptation and Alternative Sourcing
Companies are actively exploring alternative sourcing strategies to mitigate the effects of supply chain disruptions. This includes diversifying their supplier base to include regions less impacted by the conflict. They are also seeking to optimize their logistics and transportation networks, and implement inventory management strategies to buffer against future shortages. Many companies are investing in developing resilient supply chains by improving their understanding of risk factors and developing contingency plans.
The Ukraine-Russia war is clearly impacting gas stock prices, fueling inflation, and putting a strain on the US economy. It’s all a bit grim, right? But hey, amidst all the economic worries, Microsoft’s Surface X account is teasing something new, hinting at a potential tech advancement. microsofts surface x account is teasing something new. Hopefully, some innovative tech can help mitigate some of the negative economic impacts of the war, but for now, we’re still left with the ongoing challenges of the global energy market and its influence on the US economy.
Impact on Key Industries
| Industry | Product Examples | Disruption Details | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Cars, Trucks, Parts | Shortage of critical metals (e.g., palladium), semiconductor chips, and transportation disruptions | Diversifying parts suppliers, exploring alternative materials, optimizing logistics |
| Electronics | Phones, Computers, Appliances | Scarcity of semiconductors, increased shipping costs, and potential component shortages | Expanding relationships with alternative suppliers, exploring domestic production of components, and optimizing inventory management |
| Agriculture | Wheat, Sunflower Oil, Fertilizers | Reduced supply from Ukraine and Russia, leading to higher prices and potential food shortages | Exploring alternative sources of agricultural products, implementing strategies to increase domestic production, and diversifying supply chains |
| Pharmaceuticals | Medicines, Medical Supplies | Potential shortages of raw materials, packaging, and transportation difficulties | Developing backup supply chains, diversifying supplier base, and increasing production capacity |
International Relations and Trade
The war in Ukraine has profoundly reshaped the global landscape, impacting not only energy markets but also international relations and trade. The conflict has exposed existing fault lines and accelerated existing trends, forcing nations to re-evaluate their geopolitical strategies and economic dependencies. The consequences extend beyond the immediate region, affecting global supply chains, trade agreements, and the very fabric of international cooperation.
Geopolitical Implications on International Trade
The war has exacerbated existing tensions and mistrust between nations, creating a more complex and unpredictable global environment. This has led to a reassessment of economic partnerships and a renewed focus on national security concerns, influencing decisions about trade relationships and investment strategies. The conflict has also brought into sharp relief the vulnerabilities of global supply chains and the importance of diversifying sources of raw materials and manufactured goods.
Impact of Sanctions and Trade Restrictions on the US Economy
International sanctions imposed on Russia have had a multifaceted impact on the US economy. Reduced access to Russian commodities, particularly energy, has created challenges in securing energy supplies, which has been a significant factor contributing to inflationary pressures. Furthermore, disruptions to global supply chains have increased the cost of imported goods, indirectly affecting American consumers and businesses. The sanctions have also prompted a reassessment of trade relationships and the need for alternative sources of supply.
Comparison of International Responses to the Conflict
Nations have adopted varied approaches to the conflict, reflecting their individual geopolitical interests and economic priorities. Some countries have opted for stronger sanctions and trade restrictions, while others have adopted a more cautious approach, emphasizing the need for diplomacy and dialogue. This divergence in responses has created a complex web of economic and political interdependencies, impacting the future of international cooperation and trade agreements.
Potential Long-Term Impacts on International Trade Agreements, Ukraine russia war impact on gas stocks inflation and the us economy
The war in Ukraine could potentially lead to a re-evaluation of existing international trade agreements and a shift towards more protectionist policies. Concerns about supply chain vulnerabilities and national security could encourage nations to prioritize domestic production and reduce reliance on global trade networks. This could result in the renegotiation of existing agreements or the creation of new ones tailored to specific geopolitical realities.
Examples of Shifting Global Trade Patterns
The conflict is already influencing global trade patterns. For example, some companies are shifting their manufacturing bases from Russia to other countries, such as China, to maintain production levels and avoid sanctions. This shift is impacting the manufacturing industry in various regions and altering the balance of trade between countries. Furthermore, the need for alternative sources of energy and raw materials is driving increased trade and investment in countries that possess these resources, potentially altering long-term trade routes and economic relationships.
Closing Summary
In conclusion, the Ukraine Russia war’s impact on gas stocks, inflation, and the US economy is multifaceted and profound. The conflict has highlighted vulnerabilities in global energy markets, underscored the importance of energy independence, and exposed weaknesses in supply chains. The US government’s response and the actions of individual businesses will shape the long-term consequences of this crisis.
Further analysis is needed to fully grasp the implications of this conflict on the US economy and the global stage.





