Traveling salesman problem tesla superchargers explores the intricate challenge of optimizing electric vehicle charging routes. Imagine a Tesla driver needing to navigate a vast network of superchargers across a continent, maximizing efficiency while minimizing travel time and cost. This complex problem demands careful consideration of charging times, station availability, and geographical distances, all crucial factors for a smooth and cost-effective journey.
This article delves into the core concepts of the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP), highlighting its relevance to optimizing Tesla Supercharger usage. We’ll examine different TSP variations, solution methods, and the unique constraints presented by the Tesla Supercharger network. By understanding these factors, we can unveil effective strategies for maximizing charging efficiency for electric vehicle drivers.
Introduction to the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP)

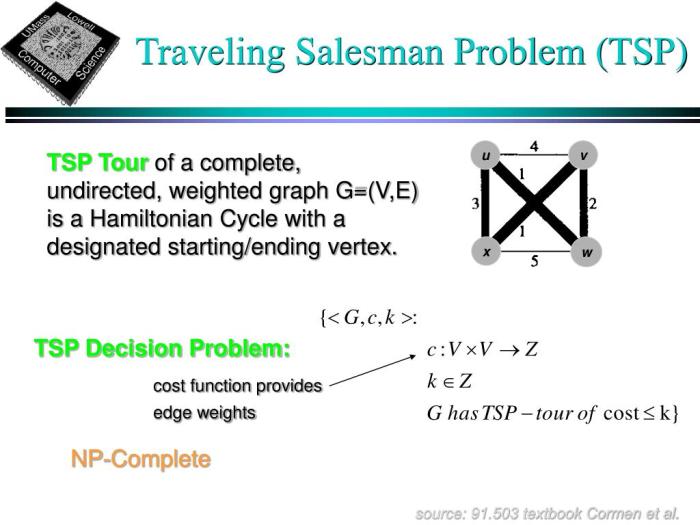
The Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) is a classic optimization problem in computer science and operations research. It’s a quintessential example of combinatorial optimization, focusing on finding the shortest possible route that visits each city exactly once and returns to the starting city. This seemingly simple task becomes computationally challenging as the number of cities increases.The core challenge of the TSP lies in its combinatorial nature.
The number of possible routes explodes exponentially with the number of cities, making exhaustive search impractical for anything beyond a handful of locations. This is where algorithmic approaches become crucial to finding near-optimal solutions efficiently.
TSP Variations
Different versions of the TSP exist, each with its own characteristics and implications for solution methods. A key distinction is the nature of the distances between cities.
- Euclidean TSP: This variation assumes the cities are points in a Euclidean space, and the distance between them is calculated using the standard Euclidean distance formula. This simplifies the problem, but it’s still computationally hard for large numbers of cities. Real-world applications often use this type of data, for example, when optimizing delivery routes across a geographic area.
- Metric TSP: A broader category, the metric TSP relaxes the Euclidean assumption. It only requires the distances to satisfy the triangle inequality (the distance between two points is always less than or equal to the sum of the distances from one point to a third point and from that third point to the second point). This is a more general case and encompasses many real-world applications, such as road networks where distances are not necessarily based on direct Euclidean measurements.
Significance in Logistics and Route Optimization
The TSP has profound implications in various fields, particularly logistics and route optimization. It underpins many real-world applications, including:
- Delivery Routing: Optimizing delivery routes for goods or packages to minimize travel time and costs.
- Vehicle Routing Problems (VRP): Extending the TSP to account for multiple vehicles and their capacities, commonly used in fleet management.
- Scheduling: Finding the optimal sequence of tasks or appointments for maximum efficiency, a problem with strong similarities to the TSP.
Common Algorithms for Solving the TSP
Several algorithms exist to tackle the TSP, each with its own trade-offs between solution quality and computational time.
- Brute-Force: This involves systematically evaluating every possible route, which is computationally infeasible for anything but the smallest problem instances. This is a fundamental algorithm, but it demonstrates the computational difficulty of the TSP.
- Nearest Neighbor: A simple heuristic that builds a solution by iteratively selecting the nearest unvisited city. This method is fast but often results in suboptimal solutions.
- Greedy Algorithms: These algorithms make locally optimal choices at each step, hoping to reach a global optimum. This can be effective but may get trapped in local optima, especially with large instances of the problem.
- Simulated Annealing: This stochastic method mimics the cooling process of metals to find optimal solutions by accepting worse solutions with a certain probability to escape local optima. This can yield high-quality solutions but takes longer than simpler heuristics.
Comparison of TSP Solution Methods
| Method | Complexity | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brute-Force | O(n!) | Evaluates all possible routes. | Guaranteed optimal solution. | Extremely slow for large n. |
| Nearest Neighbor | O(n2) | Selects nearest unvisited city. | Fast. | Suboptimal solutions. |
| Greedy | O(n2) | Makes locally optimal choices. | Relatively fast. | Prone to local optima. |
| Simulated Annealing | Variable | Stochastic method. | Potentially high-quality solutions. | Slow, requires tuning parameters. |
Tesla Supercharger Network
The Tesla Supercharger network is a vital component of the electric vehicle (EV) experience, offering a reliable and extensive charging infrastructure for Tesla owners. This network significantly impacts the range anxiety associated with long-distance travel, enabling drivers to plan and execute longer journeys with confidence. The network’s global reach and consistent high-quality charging stations play a critical role in the adoption and acceptance of EVs.The Tesla Supercharger network is strategically designed to provide convenient and rapid charging solutions for Tesla vehicles, enhancing the overall usability and appeal of electric driving.
This infrastructure supports the growing popularity of EVs by facilitating longer journeys and promoting a more seamless charging experience for owners.
Global Structure and Coverage
The Tesla Supercharger network boasts a global presence, with strategically located stations in various countries and regions. Its widespread coverage significantly aids Tesla owners in navigating diverse geographical areas, from major highways to smaller secondary roads. This global reach plays a crucial role in the network’s effectiveness for long-distance travel and the ease of EV adoption.
Features and Benefits
Tesla Superchargers offer a range of features and benefits that enhance the charging experience. These include dedicated lanes for quick charging, convenient access points, and modern amenities like restrooms and waiting areas. These features contribute to a comfortable and efficient charging process, making the charging experience more enjoyable.
Charging Speeds and Power Outputs
Tesla Superchargers offer various charging speeds and power outputs, catering to different vehicle models and charging needs. Different Supercharger models are optimized for different charging requirements, ranging from standard to high-powered stations. This variety ensures that drivers can find a suitable charging station to meet their needs.
| Supercharger Model | Typical Charging Speeds (kW) | Power Output (kW) |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | 50-150 kW | Up to 150 kW |
| High-Power | 150-250 kW | Up to 250 kW |
| V3 Supercharger | 250 kW and above | Up to 350 kW (or higher in some regions) |
Factors Influencing Charging Efficiency
Several factors influence the efficiency of charging at Tesla Superchargers. These include the specific charging station’s power output, the battery’s current charge level, and the ambient temperature. The overall efficiency is a product of the interplay between these factors.
Using a Tesla Supercharger: A Flowchart

The following flowchart illustrates the process of using a Tesla Supercharger.
- Locate a Tesla Supercharger station using the Tesla app or online resources.
- Drive to the designated charging station and park your Tesla within the designated area.
- Open the Tesla app and select the desired charging option. Initiate the charging process.
- Ensure your Tesla is properly connected to the charging station.
- Monitor the charging progress through the Tesla app or the charging station’s display.
- Once the charging is complete, disconnect your Tesla from the charging station and leave the area.
Integrating TSP with Tesla Superchargers
The Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) finds optimal routes, and its application extends beyond logistics. This article explores the potential of integrating TSP algorithms with Tesla’s supercharger network to optimize charging experiences for drivers. This involves considering various factors like charging times, geographical distances, and the availability of superchargers along a route.By incorporating TSP, Tesla drivers can significantly reduce travel time and potentially save money by optimizing charging stops.
This efficiency is crucial for long-distance journeys, ensuring drivers can reach their destinations without unnecessary delays or extra costs.
Potential Applications of TSP in Optimizing Tesla Supercharger Usage, Traveling salesman problem tesla superchargers
The application of TSP to optimize Tesla supercharger usage is multifaceted. It can enhance the efficiency of charging itineraries, enabling drivers to find the most efficient charging path between destinations. This can be especially helpful for long-distance trips where drivers need to plan their charging stops strategically to minimize overall travel time.
Geographical Data and Charging Times in the TSP
Geographical data, including the precise location of each supercharger, is fundamental to the TSP algorithm. Accurate coordinates allow the algorithm to calculate distances and travel times between charging stations. Crucially, charging times vary depending on the state of charge (SoC) of the vehicle and the capacity of the supercharger. The algorithm needs to account for these charging times to optimize the route.
The software needs to be able to incorporate this data to produce an effective route.
Real-World Scenarios Demonstrating Improved Charging Efficiency
Consider a Tesla driver planning a road trip from Los Angeles to San Francisco. Using a TSP algorithm integrated with the Tesla supercharger network, the driver can input their starting location, destination, and desired arrival time. The algorithm will then analyze the network of superchargers along the route, factoring in charging times for each station and potential traffic conditions.
The optimized route may involve charging at a supercharger located between a major city and a smaller town, allowing the driver to charge without excessive delays. This scenario highlights how TSP can help drivers avoid long waits and make more efficient use of their time.
Importance of Considering Charging Station Availability in the TSP Solution
Charging station availability is a critical constraint in the TSP solution for Tesla drivers. A robust TSP algorithm needs to dynamically account for supercharger availability. For example, if a planned supercharger is unavailable due to maintenance or high demand, the algorithm must adjust the route in real-time to find alternative charging stations. This adaptability is crucial to ensure the solution is practical and useful for drivers.
Optimization Techniques Suitable for TSP with Tesla Superchargers
Several optimization techniques are suitable for solving the TSP with Tesla superchargers. Dynamic programming, branch and bound, and genetic algorithms are examples of approaches that can find near-optimal solutions considering constraints like charging times. The choice of technique often depends on the size of the supercharger network and the desired level of optimization. The algorithms need to take into account the dynamic nature of the charging network and its constraints.
Impact of Charging Time Limits on TSP Solutions
Charging time limits are crucial constraints in the TSP solution for Tesla drivers. If a driver has a specific time limit for each charging stop, the algorithm must prioritize stations that can meet these requirements. For example, if a driver needs to charge for at least 30 minutes at each stop, the algorithm should identify superchargers capable of fulfilling this need.
Optimizing Tesla Supercharger routes for the traveling salesman problem is a fascinating challenge. Imagine needing to plan the most efficient route for a sales representative visiting multiple locations, and the same logic applies to a driver needing to hit a bunch of Supercharger stops. The sheer volume of potential routes can be mind-boggling, and thankfully, algorithms exist to solve these problems.
Recently, though, I’ve been really impressed with the recent success of Beat Saber OST 4, which has hit a major milestone of 4 million sales and has released some free tracks! beat saber ost 4 celebrates 4 million sales 4 new free songs It’s a testament to the popularity of the game, and it just reminds me that even complex optimization problems, like the ones involved in finding the best Supercharger route, can have surprising connections to popular culture.
Ultimately, finding the most efficient route for a sales representative is still a tricky problem, and a bit of inspiration can be useful in tackling these types of challenges.
This ensures the driver can adhere to their travel schedule and avoid delays. The optimization will be affected by the constraints imposed on the charging time limit. The algorithm must factor in the varying charging rates and times available at different supercharger locations.
Optimizing Tesla Supercharger placement for the traveling salesman problem is a complex issue, especially considering the recent delays in the US Postal Service’s electric delivery truck rollout. The US Postal Service’s electric delivery truck is super behind schedule , which raises questions about the reliability and practicality of electric vehicle infrastructure, and by extension, the efficiency of optimizing routes for these vehicles.
Ultimately, these issues directly impact the viability of solving the traveling salesman problem with Tesla Superchargers as a key component.
Optimizing Route Planning for EV Charging
Planning optimal routes for electric vehicles (EVs) requires more than just mapping the shortest distance. The crucial element of charging stops needs careful consideration. This is especially true when using a network like Tesla’s Supercharger system, where consistent access to sufficient power is vital for successful long-distance travel.The journey planning process must now incorporate charging station availability, estimated charging times, and the need to balance charging with other travel objectives.
This approach ensures a smooth and efficient EV trip, maximizing the user experience and minimizing the impact of range anxiety.
Charging Station Location Integration
Incorporating charging station locations into route planning algorithms is a key step. Algorithms must consider the specific location of charging stations along the planned route. This is crucial for optimizing the total trip time, factoring in the time spent at each charging station. Accurate data on charging station availability, including current usage and potential downtime, is also essential for a reliable calculation.
These algorithms need to be dynamic, capable of adjusting to real-time information about charging station availability and charging times.
Optimal Charging Schedule Determination
Determining the optimal charging schedule is a critical aspect of EV route optimization. The goal is to minimize the overall charging time required to complete the journey while ensuring the vehicle’s battery reaches a sufficient level for the remaining trip. Factors like the vehicle’s battery capacity, the desired level of charge for departure, and the charging rate at each station need to be integrated.
Predictive models, using historical data and real-time information, are instrumental in predicting optimal charging schedules.
Charging Strategy Comparison
Different charging strategies have varying advantages and disadvantages. A table summarizing these considerations is presented below.
| Strategy | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Fast Charging (Supercharger): | High charging rates, suitable for long distances. | Can lead to higher electricity costs, potential for longer waiting times. |
| Slow Charging (Home/Public): | Lower electricity costs, less waiting time. | Slower charging rates, less suitable for long distances. |
| Adaptive Charging: | Balances speed and cost, adapts to real-time conditions. | Requires more sophisticated algorithms, might not be optimal in all scenarios. |
Factors Affecting Charging Stop Selection
Several factors influence the choice of charging stops. These include the estimated time needed to reach a sufficient charge level, the charging rate at each station, the proximity to other attractions or destinations along the route, and the total cost of electricity. The availability of charging stations along the route is crucial. Considering these factors, along with the total travel time, helps in creating a balanced and efficient charging schedule.
- Charging Rate: Higher charging rates at a station allow for faster charging, reducing the overall trip time. For example, a Supercharger station with a 250kW charging rate will significantly reduce the time spent at a stop compared to a 50kW public charging station.
- Charging Station Availability: The availability of charging stations along the route is crucial. A lack of stations can significantly disrupt the route plan and lead to unexpected delays. For instance, a lack of stations between cities might force a longer charging stop, impacting the entire journey.
- Distance to Destination: The distance to the destination plays a significant role. If the destination is close to the next charging station, a shorter charging stop might be sufficient. This allows the driver to minimize the time spent at charging stations and maximize the time spent at other locations along the trip.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples: Traveling Salesman Problem Tesla Superchargers
Putting the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) into practice for optimizing EV charging routes isn’t just theoretical; real-world applications are emerging. This section dives into successful implementations, highlighting the challenges overcome and the impact on charging time and cost. We’ll look at specific regions and the data used to make these optimized routes a reality.This section showcases how TSP algorithms are being applied to enhance the EV charging experience, specifically focusing on the Tesla Supercharger network.
Optimizing Tesla Supercharger stops for a traveling salesman is a fascinating problem, akin to finding the most efficient route. Recent developments in security, like Cloudflare’s move away from CAPTCHAs towards security keys and cryptographic attestation of personhood here , are actually quite relevant. These advancements, while seemingly unrelated, could inspire new algorithms to tackle the traveling salesman problem, potentially leading to more efficient routing for electric vehicles.
We’ll examine case studies that demonstrate the practical value of these algorithms, from reducing charging time to lowering overall travel costs for EV drivers. By understanding the challenges and successes, we can gain a better appreciation for the power of optimized EV charging solutions.
California Tesla Supercharger Optimization
The California Tesla Supercharger network, being one of the largest and most densely populated, presents a significant challenge for optimal route planning. Numerous factors contribute to the complexity, including varying Supercharger availability, charging station capacities, and driver preferences. Successful optimization requires considering real-time data, such as charging station status and predicted demand.
- Data Sources: Real-time data on Supercharger availability, including the number of vehicles charging at each station, and historical charging data are critical for accurate predictions. External factors, such as weather patterns and predicted traffic, can also impact charging times and are included in the analysis.
- Challenges: Dynamic Supercharger availability is a key challenge. Sudden outages or unexpected high demand at a specific location can disrupt optimized routes. Accurately predicting future charging demands is another significant hurdle. Balancing the need for efficiency with the potential for real-time changes requires robust algorithms.
- Solutions: Advanced algorithms, incorporating machine learning and predictive models, are employed to dynamically adjust routes in response to real-time data. These solutions account for potential delays, allowing drivers to reach their destinations with minimal charging time and cost. Predictive models that account for future demand, weather, and traffic patterns are crucial for optimal planning.
- Impact: Optimized routes significantly reduce charging time, which translates to lower travel costs and increased overall satisfaction for EV drivers. For example, by predicting peak charging times, drivers can avoid long wait times at Supercharger stations. This improvement in efficiency translates to reduced environmental impact, as drivers spend less time charging, thereby reducing energy consumption.
Texas Expansion and Data Considerations
The Texas expansion of the Tesla Supercharger network necessitates a different approach to optimization, as the network density is considerably lower than in California. This difference in density influences the strategy used in developing optimal routes.
- Data Sources: Data sources for Texas include historical charging patterns, current Supercharger locations, and future expansion plans. Understanding the distribution of Tesla owners across Texas is also crucial for anticipating demand and optimizing routes. This requires incorporating data from Tesla’s user base.
- Challenges: Sparse Supercharger availability across Texas creates longer charging intervals and necessitates longer route planning horizons. Accurately predicting future demand across a larger area and with a lower density of stations is a complex challenge.
- Solutions: Longer-term planning is necessary, considering the potential for significant variations in demand and the need for more charging stops. The solution involves a combination of historical data, predictive models, and potential future Supercharger placement projections. The algorithms used need to be more robust to handle longer routes and lower density of stations.
- Impact: Optimization is vital to ensure efficient charging for long-distance journeys in Texas. Optimizing routes helps maintain a seamless EV driving experience, crucial for expanding EV adoption in the region. This, in turn, lowers the cost of travel and increases convenience.
Future Trends and Innovations
The future of EV charging route optimization is poised for significant advancements. As electric vehicle adoption accelerates, the need for sophisticated algorithms and real-time data integration becomes increasingly crucial. This evolution will impact not only individual drivers but also the broader transportation infrastructure. Intelligent route planning will play a pivotal role in maximizing efficiency and minimizing charging downtime for electric vehicles.
Potential Advancements in TSP Algorithms Tailored for EV Charging
Existing TSP algorithms can be adapted and enhanced to specifically address the unique characteristics of EV charging. This involves considering factors like charging time, available power, and charging station availability. Dynamic programming and heuristics can be further refined to account for these variables, leading to more optimal solutions. For instance, algorithms can prioritize charging stations with higher power outputs to reduce charging times for longer-range EVs.
Role of AI and Machine Learning in Optimizing Charging Routes
AI and machine learning offer the potential to revolutionize EV charging route optimization. Predictive models can forecast charging station availability and usage based on historical data and real-time traffic patterns. These models can dynamically adjust routes in response to changing conditions, ensuring the most efficient charging experience. For example, if a charging station experiences a sudden surge in demand, the AI system can reroute vehicles to alternative stations, preventing delays.
Impact of Real-Time Data on Optimizing EV Charging Strategies
Real-time data from various sources, including GPS, traffic information, and charging station status, can significantly enhance the accuracy and responsiveness of route optimization systems. Integrating this data allows for dynamic adjustments to routes based on current conditions, resulting in more efficient and reliable charging experiences. For instance, if a traffic jam develops on a planned route, the system can re-route vehicles to avoid congestion, thus minimizing charging delays.
Integrating Route Planning with Other Transportation Networks
Future systems should seamlessly integrate EV charging route planning with other transportation networks. This includes considering factors like public transit schedules and connections, enabling users to plan a complete journey from origin to destination, incorporating EV charging stops efficiently. This holistic approach will offer users a comprehensive transportation experience. For example, a route plan might combine a train journey with an EV charging stop at a designated station, optimizing the overall travel time.
Areas for Further Research and Development
Further research should focus on developing algorithms that account for fluctuating electricity prices and demand. Robust validation and testing in diverse geographic locations are essential to ensure accuracy and reliability across varying charging station densities. The development of user-friendly interfaces for planning and executing EV charging routes is also a key area for improvement. For example, exploring the use of augmented reality for real-time route guidance on the EV display.
Benefits of Using More Sophisticated Algorithms
Using more sophisticated algorithms in this context offers several significant benefits. Improved accuracy in route planning reduces charging time and associated costs, enhancing the overall EV user experience. Dynamic adjustments to routes in real-time can account for unforeseen circumstances, ensuring resilience and reliability. Furthermore, these algorithms can optimize the utilization of charging infrastructure, maximizing efficiency and minimizing environmental impact.
Epilogue
In conclusion, the traveling salesman problem, when applied to Tesla superchargers, presents a fascinating optimization challenge. By meticulously considering charging times, station availability, and geographical factors, we can significantly improve the efficiency of EV charging routes. The exploration of different algorithms and real-world case studies reveals the potential for substantial time and cost savings for Tesla drivers. Future advancements in AI and data analysis hold further promise for refining these strategies and optimizing the electric vehicle charging experience.