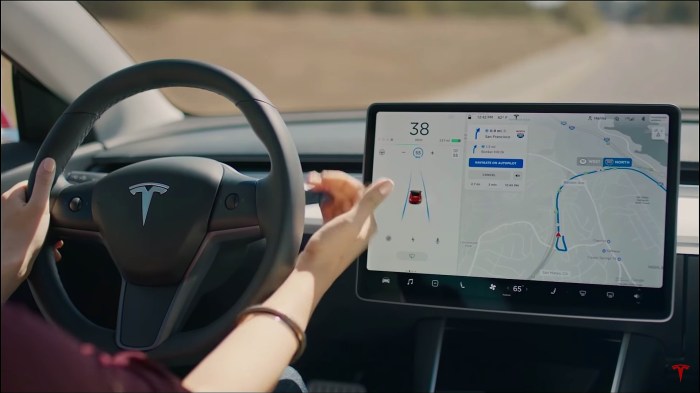
Tesla Autopilot Buddy Aftermarket NHTSA: a comprehensive look at the intersection of cutting-edge driver-assistance technology, aftermarket modifications, and regulatory oversight. This exploration delves into the intricacies of Tesla Autopilot, aftermarket enhancements, and the role of the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in shaping the future of autonomous driving. We’ll dissect the features, evolution, and safety implications of Tesla Autopilot, and examine the legality and potential risks of aftermarket modifications.
Plus, we’ll analyze NHTSA’s regulations and how they impact the use of these modifications. Finally, we’ll explore the concept of an “Autopilot Buddy” and how it might affect overall safety and reliability.
This discussion will analyze the complex interplay between these elements. We will also explore potential compatibility issues, safety considerations, and future trends. The content will include comparisons, tables, and detailed explanations of each aspect of this topic. Expect a comprehensive analysis that considers all sides of the issue.
Tesla Autopilot Overview
Tesla Autopilot, a suite of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), aims to enhance driver safety and convenience. It leverages a combination of sensors, cameras, and sophisticated algorithms to enable various driving functions. From its initial release to its current iteration, Autopilot has evolved significantly, adding features and refining its capabilities. Understanding its different levels of automation is crucial for comprehending its role in modern driving.
Features and Functionalities
Tesla Autopilot encompasses a range of features designed to automate various aspects of driving. These features include adaptive cruise control, lane keeping assist, automatic emergency braking, and more advanced maneuvers like automated lane changes and highway driving assistance. The system continuously learns and adapts to different driving conditions, making it a dynamic and responsive feature.
Evolution of Capabilities
Tesla Autopilot’s capabilities have grown significantly since its introduction. Early versions primarily focused on basic driver assistance features. Over time, the system has been refined with enhanced sensor technology, more sophisticated algorithms, and increased data sets. This continuous improvement has led to more complex and autonomous driving capabilities. For instance, the addition of over-the-air updates has enabled the company to refine the system’s algorithms and incorporate new features in a timely manner.
Levels of Automation
Tesla Autopilot offers different levels of automation, ranging from basic driver assistance to more advanced features. These levels are not standardized across all jurisdictions, and the specific capabilities of each level can vary based on location. Tesla, in its documentation, uses the concept of ‘Autopilot’ to cover the range of available features. While the specific nomenclature may change, the overall functionality remains clear.
Tesla Autopilot buddy aftermarket NHTSA issues are definitely a hot topic right now, but honestly, the whole Musk vs. Zuckerberg feud has reached a new level of absurdity. This ongoing drama is distracting from the real concerns about safety features like Autopilot. Regardless of the billionaire squabbles, it’s still crucial that aftermarket additions to Tesla Autopilot are thoroughly vetted by the NHTSA to ensure they don’t compromise safety.
Comparison with Other ADAS Systems
| Feature | Tesla Autopilot | Other ADAS Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Adaptive Cruise Control | Highly integrated with other features, responsive, and adaptive. | Varying degrees of integration and responsiveness. |
| Lane Keeping Assist | Proactive and intuitive lane-keeping functions. | Varying levels of lane-keeping support, potentially with different levels of intervention. |
| Automatic Emergency Braking | Recognizes potential hazards and reacts accordingly. | May have varying levels of responsiveness and accuracy. |
| Highway Driving Assistance | Enables semi-autonomous highway driving, managing acceleration, braking, and steering. | Limited capabilities in highway driving assistance, with potential for more limited functions. |
The table above provides a general comparison. Specific functionalities and performance characteristics may vary depending on the make and model of the vehicle and the ADAS system used.
Aftermarket Modifications for Autopilot
Tesla Autopilot, while a powerful feature, is constantly evolving. Owners often seek ways to enhance or customize its functionality. This often leads to aftermarket modifications, a realm filled with both potential benefits and significant safety and legal concerns. Understanding these modifications, their implications, and the associated risks is crucial for any Tesla owner considering them.Aftermarket modifications for Tesla Autopilot encompass a wide range of components and software tweaks.
These modifications can range from simple radar/camera upgrades to more complex alterations affecting the car’s overall control systems. The allure is clear – potential improvements in performance, reliability, and even the range of functionalities. However, the legal and safety implications are often overlooked.
Popular Aftermarket Modifications
Many Tesla owners explore aftermarket upgrades for their Autopilot systems. Popular modifications include upgraded radar sensors, cameras, and software tweaks aiming to improve object detection, lane keeping, and overall driving assistance. Specific software adjustments often aim to address perceived limitations of the factory system, like enhancing performance in challenging conditions. However, these enhancements are not always straightforward and can sometimes negatively impact the car’s overall performance or stability.
Legality and Safety Concerns
The legality of aftermarket Autopilot modifications varies greatly depending on the jurisdiction and the nature of the modification. Many modifications void the vehicle’s warranty and can potentially compromise the safety of the driver and other road users. This is a serious concern as the modification could significantly affect the safety and reliability of the driver assistance system. Using modified components or software may lead to unexpected behavior and malfunctioning of the Autopilot system.
Performance and Reliability Comparison
Comparing the performance and reliability of aftermarket Autopilot components is difficult, as there’s a lack of standardized testing and quality control. Some aftermarket components may offer enhanced performance, but this often comes at the cost of reliability. The quality of the components and the installation procedures significantly impact the overall performance and reliability. Potential issues include decreased responsiveness, increased latency, or even system instability.
Potential Risks and Liabilities
Installing aftermarket Autopilot components carries potential risks and liabilities. If an accident occurs due to a malfunctioning or poorly installed component, the owner may be held responsible. Furthermore, the modification may not meet safety standards, potentially leading to harm or injury to the driver or others. It’s crucial to weigh the potential benefits against the risks and liabilities.
Table: Pros and Cons of Aftermarket Autopilot Modifications
| Modification | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Upgraded Radar Sensors | Potentially improved object detection in low-light or adverse weather conditions. | Increased cost, potential for interference with other vehicle systems, possible reduced reliability. |
| Upgraded Cameras | Improved image clarity and processing, potentially enhanced lane departure warnings. | Cost, compatibility issues with existing system, potential for reduced reliability. |
| Software Tweaks | Potentially enhanced performance and responsiveness, targeted addressing of specific limitations. | Potential for instability and unpredictable system behavior, security risks, possible voiding of warranty. |
NHTSA Regulations and Tesla Autopilot
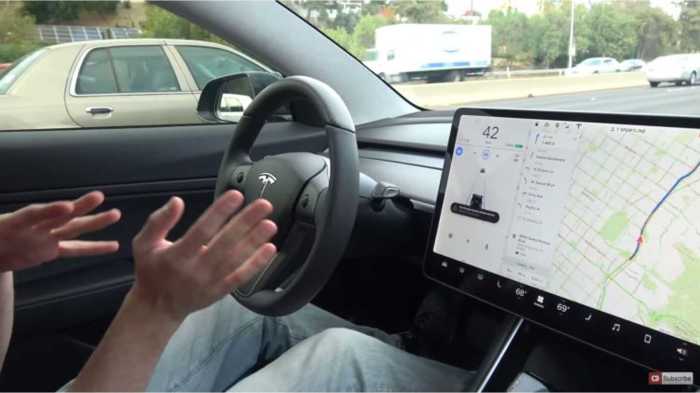
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and effectiveness of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). Their regulations aim to prevent accidents and protect consumers by setting standards for the development and deployment of these technologies. This section delves into NHTSA’s role in regulating Tesla Autopilot, outlining specific regulations, potential violations, and the agency’s current and proposed guidelines.Tesla Autopilot, while promising, operates within a complex regulatory landscape.
Understanding the interplay between technological advancement and safety standards is critical for both consumers and the automotive industry.
NHTSA’s Role in Regulating ADAS
The NHTSA is responsible for establishing safety standards for vehicles and their systems. This includes ADAS like Tesla Autopilot, ensuring that these technologies are designed and implemented in a manner that minimizes risk and enhances overall safety. They conduct thorough evaluations of ADAS to determine their effectiveness and potential hazards.
Specific NHTSA Regulations Concerning Tesla Autopilot
NHTSA’s regulations for ADAS encompass various aspects, including labeling, functionality, and warnings. While no single document explicitly details “Tesla Autopilot” regulations, the agency’s overall framework applies to all ADAS. This means Tesla Autopilot must meet standards for driver monitoring, intervention requirements, and the clear delineation of the system’s capabilities and limitations. Regulations also address the accuracy and reliability of sensors and algorithms crucial for autonomous driving features.
This includes the explicit requirement that ADAS systems must not create a false sense of safety, and that they do not override the driver’s ability to maintain control of the vehicle.
Reported Violations or Investigations Related to Tesla Autopilot and NHTSA
Several instances of reported issues with Tesla Autopilot have led to NHTSA investigations. These investigations often center on incidents where the system failed to function as intended, leading to accidents or near-misses. Specific investigations and violations are usually detailed in the NHTSA’s public reports, and they can include concerns about the system’s overreliance, inadequate driver monitoring, and misleading marketing regarding the system’s capabilities.
Summary of NHTSA’s Current and Proposed Guidelines for Autopilot
NHTSA’s current guidelines emphasize the need for clear communication between the driver and the system. They advocate for transparent labeling regarding the system’s capabilities and limitations. Furthermore, the agency aims to enforce stricter requirements for testing and validation of ADAS systems to ensure they function as intended and do not create a false sense of safety. Proposed guidelines might include more stringent requirements for driver monitoring and intervention protocols.
Compliance Table: Tesla Autopilot and NHTSA Regulations
| Regulation Aspect | Tesla Autopilot Compliance (Likely) | Justification/Details |
|---|---|---|
| Driver Monitoring | Partial | Tesla Autopilot relies on driver monitoring, but the extent of this monitoring and the response to driver disengagement are under scrutiny. |
| Intervention Requirements | Partial | The system’s ability to gracefully transition from autonomous to manual control is a critical aspect of compliance. This requires clear and prompt intervention mechanisms. |
| Accuracy and Reliability of Sensors | Likely | The sophisticated sensor suite employed by Tesla Autopilot suggests high accuracy and reliability; however, this needs constant validation and scrutiny to maintain compliance. |
| Labeling and Warnings | Inconsistent | While Tesla provides warnings, the clarity and comprehensiveness of these warnings regarding the system’s limitations are often debated. This is an area where more consistent and explicit labeling is needed. |
Tesla Autopilot Buddy
The concept of an “Autopilot Buddy” is a fascinating and potentially transformative extension of Tesla’s Autopilot system. It suggests a level of human-machine interaction that goes beyond the current capabilities of the system, potentially offering greater autonomy and assistance to drivers. However, this enhanced capability also raises significant safety and ethical concerns that must be addressed before widespread adoption.This discussion delves into the potential features, functionalities, and associated risks of Autopilot Buddies.
It analyzes the interactions between such a system and the vehicle’s existing components, examining both positive and negative scenarios. The aim is to provide a comprehensive understanding of this emerging technology.
Defining Tesla Autopilot Buddy, Tesla autopilot buddy aftermarket nhtsa
An Autopilot Buddy, in its various forms, is a software-based system that enhances Tesla’s Autopilot. It’s not a physical component but rather an add-on, perhaps an app or a dedicated interface, that aims to improve the driver’s experience and the vehicle’s automated driving capabilities. This could involve more sophisticated route planning, adaptive speed adjustments, and more proactive hazard detection, surpassing the current Autopilot’s capabilities.
Different forms could include advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) designed to assist with parking, navigation, and even potentially some aspects of driving in complex traffic situations.
Safety and Ethical Considerations
Safety is paramount when discussing autonomous driving. Autopilot Buddies, with their expanded functionalities, introduce new levels of complexity. Unforeseen circumstances and interactions with external factors, like pedestrian behavior or unexpected road conditions, could lead to unexpected and potentially dangerous situations. Ethical considerations arise with the increased autonomy, especially in scenarios where the system must make split-second decisions involving potential harm.
Who is responsible if the system makes an error? The driver, the manufacturer, or the software developer? These questions need clear answers and protocols to mitigate risk.
Interaction with Existing Systems
An Autopilot Buddy would need to seamlessly integrate with Tesla’s existing vehicle systems. This includes the sensors, the vehicle’s control units, and the existing Autopilot algorithms. The integration must be robust and reliable, minimizing the possibility of conflicting commands or unexpected system failures. Data sharing and communication protocols are critical for the Buddy to accurately assess the driving environment and make appropriate adjustments to the vehicle’s behavior.
Potential Scenarios: Enhancing and Compromising Safety
An Autopilot Buddy could enhance safety by proactively identifying and responding to potential hazards. For example, it could anticipate traffic congestion ahead, adjust speed accordingly, and offer alternative routes. However, the same technology could compromise safety. A poorly designed or programmed system might misinterpret a situation, leading to dangerous maneuvers. If the system is overly reliant on sensor data from a single source, it could be vulnerable to sensor failures or misleading data, leading to an accident.
Real-world examples of advanced driver assistance systems failing to meet expectations highlight the importance of rigorous testing and thorough safety protocols.
User Experiences and Expectations
| User Experience Category | Potential Expectation | Potential Reality |
|---|---|---|
| Intuitive Interface | Easy to understand and use, with clear instructions and feedback. | May require a learning curve, potentially presenting challenges for novice users. |
| Enhanced Safety | Increased confidence in the vehicle’s ability to handle diverse driving conditions. | Requires meticulous testing and verification to ensure safety. |
| Improved Efficiency | Reduced travel time and fuel consumption due to optimized routes and speed adjustments. | Benefits will depend on traffic conditions, road network, and system performance. |
| Increased Autonomy | Driver can delegate more driving tasks to the system. | Ethical considerations and liability issues require careful handling. |
This table Artikels potential user experiences and expectations of an Autopilot Buddy. The difference between expectation and reality emphasizes the importance of thorough testing and careful consideration of real-world implications.
Interactions and Integration
Aftermarket modifications for Tesla Autopilot, while offering potential enhancements, can significantly impact the system’s intended functionality and safety. Understanding how these modifications interact with the existing Autopilot architecture is crucial for both users and potential installers. Careful consideration must be given to compatibility issues and the overall safety implications.
Tesla Autopilot’s aftermarket “buddy” systems are getting a lot of scrutiny from the NHTSA, which is important for driver safety. It’s interesting to note that, while safety concerns with advanced driver-assistance systems are paramount, initiatives like the Jeff Bezos Day One Fund’s support for nonprofit preschools at Amazon jeff bezos day one fund nonprofit preschool amazon highlight a different kind of technological impact.
Ultimately, though, the focus should remain on ensuring these systems are safe and reliable, so we can all enjoy the benefits of self-driving technology while prioritizing safety.
Autopilot System Interactions
Aftermarket modifications, such as radar and camera enhancements, can potentially interfere with the Tesla Autopilot’s sensor fusion process. This interference can result in inaccurate data interpretation, potentially causing unexpected or dangerous behaviors. For instance, if a modification introduces additional signals that conflict with the vehicle’s existing sensor data, the Autopilot system might struggle to make accurate decisions about the environment, leading to unintended maneuvers.
The complexity of the Autopilot system necessitates a thorough understanding of its internal workings for any modification.
Compatibility Issues
Potential compatibility issues stem from the proprietary nature of the Tesla Autopilot system. Modifications might not be fully integrated with the existing software and hardware, resulting in conflicts and unexpected behaviors. For example, a poorly designed radar module might produce signals that the Autopilot system misinterprets, leading to an inaccurate assessment of the driving environment. These misinterpretations can manifest in erratic braking, acceleration, or lane-keeping assistance.
Impact on Safety Features
An Autopilot Buddy, while potentially adding features, can compromise the integrity of the vehicle’s safety systems. Any modification that alters the way the Autopilot system perceives the environment could potentially decrease safety. For example, an improperly calibrated radar module might lead to an inability to detect obstacles accurately, which can have disastrous results. Furthermore, integration problems could cause the vehicle to react unexpectedly in critical situations.
Integration Methods
Integrating an Autopilot Buddy requires careful consideration of the existing Tesla Autopilot architecture. The modifications should ideally be designed to communicate seamlessly with the existing system, without introducing conflicts or introducing inaccurate data. This usually involves utilizing existing communication channels or creating dedicated interfaces for the aftermarket component.
Integration Scenarios and Outcomes
| Integration Scenario | Outcome | Impact on Safety |
|---|---|---|
| Properly designed and tested aftermarket radar system integrated using a dedicated interface. | Enhanced sensor capabilities, potentially improving object detection and safety in specific conditions. | Positive, providing increased situational awareness. |
| Aftermarket camera system with conflicting data streams from existing sensors. | Potential for inaccurate data fusion, causing the Autopilot system to react erratically or fail to recognize critical elements of the environment. | Negative, leading to decreased safety and potential accidents. |
| Modification that bypasses existing Autopilot safety protocols. | Compromised vehicle safety, as the system is no longer able to function within its designed parameters. | Negative, drastically reducing safety and potentially causing hazardous situations. |
Safety and Reliability: Tesla Autopilot Buddy Aftermarket Nhtsa
Tesla Autopilot, while offering impressive features, presents a complex interplay of safety and reliability, particularly with aftermarket modifications. Understanding the inherent risks and the impact of these modifications is crucial for responsible use. This section delves into the intricacies of Tesla Autopilot’s safety profile, examining potential liabilities, the role of an Autopilot Buddy, user experiences, and the evaluation of aftermarket components.The core functionality of Tesla Autopilot relies on a sophisticated combination of sensors, algorithms, and software.
However, the system’s performance is inherently dependent on environmental conditions, road quality, and driver input. Furthermore, the integration of aftermarket components can introduce unforeseen vulnerabilities and degrade the overall reliability of the system.
Assessing Tesla Autopilot’s Baseline Safety
Tesla Autopilot’s safety record is a subject of ongoing debate and scrutiny. While the system has demonstrated capabilities in certain scenarios, real-world incidents highlight the limitations and potential hazards. These incidents often involve complex interactions between the vehicle’s automated systems and unpredictable driving environments.
Tesla Autopilot’s aftermarket “buddy” systems are raising some safety concerns with the NHTSA. It’s interesting to consider how these advancements in driver-assistance technology interact with user privacy and web security, like how Mozilla’s ad-blocking initiatives in Firefox and Chrome, through the Privacy Manifest V3 and Web Request API, which impacts user experience and data handling. Ultimately, the safety and responsible development of these systems, like Tesla’s autopilot, are crucial for the future of autonomous driving.
Potential Risks and Liabilities of Aftermarket Modifications
Aftermarket modifications to Tesla Autopilot systems, while potentially enhancing features, can introduce significant safety risks. These modifications often lack the rigorous testing and validation processes employed by Tesla, potentially leading to malfunctions and unexpected behaviors. Moreover, the warranty implications for such modifications need to be carefully considered.
The Role of an Autopilot Buddy in Enhancing Safety
An Autopilot Buddy can serve as a crucial safety mechanism, providing a second set of eyes and a human element to monitor the vehicle’s automated systems. This oversight is particularly vital during complex maneuvers, unusual weather conditions, or unfamiliar road environments. The Buddy acts as a safety net, allowing for immediate intervention in case of system malfunction or unexpected behavior.
User Experiences Regarding Safety and Reliability
User experiences regarding Tesla Autopilot’s safety and reliability vary widely. Positive accounts often focus on the system’s convenience and assistance in certain situations. Conversely, negative experiences frequently highlight instances of unexpected behavior, system failures, and the need for constant human vigilance. Crucially, users should report any unusual or concerning experiences to Tesla and/or relevant authorities.
Evaluating the Reliability of Aftermarket Autopilot Components
Assessing the reliability of aftermarket Autopilot components requires careful consideration of several factors. The manufacturer’s reputation, available documentation, third-party reviews, and physical inspection of the components are crucial. Additionally, independent testing and validation of the component’s compatibility with the Tesla vehicle’s system are recommended to ensure safety and reliability. A comprehensive understanding of the component’s limitations and potential interactions with other systems is essential for responsible integration.
Factors Affecting Tesla Autopilot’s Performance
Several factors significantly impact Tesla Autopilot’s performance and reliability. These factors include:
- Environmental conditions, such as weather (rain, snow, fog), lighting, and visibility, can affect the sensors’ accuracy.
- Road conditions, including lane markings, road surfaces, and the presence of obstacles, can affect the system’s ability to maintain safe operation.
- Driver behavior, including distraction, inattention, and failure to maintain a safe following distance, can impact the system’s effectiveness.
- Software updates and system maintenance are critical for maintaining the system’s integrity and performance.
Future Trends and Projections
The future of Tesla Autopilot and aftermarket modifications is intertwined with evolving technological advancements and regulatory landscapes. Predicting precise timelines and outcomes is challenging, but exploring potential trajectories provides valuable insight into the likely direction of development. This section will Artikel anticipated advancements in Autopilot functionality, aftermarket modifications, and the regulatory environment.
Future Development of Tesla Autopilot
Tesla’s commitment to continuous improvement in Autopilot’s capabilities suggests a trajectory of enhanced safety and driver assistance features. Expect further integration of advanced sensor technologies, including more sophisticated cameras, radar, and lidar systems. This integration will likely lead to more robust object detection and improved decision-making in complex driving scenarios. The company has shown a tendency to progressively increase the sophistication of its algorithms, enabling more autonomous driving capabilities.
Evolution of Aftermarket Modifications for Autopilot
The aftermarket modification sector is likely to respond to the evolving needs of Autopilot’s functionality. As Tesla’s Autopilot system evolves, aftermarket companies will need to adapt to ensure compatibility and provide additional features. We can anticipate the emergence of modifications that enhance specific aspects of the system, like improved lane-keeping assistance, enhanced obstacle avoidance, and expanded sensor coverage.
Changes in NHTSA Regulations
NHTSA regulations regarding advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) are expected to become more stringent. The agency is likely to require higher standards of safety and performance from manufacturers. The evolution of self-driving technology will influence the regulations surrounding the use of aftermarket modifications, aiming to maintain safety standards across all involved parties. The focus will likely shift towards establishing clear guidelines and safety protocols for these modifications to ensure compatibility and prevent potentially hazardous interactions with the original system.
Potential Advancements and New Features for Autopilot Buddies
Autopilot Buddies are likely to see advancements in functionality. Improvements in sensor fusion, data processing, and communication protocols could enable more sophisticated features, such as enhanced adaptive cruise control, improved pedestrian and cyclist detection, and expanded functionality in challenging weather conditions. The integration of AI-powered decision-making could lead to more proactive and intuitive responses in complex driving scenarios.
Future of Driver-Assistance Systems and Aftermarket Modifications
Driver-assistance systems are poised for a significant transformation. Expect to see a growing convergence of different ADAS systems, leading to a more integrated and comprehensive driving experience. Aftermarket modifications will play a crucial role in shaping this future. By providing solutions that enhance existing systems or fill gaps in capabilities, aftermarket companies can facilitate the evolution of driver-assistance systems.
This could include providing add-on features for enhanced safety, convenience, and performance. Examples could include more sophisticated driver-monitoring systems or real-time environmental data integration.
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, Tesla Autopilot Buddy Aftermarket NHTSA presents a multifaceted challenge for both users and regulators. The interplay between advanced driver-assistance systems, aftermarket modifications, and regulatory frameworks is a dynamic one, demanding careful consideration. The future of autonomous driving hinges on responsible innovation and adherence to safety standards, which will ultimately be shaped by the ongoing dialogue between industry, consumers, and regulatory bodies.
This discussion offers a framework for understanding the evolving landscape and the crucial role NHTSA plays in ensuring safety and responsible technological advancement.