Stop Facebook memories before they have a chance to pop up sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. We’ll delve into the reasons why someone might want to proactively prevent these digital reminders, exploring various emotional states and motivations behind this desire.
From understanding the user’s needs to exploring alternative methods for managing the emotional impact, this article is your guide to reclaiming control over your digital memories.
This article examines the intricacies of managing Facebook memories. It delves into the reasons people want to prevent these reminders, outlining various situations, emotions, and motivations. We’ll also explore the technical aspects of Facebook’s memory generation and display algorithms, allowing you to understand the mechanisms behind these digital triggers. Ultimately, we’ll present practical methods for preventing these memories, examining the potential impact of these actions on both your psychological well-being and social interactions.
Additionally, we’ll explore alternatives to blocking memories, offering strategies for coping with the feelings triggered by these digital reminders.
Understanding the User’s Need
Facebook memories, while often intended to evoke pleasant nostalgia, can sometimes trigger unwanted emotions or unwanted reminders of past experiences. Understanding the motivations behind the desire to prevent these memories from surfacing is crucial for developing effective solutions. This section delves into the diverse reasons why users might want to suppress these reminders, exploring the emotional and situational contexts.
Reasons for Preventing Facebook Memories
Individuals might want to prevent Facebook memories from appearing for a variety of personal reasons. These reasons can be rooted in emotional responses to certain memories, situational factors, or even strategic considerations. The following points detail these various motivations.
- Emotional distress: Some memories can evoke significant emotional distress, ranging from sadness and regret to anxiety and fear. A breakup, a significant loss, or a difficult life event can make revisiting associated memories emotionally challenging. For example, a user who experienced a painful divorce might find seeing photos and posts related to that period distressing, triggering feelings of grief and regret.
Likewise, someone who struggled with a past illness might find reminders of that time overwhelming and emotionally taxing.
- Situational sensitivity: Certain life events or transitions can make revisiting specific memories undesirable. For instance, a user preparing for a new relationship might find seeing photos and posts of a past relationship to be distracting or triggering. Similarly, someone starting a new job might prefer to not be reminded of their previous role. In a similar vein, people in the midst of a major life change might wish to minimize reminders of the previous status quo.
- Privacy concerns: Users might wish to prevent certain memories from appearing to maintain a sense of privacy or discretion. For example, a user might have a memory associated with a past embarrassing situation and prefer to not have it publicly revisited. Similarly, some might prefer to not have memories of personal milestones or relationships viewed by friends and family members they are currently not comfortable sharing with.
The user may also wish to maintain a particular image or narrative in their online presence.
- Strategic use: Some users might intentionally want to suppress certain memories to avoid triggering certain feelings or to create a desired narrative. For example, someone who wants to move on from a past relationship might want to avoid seeing photos or posts related to that period. Similarly, a person who wants to project a specific image might want to prevent certain memories from being publicly viewed.
Tired of those Facebook memories popping up? I’ve been trying to stop them before they have a chance to trigger a wave of nostalgia, and I’ve found a surprisingly effective technique. One thing that’s really helping is learning to use my Google Pixel Buds Pro, where you can use touch and hold to hear notifications google pixel buds pro touch and hold hear notifications.
This lets me keep my phone in my pocket and still stay on top of important stuff, which in turn helps me stay focused and avoid those Facebook memory rabbit holes. Now, back to my Facebook memory avoidance strategy!
Emotional States Triggering Memory Suppression
Different emotional states can heighten the desire to stop Facebook memories from appearing. These states can vary from mild discomfort to significant distress. Understanding these emotional triggers can help in developing targeted solutions for memory suppression.
- Regret: Memories associated with past choices or actions that now appear regrettable might be actively suppressed to avoid dwelling on the negative feelings. This could include a memory of a decision that has led to a negative outcome.
- Shame: Memories associated with past behaviors or situations that induce feelings of shame or embarrassment might be actively avoided to prevent further emotional distress. A past transgression, or an embarrassing moment from the past could trigger such a response.
- Grief: Memories of a loved one who has passed away or a significant loss can evoke intense grief. The desire to suppress these memories stems from a need to cope with the emotional pain associated with the loss.
- Anxiety: Memories associated with past anxieties or fears can cause significant distress. The need to suppress these memories is driven by a desire to avoid reliving those experiences.
Motivations for Suppressing Memories
Users’ motivations for wanting to suppress Facebook memories can be categorized into several groups. These range from self-preservation to social considerations. The following points explain these various motivations in detail.
- Maintaining mental well-being: Suppressing certain memories can help maintain a positive emotional state. Avoiding potentially upsetting memories can prevent the resurgence of negative emotions and maintain emotional stability.
- Managing social perception: Users might want to control the narrative or image they present to others. Avoiding specific memories can help maintain a desired social perception.
- Self-improvement: Suppressing reminders of past mistakes or behaviors can aid in personal growth and self-improvement. Avoiding such memories allows for the focus on the present and future.
Illustrative Table
| Situation | Emotion | Reason for wanting to stop memories |
|---|---|---|
| Recent breakup | Sadness, regret | Avoid revisiting painful memories and associated emotions. |
| Past financial hardship | Anxiety, fear | Prevent reminders of past struggles and potential future anxieties. |
| Embarrassing moment | Shame, embarrassment | Maintain a positive self-image and avoid public scrutiny. |
| Death of a loved one | Grief, sadness | Cope with the loss and avoid constant reminders of the absence. |
Methods for Preventing Facebook Memories
Facebook Memories, while often nostalgic, can sometimes be overwhelming or irrelevant. Understanding how to manage and customize these features is key to a more controlled Facebook experience. This section delves into various methods for preventing Facebook Memories from appearing, or for adjusting their frequency and content.Adjusting your Facebook Memories settings allows for a more tailored experience, preventing unwanted or irrelevant content from cluttering your feed.
This control empowers you to curate your memory experience, focusing on what’s meaningful to you.
Disabling Facebook Memories
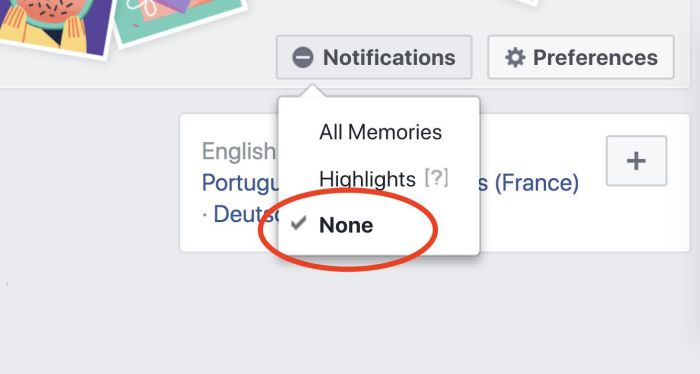
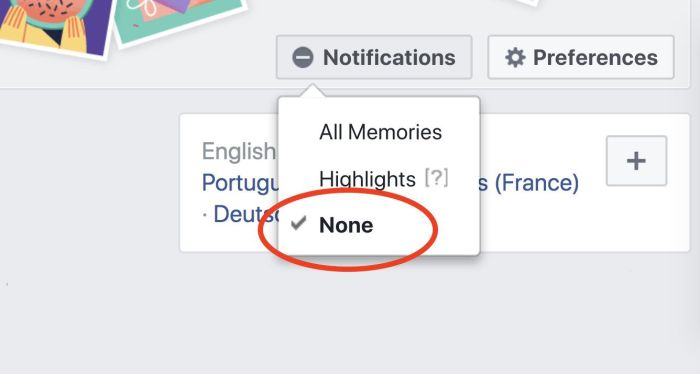
Facebook offers complete disablement of the Memories feature. This is a comprehensive option for users who wish to completely prevent the display of any memories. To achieve this, navigate to your Facebook settings, locate the Memories section, and actively disable the feature.
Customizing Memory Settings
Facebook provides a range of customization options within the Memories settings. These settings allow users to fine-tune the frequency, types, and visibility of memories. This allows users to maintain a balance between the nostalgic and the practical.
Tired of those Facebook memories popping up, reminding you of past awkward moments? I’m not alone! Companies need to stop removing fan-favorite features like this; it’s like dear companies stop removing fan favorite features , right? Ultimately, I’d rather just prevent those memories from surfacing in the first place, so I can avoid the inevitable cringe-worthy flashbacks.
So, how about a simple option to disable them altogether?
Adjusting Memory Frequency
Controlling the frequency of memories appearing in your feed is possible through the Facebook Memories settings. You can adjust the display frequency from constant to less frequent or even to never. This level of granular control allows for a more manageable stream of memories, preventing the feature from becoming intrusive.
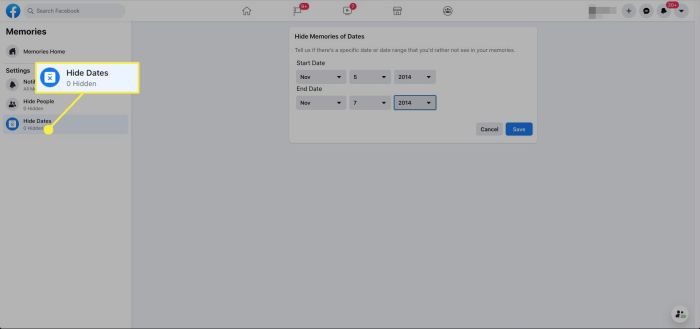
Preventing Specific Types of Memories
Facebook allows users to filter and prevent specific types of memories from appearing. This can include the ability to exclude memories from certain time periods, or to block specific people from appearing in the memories. This level of control helps curate a more personal and desired memory experience.
Table of Memory Prevention Methods
| Method | Description | Strengths | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Disable Memories Feature | Completely turns off the Memories feature. | Eliminates all memories from display. | High. Complete prevention. |
| Adjust Frequency Settings | Controls how often memories appear. | Allows for a more manageable feed. | Moderate to High. Dependent on chosen frequency. |
| Filter by Time Period | Exclude memories from specific dates or ranges. | Allows focusing on specific timeframes. | High. Precise control over displayed memories. |
| Exclude Specific People | Prevent memories featuring specific individuals. | Maintains privacy and relevance. | High. Controls the visibility of specific individuals. |
Impact of Preventing Memories
Curating your digital footprint is increasingly important in today’s interconnected world. One aspect of this curation is the control we have over the memories Facebook presents. This control, while seemingly simple, can have significant ripple effects on our emotional well-being and social interactions. The act of preventing these memories from surfacing raises a multitude of potential benefits and drawbacks that deserve careful consideration.
Potential Positive Effects of Suppressing Memories
The decision to suppress Facebook memories can lead to several positive outcomes. Reduced exposure to potentially triggering content, for example, can lessen feelings of inadequacy or regret, especially for those struggling with self-esteem issues. This is particularly true for users who are acutely aware of their past posts or interactions and find those memories distressing. Moreover, by removing the constant visual reminders of past behaviors or relationships, individuals can potentially maintain a more positive and less critical self-image.
The conscious effort to prevent the surfacing of these memories can also be a tool to promote personal growth and move forward without being constantly reminded of past mistakes or regrets.
Potential Negative Effects of Suppressing Memories
Conversely, suppressing Facebook memories can also have negative consequences. A significant drawback is the potential for detachment from personal history. By actively removing reminders of past experiences, users might lose the opportunity to learn from their mistakes or appreciate the evolution of their lives. This intentional distancing from past selves could also lead to a lack of personal growth, as the ability to reflect on past experiences is vital for personal development.
Moreover, an overreliance on suppressing memories could foster a fear of confronting the past, creating a barrier to personal healing and acceptance.
Impact on Social Interactions
The act of suppressing memories can subtly alter social interactions. Individuals might feel less inclined to share or discuss aspects of their past if they fear negative reactions from others. This can lead to a reduced sense of community and openness in online interactions, as individuals may become less transparent about their life journeys. On the other hand, it can also lead to a stronger sense of self-control and greater ability to choose the narrative they wish to share.
Psychological Consequences of Blocking Memories
Preventing Facebook memories from surfacing can have significant psychological implications. The constant avoidance of these memories might lead to feelings of guilt, regret, or even anxiety. These feelings, if left unaddressed, can escalate into more significant mental health challenges. Furthermore, the lack of introspection that comes with suppressing these reminders can hinder personal growth and self-awareness. Instead of processing and accepting these experiences, individuals might push them further into the subconscious, potentially exacerbating any underlying emotional issues.
Comparison of Advantages and Disadvantages
| Potential Impact | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Reduced feelings of inadequacy | Suppression can lessen negative self-perception by limiting exposure to past posts perceived as embarrassing or regrettable. |
| Potential for increased self-esteem | By removing triggers, users might experience a more positive self-image, fostering greater confidence. |
| Detachment from personal history | Suppression can lead to a lack of opportunity to learn from past experiences or appreciate personal growth. |
| Reduced social openness | Fear of negative reactions to past actions may hinder transparent communication and sharing of life experiences. |
| Increased feelings of guilt or anxiety | Avoiding confronting past memories can lead to unresolved emotional issues and potentially worsen existing mental health concerns. |
Alternatives to Blocking Memories
Facebook memories, while often nostalgic, can sometimes trigger unwanted emotions. Instead of completely blocking them, there are strategies to manage their impact without resorting to a complete digital blackout. These approaches focus on reframing, reinterpreting, and actively managing the feelings associated with these reminders. This allows for a more balanced and controlled interaction with the platform.
Reframing and Reinterpreting Memories
Managing the emotional impact of memories involves a shift in perspective. Instead of viewing them as solely negative or overwhelming, we can actively choose to reinterpret them in a more positive or neutral light. This involves consciously focusing on the positive aspects of the experience or understanding the context of the situation more broadly. For example, a memory of a difficult conversation can be reframed as an opportunity for growth and learning, rather than just a source of stress.
Strategies for Managing Emotional Responses
Effective strategies for dealing with the emotional responses triggered by Facebook memories are crucial. These strategies aim to acknowledge and process the feelings without being overwhelmed by them. The key is to create a space for understanding and acceptance, rather than avoidance.
- Mindfulness and Emotional Regulation: Practicing mindfulness techniques can help in acknowledging and accepting the feelings associated with memories without judgment. This involves focusing on the present moment and observing thoughts and feelings as they arise, without getting carried away by them. For example, deep breathing exercises or meditation can help to calm the mind and body when a particularly strong emotional response arises.
It’s about acknowledging the feeling without being consumed by it.
- Journaling: Writing down thoughts and feelings related to the memories can be a powerful tool for processing emotions. Journaling allows for a safe space to explore the complexities of the experience and develop a more nuanced understanding of the situation. It allows for the feelings to be acknowledged and processed without necessarily needing a response.
- Distraction Techniques: Engaging in activities that distract from the memories can be beneficial. This could involve listening to music, spending time in nature, engaging in hobbies, or pursuing other interests. These activities provide a healthy outlet for emotions and help shift focus away from the memories.
- Seeking Support: Talking to a friend, family member, therapist, or support group about the feelings triggered by memories can be incredibly helpful. Sharing experiences and perspectives with others can provide a sense of validation and support, which is often critical in managing complex emotions. Support groups or talking to trusted people can often offer a broader perspective.
Creating a Positive Narrative
It’s essential to cultivate a positive narrative around memories. This involves actively choosing to focus on the positive aspects of the past, even when negative experiences are present. This doesn’t mean ignoring the negative, but rather acknowledging it as a part of a broader experience and choosing to focus on the lessons learned or the positive outcomes that emerged.
- Focus on Positive Outcomes: Instead of dwelling on the struggles or difficulties associated with a memory, focus on the positive outcomes or lessons learned. This could be personal growth, relationships strengthened, or valuable experiences gained. This approach involves acknowledging both sides of the experience and recognizing the value of the memory as a whole.
- Celebrate Achievements: Highlighting personal achievements and milestones captured in memories can help in shifting the focus away from potentially painful aspects. This can be as simple as remembering a successful project or a personal triumph. These small wins can create a positive narrative around the memory.
- Recognize Growth: Reflect on how the memory contributed to personal growth or development. Identifying the lessons learned and the impact of the experience on personal growth can transform a potentially negative memory into a valuable experience.
Technical Aspects of Memory Suppression
Facebook’s memory generation and display system relies on a complex interplay of algorithms and data points. Understanding these technical mechanisms is crucial for comprehending how to effectively manage and potentially suppress the appearance of these memories. This system isn’t simply a chronological record; it’s a dynamic presentation tailored to each user’s unique interactions and activity on the platform.The core of Facebook’s memory engine is a sophisticated algorithm that sifts through a massive dataset of user activity.
This dataset encompasses a wide range of information, including posts, comments, photos, videos, and interactions with friends and groups. Crucially, the algorithm considers the context surrounding each interaction, evaluating factors like time, location, and associated individuals.
Memory Generation Process
The process of generating memories involves several key steps. First, the system identifies potential memory candidates based on user activity. This initial filtering process involves sophisticated pattern recognition algorithms, which analyze the user’s activity streams for specific patterns and correlations. Second, the system analyzes the content of these interactions. This includes evaluating the emotional content of the posts and the significance of the associated individuals or groups.
Finally, the system aggregates and curates the selected interactions into coherent memory units. This final stage focuses on presenting the memories in a visually appealing and contextually relevant manner, often incorporating relevant visual elements.
Algorithm Considerations
The algorithms used by Facebook to determine which memories are shown are complex and proprietary. However, several factors are likely considered. Frequency of interaction plays a significant role. Frequent interactions between users are more likely to trigger memory generation. Similarly, interactions associated with significant events (birthdays, anniversaries, holidays, etc.) are prioritized.
Sentiment analysis is also employed to determine the emotional tone of the interactions, with positive memories often prioritized. Furthermore, the algorithm likely considers the recency of the interactions, with more recent events being more prominent in the generated memories.
Memory Curating and Display
Facebook curates memories to present a coherent and engaging narrative of a user’s activity. This curation process likely involves several stages. Initially, the system selects relevant interactions and arranges them chronologically. Next, it applies visual enhancements, such as adding photos and videos, to make the memories more engaging. Finally, it considers the user’s preferences and activity patterns to tailor the display of memories.
This personalized approach ensures that the user experience remains relevant and meaningful.
Technical Factors Influencing Memory Appearance
Several technical factors can influence the appearance of memories. These factors include the user’s activity level, the frequency of interaction with specific people, the type of content shared (photos, videos, text), and the context surrounding the interactions. Moreover, the algorithm may consider the user’s privacy settings, ensuring that memories are displayed in accordance with these settings. Finally, changes in Facebook’s algorithms and data storage techniques may impact memory generation and display over time.
Diagram of Memory Generation
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
| User Activity | --> | Data Collection | --> | Memory Candidate|
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
| |
| |
V V
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
| Pattern Matching | --> | Interaction Analysis | --> | Memory Curation|
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
| |
| |
V V
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
| Memory Display | <-- | User Preferences | <-- | Privacy Settings|
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
Examples of Memory Types
Facebook memories, while often intended to be nostalgic, can sometimes trigger unwanted emotions or feelings.
Understanding the different types of memories that people might want to suppress is crucial for effectively managing these digital reminders. This section will explore various categories of memories, from positive recollections that become unwelcome reminders to negative experiences that Facebook can unfortunately resurrect.
Types of Unwanted Memories
Memories can be categorized in several ways, based on the emotional impact and the associated context. This understanding is vital for tailoring memory suppression strategies.
- Memories related to specific events: These can range from significant life events like weddings or graduations to less joyous occasions such as accidents or breakups. These events, while often associated with positive emotions, can become unwanted reminders if the current circumstances are less favorable. For example, a graduation photo might evoke feelings of longing for a simpler time or past relationships if the current relationship isn't going well.
- Memories related to relationships: Past relationships, whether positive or negative, can trigger complex emotions. A cherished memory of a long-lost friend might evoke feelings of loneliness if the friend is no longer in contact. Conversely, a painful memory of a toxic relationship can be reactivated by Facebook posts from that person, causing distress.
- Memories related to periods of life: Specific periods, like childhood, adolescence, or a particular job, might hold a variety of memories. A photo from a childhood trip might trigger positive nostalgia, but also feelings of longing for a simpler time, especially if the current circumstances feel less enjoyable. Similarly, memories from a previous job might resurface feelings of regret or dissatisfaction if the current job is unsatisfying.
Tired of Facebook memories popping up unexpectedly? Want to control the digital time machine? Learning how to use Google Meet annotations while presenting can be a useful tool for engagement, but ultimately, you might want to turn off Facebook memories before they have a chance to trigger a wave of unwanted nostalgia. This could be a good way to prevent those Facebook memories from surfacing, giving you more control over your digital experience.
Perhaps a simple "no memories" setting in Facebook might be a good start. Check out this article on google meet annotations while presenting for some cool presentation tips! Then, you can really focus on blocking those memories from popping up, preventing the urge to revisit the past.
Positive Memories as Unwanted Reminders
Even positive memories can become unwanted reminders under certain circumstances. These memories, while potentially joyful, can lead to feelings of longing, regret, or inadequacy if they are triggered at inopportune times.
- Nostalgia-inducing memories: Photos from a fun vacation or a celebratory event might trigger feelings of longing for a past life or a time when things felt easier or happier. These memories can become unwanted reminders if the present circumstances feel challenging or stressful.
- Memories of past achievements: Photos or posts showcasing past accomplishments might trigger feelings of inadequacy if current achievements don't feel as significant. This is especially true if the user feels they have not kept up with their past self.
- Memories associated with past relationships: Happy memories from a past relationship might trigger sadness or longing for a time when things were different. These reminders can become unwelcome if the user is currently struggling with a current relationship or feelings of isolation.
Negative Memories Triggered by Facebook
Facebook memories can inadvertently resurface negative experiences, potentially causing emotional distress. The context in which these memories are triggered is often crucial in determining the level of impact.
- Memories of past traumas: Accidentally encountering old photos from a traumatic event can cause significant emotional distress. For example, a photo of an accident could trigger intense feelings of fear or anxiety.
- Memories of past failures or disappointments: A post from a past friend group or a work project might evoke feelings of failure or regret. This can be particularly impactful if the user is experiencing similar negative feelings in their current life.
- Memories associated with negative relationships: Photos from a past toxic relationship might trigger feelings of anger, resentment, or sadness. These memories can be unwelcome if the user is still grappling with the effects of that relationship.
Table of Memory Types, Stop facebook memories before they have a chance to pop up
The following table summarizes the various types of memories that individuals might wish to prevent from surfacing on Facebook.
| Memory Type | Example |
|---|---|
| Specific Events | Graduation photos, wedding photos, accidents, breakups |
| Relationships | Photos with ex-partners, memories of lost friends |
| Periods of Life | Childhood photos, memories from a particular job, adolescence |
| Positive Reminders | Vacation photos, celebratory events, past achievements |
| Negative Triggers | Photos from traumatic events, past failures, toxic relationships |
Impact on Digital Wellbeing
Social media platforms, like Facebook, deeply intertwine with our daily lives. While offering connection and shared experiences, they can also contribute to digital overload and negatively impact mental health. Controlling the constant influx of memories, particularly those that might evoke unwanted emotions or comparisons, is a critical aspect of managing our digital wellbeing. This intentional control can foster a healthier relationship with social media, reducing stress and promoting a more balanced online experience.
Controlling Facebook memories can significantly improve mental health and reduce stress. By curating the memories we see, we can avoid triggers that might lead to feelings of inadequacy, regret, or comparison. This proactive approach to managing digital intake can foster a more positive and mindful engagement with the platform.
Relationship Between Memory Suppression and Digital Wellbeing
Controlling Facebook memories is directly linked to digital wellbeing. Suppressing unwanted memories allows for a more curated and positive online experience, reducing the potential for negative emotions and promoting a healthier relationship with social media. This conscious choice to manage the flow of information contributes to a sense of control and agency, which is crucial for digital wellbeing.
Factors Influencing Digital Wellbeing
Several factors influence digital wellbeing when dealing with Facebook memories. Personal experiences, past traumas, and current life situations all play a role in how we react to these memories. Additionally, the nature of the memories themselves—positive, negative, or neutral—significantly impacts our emotional responses. Finally, the individual's social comparison tendencies and their current emotional state also play a vital role in how they interpret and process these memories.
Benefits of Controlling Digital Memories
- Reduced stress and anxiety: By limiting exposure to memories that trigger negative emotions, users can experience a noticeable decrease in stress and anxiety levels. This is particularly important for individuals who are prone to social comparison or who struggle with self-esteem issues.
- Improved self-esteem: Avoiding memories that highlight past shortcomings or perceived failures can positively impact self-esteem. Users can focus on present accomplishments and future goals without being constantly reminded of past experiences.
- Enhanced focus and productivity: A curated online experience, free from triggering memories, allows for greater focus and productivity. This is because users are less likely to be distracted by emotional responses to past events.
- Increased mindfulness: The process of actively managing digital memories encourages a more mindful approach to social media use. Users become more aware of how specific memories impact their emotions and can make conscious choices about engagement.
Drawbacks of Controlling Digital Memories
- Potential for missing out on positive memories: Actively suppressing memories might lead to the unintentional exclusion of positive experiences. This requires a careful balance between controlling negative memories and appreciating positive ones.
- Risk of social isolation: If users become overly focused on controlling their online experience, they might miss out on important social connections and updates. A balance between controlling memories and maintaining social connections is essential.
- Potential for emotional suppression: In some cases, suppressing memories could lead to unresolved emotions. This requires users to address these feelings outside of the digital realm, possibly through therapy or other support systems.
- Difficulty in adjusting to changes: The process of managing memories might require users to adapt to new habits and routines. This can be challenging for individuals who have developed ingrained patterns of online interaction.
Tips for Improving Digital Wellbeing
- Develop a personalized memory management strategy: Identify specific memories that trigger negative emotions and develop strategies to address them. This could involve setting time limits for Facebook use or using filtering options to avoid specific types of content.
- Set boundaries on social media use: Establish clear limits on daily social media use and stick to them. This helps to avoid becoming overly immersed in the platform and experiencing overwhelming memories.
- Practice self-compassion: Treat yourself with kindness and understanding. Recognize that everyone experiences setbacks and negative memories. Avoid dwelling on them and focus on moving forward.
- Seek support from friends and family: Connect with trusted individuals who can provide emotional support and guidance. Discussing feelings and experiences can help to manage negative emotions.
Ending Remarks: Stop Facebook Memories Before They Have A Chance To Pop Up
In conclusion, controlling Facebook memories is a multifaceted issue with personal implications. We've explored the user's needs, the methods for prevention, and the potential impact on digital well-being. While preventing these memories might seem like a simple technical fix, the emotional and social implications are significant. Ultimately, the choice to suppress or manage these reminders rests with the individual, informed by a deeper understanding of the reasons behind their desire to do so.
This article provides a comprehensive guide to navigating the complexities of managing Facebook memories, empowering you to take control and create a more positive digital experience.