Smart cities in the age of 5G and IoT are poised to revolutionize urban living. Imagine cities where seamless connectivity and intelligent systems work together to optimize everything from traffic flow to waste management. This exploration delves into the exciting possibilities and challenges of integrating 5G and IoT technologies into urban environments, examining how they enhance services, improve quality of life, and shape the future of cities.
From the foundational infrastructure to the innovative applications, we’ll uncover the intricate workings of these smart city solutions. We’ll examine the role of 5G in enabling the rapid growth of IoT devices, the data collection and analysis processes involved, and the potential security concerns. This discussion will also highlight the key differences between traditional and smart cities, and explore the opportunities and challenges in deploying these transformative technologies.
Introduction to Smart Cities
Smart cities represent a paradigm shift in urban development, leveraging technology to enhance the quality of life for residents. They are more than just collections of interconnected devices; they are sophisticated ecosystems where data-driven insights optimize infrastructure, services, and community engagement. This integration of technology across various sectors creates a more efficient, sustainable, and responsive urban environment.Smart cities are characterized by the seamless integration of diverse technologies, creating a holistic approach to urban planning and management.
The interconnected nature of these systems allows for real-time data analysis, leading to proactive solutions and improved outcomes for citizens. From optimized traffic flow to enhanced public safety, smart city initiatives are reimagining the urban experience.
Key Components of Smart City Infrastructure
The infrastructure of a smart city is built upon the interconnectivity of various components. These components work in harmony to collect, process, and act upon data, creating a responsive and adaptive urban environment.
- Smart Transportation Systems: These systems encompass intelligent traffic management, public transportation optimization, and parking management. Real-time data from sensors and GPS systems allows for dynamic adjustments to traffic signals, reducing congestion and travel times. For example, a smart traffic light system that adjusts timing based on real-time traffic flow can significantly improve commute times and reduce fuel consumption.
- Smart Energy Management: Smart grids and energy-efficient buildings are vital components. These systems optimize energy consumption, reduce waste, and promote renewable energy sources. Smart meters, for example, allow residents to monitor and manage their energy usage, leading to cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
- Smart Public Safety: This component includes integrated security systems, surveillance technologies, and emergency response coordination. Data analysis can identify potential risks and enhance emergency response times. For instance, smart cameras equipped with facial recognition technology can help identify and track individuals in real-time, which is useful in situations involving crimes and security concerns.
- Smart Water Management: This focuses on optimizing water usage, detecting leaks, and ensuring efficient water distribution. Sensors and data analysis can identify and address water wastage issues. For example, sensors embedded in water pipes can detect leaks and alert authorities immediately, minimizing water loss and preventing costly damage.
The Role of 5G and IoT in Smart Cities
G and the Internet of Things (IoT) are revolutionizing urban environments by enabling a more interconnected and data-driven approach. 5G’s high bandwidth and low latency are essential for the real-time data transmission required for many smart city applications.
- Enhanced Connectivity: 5G provides the necessary infrastructure for connecting a vast network of IoT devices, creating a seamless flow of data between various components of the smart city.
- Real-time Data Analysis: IoT devices collect massive amounts of data, which 5G networks transmit rapidly. This allows for real-time analysis and the implementation of immediate solutions to issues like traffic congestion or energy consumption.
- Improved Efficiency: The integration of 5G and IoT allows for automated processes and dynamic adjustments to various systems. This leads to a more efficient use of resources and improved service delivery.
Traditional Cities vs. Smart Cities
| Feature | Traditional Cities | Smart Cities |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure Management | Reactive maintenance, limited data-driven insights. | Proactive maintenance, real-time data analysis for optimization. |
| Resource Management | Inefficient resource allocation, higher waste levels. | Optimized resource allocation, reduced waste, and greater sustainability. |
| Public Services | Limited access to real-time information and services. | Enhanced public services with access to real-time information and services. |
| Citizen Engagement | Limited opportunities for citizen feedback and participation. | Increased citizen engagement through interactive platforms and feedback mechanisms. |
5G Infrastructure and its Impact
The dawn of 5G technology marks a pivotal moment in the evolution of smart cities. This next-generation wireless network offers unprecedented speed, reliability, and low latency, opening doors to a plethora of innovative applications that were previously unimaginable. Its influence on the Internet of Things (IoT) is particularly profound, enabling a more interconnected and responsive urban environment.G’s superior performance compared to its predecessors allows for a seamless integration of a significantly increased number of IoT devices, dramatically expanding the possibilities for smart city solutions.
This enhanced connectivity enables real-time data exchange, enabling sophisticated analyses and faster responses to urban challenges.
Technological Advancements of 5G Networks
G networks represent a significant leap forward in wireless communication technology. Key advancements include substantially higher data transmission rates, significantly improved network reliability, and dramatically reduced latency. These enhancements are crucial for supporting the burgeoning number of IoT devices and the real-time data demands of smart city applications. The increased bandwidth allows for simultaneous communication from numerous devices without noticeable slowdowns.
Improved reliability ensures consistent connectivity, minimizing disruptions in critical services. Lower latency enables near-instantaneous data transfer, essential for applications requiring rapid response times.
5G Support for IoT Devices in Smart Cities
G’s enhanced capabilities directly address the needs of IoT devices in smart cities. The increased data transfer rate allows more devices to connect simultaneously without impacting performance. The network’s reduced latency is crucial for real-time data transmission, essential for applications such as traffic management and smart grids. Furthermore, 5G’s enhanced reliability minimizes interruptions in critical services, guaranteeing consistent data flow for smart city applications.
This reliability is particularly important for applications that require uninterrupted operation, such as public safety monitoring systems.
5G Applications in Smart City Services
G’s potential extends to numerous smart city services. For instance, in traffic management, 5G can enable real-time traffic monitoring, optimizing traffic flow, and reducing congestion. This is achieved by connecting sensors embedded in roads, traffic lights, and vehicles to the network. In public safety, 5G enables real-time video feeds from surveillance cameras, enabling faster response times to emergencies.
Furthermore, 5G can power smart grids, allowing for real-time monitoring and control of energy distribution, leading to greater efficiency and reduced waste.
Technical Specifications of 5G Networks
| Feature | Description | Impact on Smart Cities ||—|—|—|| Data Transmission Rate | Gigabit speeds (Gbps) | Enables real-time data exchange from numerous IoT devices without noticeable slowdowns, essential for traffic monitoring, and energy management. || Latency | Milliseconds (ms) | Enables near-instantaneous data transfer, crucial for applications requiring rapid response times, such as public safety monitoring and traffic control.
|| Bandwidth | Significantly increased | Supports a massive influx of IoT devices without impacting performance. This is critical for supporting the growing number of sensors and actuators in smart cities. || Reliability | High availability | Minimizes interruptions in critical services, ensuring consistent data flow for smart city applications, especially those concerning public safety. || Network Capacity | Supports a large number of connected devices | Enables seamless integration of a significantly increased number of IoT devices, expanding the possibilities for smart city solutions.
|
IoT Applications in Smart Cities
The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing urban landscapes, enabling smarter, more efficient, and responsive cities. Integrating sensors, actuators, and data analytics allows for the optimization of various urban services, from energy management to transportation. This interconnected system, fueled by 5G infrastructure, provides unprecedented opportunities to improve quality of life and enhance urban sustainability.
Smart cities in the age of 5G and IoT are all about seamless data collection and analysis, right? Imagine a network of sensors, constantly monitoring everything from traffic flow to energy consumption. A great example of a component that could be used in these smart city applications is the elgato eve degree relase temperature sensor , providing precise temperature readings.
This kind of granular data is key to optimizing resource allocation and creating truly efficient urban environments.
Smart Grids
Smart grids leverage IoT to enhance the efficiency and reliability of energy distribution. Sensors embedded in power lines, substations, and consumer appliances provide real-time data on energy consumption and supply. This data allows for predictive maintenance, optimized energy distribution, and reduced energy waste. For instance, smart meters can detect anomalies in energy consumption patterns, alerting utility companies to potential equipment failures or fraudulent activity.
- Real-time monitoring of energy flow and consumption patterns.
- Automated demand response systems, adjusting energy supply to meet fluctuating demand.
- Predictive maintenance of grid infrastructure, reducing downtime and improving reliability.
Smart Transportation
IoT plays a crucial role in optimizing urban transportation systems. Connected vehicles, equipped with sensors, communicate with each other and traffic infrastructure to enhance traffic flow and safety. Smart traffic lights, equipped with sensors, adjust timing based on real-time traffic conditions, minimizing congestion. This allows for optimized routes and real-time traffic updates for commuters, ultimately improving efficiency and reducing travel time.
- Real-time traffic monitoring and congestion management.
- Optimized traffic signal control, improving traffic flow and reducing delays.
- Smart parking systems, helping drivers find available parking spaces quickly.
Smart Homes
IoT technology is transforming the way we live within our homes. Smart home devices, equipped with sensors, automate various tasks, from adjusting lighting and temperature to managing security systems. This integration of devices improves energy efficiency and provides enhanced security and comfort. Smart appliances, such as refrigerators and washing machines, communicate with each other and with central hubs to optimize energy use and reduce waste.
- Automated home security systems, utilizing sensors and cameras to monitor and respond to potential threats.
- Automated lighting and climate control systems, optimizing energy consumption and improving comfort.
- Integration of appliances and devices to optimize energy usage and reduce waste.
Data Collection and Analysis
The core of IoT applications in smart cities relies on efficient data collection and analysis. Sensors collect various data points, from environmental conditions to energy consumption patterns. This data is then processed and analyzed to identify trends, patterns, and insights. Sophisticated algorithms and machine learning models are employed to interpret the data and generate actionable information for city planners and administrators.
This process allows for proactive interventions and optimized resource allocation.
Security Concerns
The increasing reliance on IoT devices raises critical security concerns. Vulnerable devices can be exploited by malicious actors, leading to unauthorized access to sensitive data or disruption of critical infrastructure. Robust security protocols and measures are essential to safeguard data and prevent unauthorized access. Data encryption, authentication, and regular security updates are crucial for maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of IoT systems.
Smart cities, powered by 5G and IoT, are poised for incredible advancements. Imagine the seamless integration of everything, from traffic management to energy grids. However, even with these exciting technological leaps, unexpected changes in the tech world, like Facebook’s recent decision to drop Blackberry support for WhatsApp, highlights the rapid evolution of digital ecosystems. These shifts, while sometimes surprising, ultimately contribute to the dynamic landscape of smart city development.
| IoT Application | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Grids | Reduced energy waste, improved reliability, enhanced grid efficiency | High initial investment costs, potential security vulnerabilities in smart meters |
| Smart Transportation | Improved traffic flow, reduced congestion, enhanced safety | Privacy concerns regarding vehicle tracking data, reliance on reliable communication networks |
| Smart Homes | Enhanced comfort, improved energy efficiency, increased security | Potential for data breaches, dependence on reliable internet connectivity |
Smart City Services and Solutions
Smart cities leverage 5G and IoT to deliver enhanced services and improved quality of life for citizens. The real-time data and communication capabilities of these technologies empower innovative solutions across various urban functions, from public safety to environmental sustainability. This transformation is not just about technological advancement; it’s about creating more efficient, resilient, and citizen-centric urban environments.
Public Safety Enhancement
Real-time crime monitoring and response are significantly enhanced by 5G and IoT. Smart cameras equipped with advanced image recognition software, combined with sensors monitoring traffic patterns and pedestrian flow, can help identify potential threats and alert authorities quickly. The improved communication speed and reliability of 5G networks ensure that critical information reaches emergency responders in real-time, enabling faster response times and potentially saving lives.
Waste Management Optimization
IoT sensors deployed in waste collection vehicles and bins provide real-time data on fill levels, location, and even the type of waste. This data enables optimized collection routes, reducing fuel consumption and improving efficiency. Smart waste management systems can also predict future waste generation patterns, allowing for proactive adjustments in collection schedules. This leads to reduced costs and a cleaner environment.
Urban Planning and Mobility
Smart cities use IoT sensors to monitor traffic flow, pedestrian activity, and parking availability in real-time. This data informs urban planners about the optimal use of resources and the identification of traffic bottlenecks, enabling better traffic management strategies. Data analysis from IoT devices can also provide insights into the needs of different neighborhoods, allowing for targeted urban development projects and sustainable infrastructure planning.
Improved Citizen Services
Smart city solutions improve various aspects of citizen life, from transportation to utility management. Real-time information on public transportation delays, combined with improved communication channels, allows for proactive management of disruptions and ensures smoother journeys. Smart parking systems guide drivers to available parking spots, reducing wasted time and frustration. Furthermore, IoT devices can monitor the condition of infrastructure, enabling timely repairs and preventing potential failures.
Smart cities, fueled by 5G and IoT, promise incredible efficiency and convenience. However, as these systems collect and analyze vast amounts of data, issues like those highlighted in the recent Google FTC YouTube child privacy violations fine of $170 million for COPPA ads ( google ftc youtube child privacy violations fine 170 milliion coppa ads ) demand serious consideration.
We need to balance technological advancements with robust data protection measures in these futuristic urban landscapes.
These features collectively contribute to a more efficient and convenient urban experience.
Summary of Smart City Services and IoT Applications, Smart cities in the age of 5g and iot
| Smart City Service | Corresponding IoT Applications |
|---|---|
| Public Safety | Smart cameras with image recognition, sensors for traffic/pedestrian flow, real-time communication channels |
| Waste Management | Sensors in collection vehicles/bins for fill levels, route optimization, waste type identification |
| Urban Planning & Mobility | Sensors monitoring traffic flow, pedestrian activity, parking availability, infrastructure condition monitoring |
| Citizen Services | Real-time public transport information, smart parking systems, infrastructure condition monitoring |
Challenges and Opportunities
Smart cities, fueled by 5G and IoT, promise a brighter future. However, realizing this vision faces numerous hurdles and exciting possibilities. From the initial investment in infrastructure to the ethical implications of data collection, the journey toward a truly intelligent urban landscape is complex and nuanced. This section delves into the critical challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
Infrastructure Costs and Deployment
Deploying 5G networks and expanding IoT infrastructure across a city is a substantial undertaking. The initial investment required for building out the necessary communication towers, sensors, and data centers can be daunting for municipalities. Furthermore, ensuring consistent and reliable service across diverse geographical terrains, including mountainous areas or densely populated urban centers, adds another layer of complexity. The cost of upgrading existing infrastructure and adapting older buildings for smart technologies also poses a challenge.
For example, retrofitting older buildings with smart thermostats or lighting systems requires significant capital investment.
Data Security and Privacy
The sheer volume of data generated by IoT devices in a smart city presents a significant security concern. Protecting this data from cyberattacks and ensuring user privacy are paramount. Sophisticated security measures and robust data encryption protocols are crucial to safeguard sensitive information. Furthermore, establishing clear data governance policies and protocols is essential to ensure that data is collected, used, and shared responsibly.
Regulations and compliance with privacy laws, such as GDPR, also need to be factored into the design and implementation of smart city projects.
Innovation and Economic Growth
Smart city initiatives offer immense opportunities for economic growth. The implementation of smart traffic management systems can reduce congestion and improve transportation efficiency, leading to fuel savings and reduced emissions. Smart energy grids can optimize energy consumption, potentially lowering utility bills for residents and businesses. Smart waste management systems can improve recycling rates and reduce landfill costs.
These innovations can create new job opportunities in areas like data analysis, software development, and smart technology maintenance. For example, a smart parking system can boost economic activity by making parking more accessible and efficient, thereby reducing delays and attracting more customers.
Social and Ethical Implications
The increasing reliance on data and automation in smart cities raises important social and ethical concerns. Ensuring equitable access to smart city services for all residents, regardless of socioeconomic status or location, is crucial. Potential biases in algorithms used for decision-making, such as in traffic management or public safety, need to be carefully addressed. Transparency and accountability in the use of data are vital to build public trust and prevent the potential for misuse or discrimination.
Comparison of Challenges and Opportunities
| Aspect | Challenges | Opportunities |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure | High initial investment costs, complex deployment in diverse terrains, need to upgrade existing infrastructure. | Improved efficiency and sustainability, reduced congestion and emissions, new job creation in the smart city sector. |
| Data Security | Potential for cyberattacks, ensuring user privacy, complex data governance. | Enhanced security and trust, data-driven insights for optimized services, improved public safety. |
| Innovation | Overcoming technological limitations, adapting existing infrastructure, attracting skilled talent. | Economic growth through new businesses and services, reduced operational costs, improved quality of life for citizens. |
| Social Equity | Ensuring equitable access to services, avoiding biases in algorithms, maintaining public trust. | Improved quality of life for all citizens, increased social inclusion, reduced inequalities. |
Future Trends and Predictions
The smart city landscape is rapidly evolving, driven by the integration of 5G and IoT. This fusion is poised to dramatically reshape urban environments, introducing new levels of efficiency, connectivity, and convenience. Predicting the future is inherently complex, but by analyzing current trends and potential technological advancements, we can paint a picture of what smart cities might look like in the coming years.The convergence of AI, machine learning, and sophisticated data analytics is set to become a cornerstone of future smart city development.
By analyzing vast datasets from interconnected sensors and devices, cities can gain unprecedented insights into citizen needs and operational efficiency. This data-driven approach will be crucial in optimizing resource allocation, improving public services, and creating more resilient urban ecosystems.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is rapidly transforming numerous sectors, and smart cities are no exception. AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of data collected from various sources, such as traffic flow, energy consumption, and citizen feedback. This analysis can identify patterns, predict future needs, and automate responses to various situations. For example, AI algorithms can predict traffic congestion and adjust traffic light timings in real-time, optimizing traffic flow and reducing commute times.
Furthermore, AI-powered predictive maintenance can identify potential equipment failures in infrastructure, such as water pipes or power grids, allowing for proactive repairs and preventing disruptions.
Advancements in Machine Learning (ML)
Machine learning algorithms can further enhance the capabilities of smart city systems. By continuously learning from data, ML models can improve their predictive accuracy and adapt to changing conditions. For instance, ML algorithms can analyze crime data to identify high-risk areas and deploy resources proactively, thereby enhancing public safety. Similarly, ML can optimize energy consumption in buildings by learning from real-time data on occupancy and environmental conditions.
The ability of ML to adapt to new data and improve its performance over time is critical to the ongoing development and refinement of smart city solutions.
Impact on Urban Life
The integration of AI and ML will significantly impact various aspects of urban life. Improved traffic management, optimized energy consumption, enhanced public safety, and more efficient public services are just a few examples. However, the potential societal impact goes beyond these immediate benefits. The ability to personalize services based on individual needs and preferences, as well as provide real-time information on various aspects of city life, will significantly enhance the quality of life for urban residents.
Potential Future Challenges and Opportunities
Implementing smart city technologies presents both challenges and opportunities.
- Data Security and Privacy: The increasing reliance on data collection raises significant concerns about data security and privacy. Robust data protection measures are crucial to ensure that sensitive information remains confidential and is used responsibly. This requires stringent regulations and ethical guidelines to prevent misuse and ensure the trust of citizens.
- Digital Divide: Ensuring equitable access to smart city technologies and services is essential to avoid exacerbating existing inequalities. Efforts should be made to bridge the digital divide and ensure that all citizens have access to the benefits of these technologies.
- Integration with Existing Infrastructure: Seamless integration of new technologies with existing infrastructure is a significant challenge. This requires careful planning and investment to ensure that new systems can effectively communicate and interact with existing ones.
- Cost of Implementation: The initial investment required for implementing smart city technologies can be substantial. However, the long-term benefits, including increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved quality of life, can outweigh these initial costs.
Illustrative Examples
Imagine a bustling city, seamlessly integrated with technology. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the potential of smart cities powered by 5G and IoT. This section delves into a hypothetical project, highlighting the practical applications and the challenges inherent in such an endeavor.
A Hypothetical Smart City Project
This project envisions a pilot program in a mid-sized city, focusing on enhanced traffic management and environmental monitoring. 5G infrastructure is deployed across the city, providing ultra-reliable and low-latency connectivity. The IoT network consists of sensors embedded in traffic lights, streetlights, and environmental monitoring stations. This allows for real-time data collection and analysis, enabling proactive responses to issues.
Benefits of the Project
The project promises numerous benefits. Improved traffic flow reduces congestion, leading to significant time savings for commuters and businesses. Real-time data on air quality and pollution levels allows the city to proactively address environmental concerns, potentially leading to reduced health risks. Predictive maintenance of city infrastructure through sensor data ensures efficient resource allocation and reduces costly repairs.
Challenges of the Project
Implementing such a project presents several challenges. The initial investment in 5G infrastructure and IoT devices is substantial. Ensuring data security and privacy is paramount to building public trust and confidence. Integrating diverse systems and ensuring interoperability can also prove complex. The challenge of managing large volumes of data and developing effective data analysis models is significant.
Furthermore, ensuring equitable access to the benefits of the smart city for all citizens is critical.
Data Flow and Analysis
The data flow in this project is crucial. Sensors collect data on traffic patterns, air quality, and environmental factors. This data is transmitted via the 5G network to central servers for processing. Sophisticated algorithms analyze the data to identify patterns and trends. This allows for real-time adjustments to traffic signals, pollution mitigation strategies, and maintenance schedules.
For example, traffic light timings can be adjusted in real-time based on traffic density, and pollution alerts can trigger the activation of anti-pollution measures.
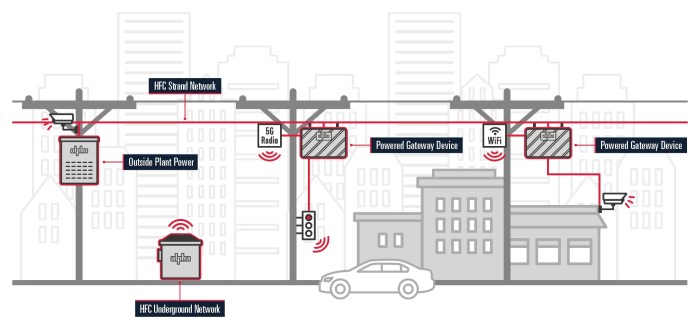
Smart City Street Scene Illustration
Imagine a street scene. Traffic lights equipped with sensors automatically adjust their timings based on real-time traffic flow data, minimizing congestion. Streetlights are equipped with sensors to detect pedestrian movement, automatically adjusting brightness and activating pedestrian safety features. Air quality sensors continuously monitor pollution levels and display the data on digital screens. Smart bins monitor fill levels and alert authorities to optimize collection schedules.
Security cameras equipped with facial recognition technology assist in public safety and incident response.
Detailed Illustration of a Smart City Street Scene
| Component | Function | Integration with 5G and IoT |
|---|---|---|
| Traffic Lights | Regulate traffic flow | Sensors monitor traffic density; 5G transmits data for real-time adjustments. |
| Streetlights | Provide illumination | Sensors detect pedestrian presence; 5G controls brightness and activates pedestrian safety features. |
| Air Quality Sensors | Monitor pollution levels | Sensors measure pollutants; 5G transmits data to display real-time readings. |
| Smart Bins | Optimize waste collection | Sensors monitor fill levels; 5G triggers collection alerts. |
| Security Cameras | Enhance public safety | Facial recognition technology; 5G facilitates real-time monitoring and incident response. |
Outcome Summary: Smart Cities In The Age Of 5g And Iot
In conclusion, smart cities in the age of 5G and IoT represent a significant leap forward in urban development. While challenges such as infrastructure costs and data security remain, the potential for innovation and economic growth is immense. The integration of AI and machine learning promises to further refine these systems, paving the way for a future where cities are more efficient, sustainable, and responsive to the needs of their citizens.
The future of urban living is bright, and these technologies are at the forefront of this exciting transformation.