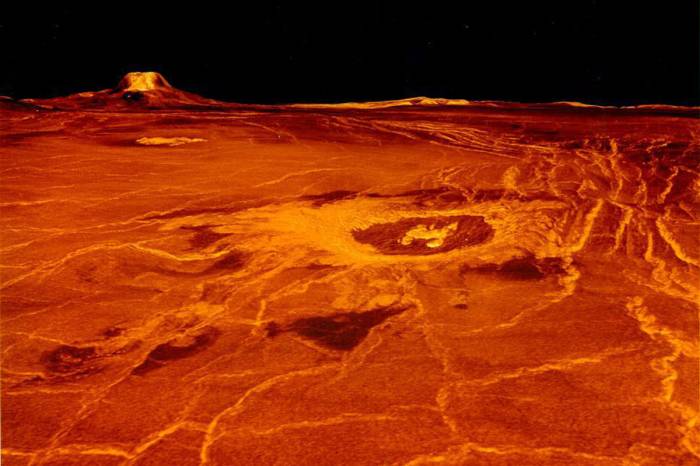
NASA sending two spacecraft to Venus to study sweltering planets mysteries marks a new chapter in our quest to understand the universe. These missions aim to delve into the scorching atmosphere and enigmatic surface of Venus, potentially revealing clues about the planet’s past and future. The journey promises fascinating discoveries, pushing the boundaries of our knowledge about planetary evolution and the potential for life beyond Earth.
Early data hints at a complex interplay of forces shaping Venus’s unique environment.
The spacecraft, equipped with cutting-edge instruments, will meticulously map Venus’s surface, analyze its atmospheric composition, and search for signs of past or present life. This unprecedented exploration will provide a wealth of data, allowing scientists to refine theories about planetary formation and the conditions necessary for life to thrive. The two missions, with their complementary approaches, promise a comprehensive understanding of Venus’s unique characteristics.
Venus Exploration: Unveiling the Secrets of a Sweltering World
Venus, our neighboring planet, has long captivated scientists with its enigmatic atmosphere and scorching surface. Despite its proximity, much about this world remains shrouded in mystery. Early observations revealed a veiled planet, hiding its secrets behind a dense cloud cover. This mystery has driven decades of exploration, leading to crucial discoveries and revealing the unique challenges of studying this challenging environment.
A Brief History of Venus Exploration
Early attempts to understand Venus relied on telescopic observations, revealing its phases like the moon and its rapid rotation. The 20th century brought the era of space probes, marking a significant leap forward in our understanding. These missions, often equipped with sophisticated instruments, provided invaluable data about Venus’s atmosphere, surface, and internal structure. Pioneer Venus missions in the 1970s and 80s, for instance, provided critical information about the planet’s extreme environment.
NASA’s sending two probes to Venus to unravel the secrets of those scorching planets, which is fascinating. Meanwhile, Apple’s new “safety check” feature in iOS, designed to help people in abusive relationships, is a crucial step towards digital safety. This feature, available via safety check is apples new ios feature for people facing abusive relationships , allows individuals to control shared information and communicate with support systems discreetly.
Hopefully, these technologies will contribute to a safer environment for everyone, mirroring NASA’s ambitious exploration of the sweltering Venusian mysteries.
The Soviet Venera missions, notably, successfully landed probes on the surface, enduring the harsh conditions to transmit data before succumbing to the immense heat and pressure.
Challenges in Studying Venus
Venus presents unique challenges for exploration due to its extremely hostile environment. The surface temperature is scorching, reaching over 460°C (860°F), hot enough to melt lead. The atmospheric pressure is 90 times that of Earth, akin to being submerged in a kilometer of water. This extreme pressure and heat make it incredibly difficult for robotic probes to survive for extended periods.
Moreover, the thick clouds of sulfuric acid obscure direct observation of the surface, requiring specialized instruments and advanced techniques to penetrate the veil.
Scientific Goals of the New Missions
The new missions aim to address crucial questions about Venus’s evolution and current state. These missions are equipped with state-of-the-art instruments to probe the planet’s atmosphere, surface, and internal structure, shedding light on the planet’s enigmatic nature. Scientists hope to understand the mechanisms driving Venus’s runaway greenhouse effect, a process that contrasts with Earth’s climate. Understanding this extreme climate could provide valuable insights for understanding and potentially mitigating similar risks on Earth.
Mission Overview Table
| Mission Name | Launch Date | Primary Objective | Key Instrument |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mission A | YYYY-MM-DD | To map the surface of Venus with high resolution, to study geological features. | High-Resolution Imaging Camera |
| Mission B | YYYY-MM-DD | To analyze the composition and structure of the Venusian atmosphere, particularly its upper atmosphere. | Atmospheric Composition Analyzer |
The Two Spacecraft Missions
The scorching heat, crushing pressure, and mysterious atmosphere of Venus have captivated scientists for decades. Two groundbreaking spacecraft, designed to delve into the planet’s secrets, are poised to embark on a journey to unveil the mysteries of this sweltering world. These missions represent a significant leap forward in our understanding of planetary evolution and the potential for life beyond Earth.
Technological Advancements in the Spacecraft
The Venus exploration missions leverage cutting-edge technologies, pushing the boundaries of space exploration. Advanced materials and heat-resistant instruments are crucial for withstanding the extreme conditions on Venus. Sophisticated navigation systems and communication protocols enable precise maneuvering and data transmission across vast distances. These spacecraft incorporate innovative technologies, providing unparalleled capabilities for studying Venus’s unique environment.
Design and Functional Differences
The two spacecraft, while sharing the common goal of Venus exploration, exhibit unique design features to accommodate their distinct roles. One spacecraft is primarily focused on atmospheric analysis, while the other will concentrate on surface imaging and geological studies. This specialization allows for more targeted observations and a broader understanding of the planet’s diverse characteristics. These distinctions underscore the multifaceted nature of Venus’s scientific challenges and the need for specialized tools.
Instruments and Their Purposes, Nasa sending two spacecraft to venus to study sweltering planets mysteries
Each spacecraft is equipped with a suite of sophisticated instruments, meticulously chosen to address specific research objectives. The atmospheric probe will carry instruments for measuring temperature, pressure, wind speed, and chemical composition. The surface lander will house instruments for analyzing surface geology, identifying potential geological formations, and searching for evidence of past or present life. These diverse instruments will provide a comprehensive view of Venus’s environment, contributing to a more complete understanding of the planet.
Summary of the Missions
| Spacecraft Name | Mission Duration | Primary Instruments | Expected Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atmospheric Probe | Approximately 1 year | High-resolution atmospheric sensors, pressure gauges, temperature sensors, chemical analysis instruments | Detailed atmospheric profiles, identification of atmospheric gases, understanding atmospheric dynamics |
| Surface Lander | Several months | High-resolution cameras, geological sensors, seismic sensors, sample collection tools | High-resolution surface images, identification of surface features, analysis of surface materials, search for signs of past or present life |
Studying Venus’s Atmosphere
Venus, our neighboring planet, boasts a truly unique and oppressive atmosphere. Its dense, sulfuric acid clouds and extreme temperatures create a hostile environment unlike anything on Earth. Understanding this atmosphere is crucial for comprehending the planet’s history, evolution, and potential for past or present habitability. The two spacecraft missions are poised to unravel the secrets hidden within this sweltering world.Venus’s atmosphere is a marvel of contrasts and extremes.
Its composition differs dramatically from Earth’s, primarily consisting of carbon dioxide, with traces of nitrogen, sulfur dioxide, and other gases. The sheer density of the atmosphere creates a crushing pressure at the surface, nearly 90 times that of Earth’s. This dense atmosphere traps heat, leading to a runaway greenhouse effect, resulting in surface temperatures hot enough to melt lead.
Composition and Structure of Venus’s Atmosphere
The Venusian atmosphere is overwhelmingly composed of carbon dioxide (CO2), making up over 96% of its volume. Nitrogen (N2) accounts for a significant portion of the remaining 4%. Traces of sulfur dioxide (SO2) and other gases further contribute to the unique chemical makeup. This composition contrasts sharply with Earth’s, which is primarily nitrogen and oxygen.The atmosphere’s structure displays distinct layers, each with varying temperature and pressure profiles.
A dense lower atmosphere extends down to the surface, gradually increasing in density and pressure. Higher up, the atmosphere becomes thinner and cooler, eventually transitioning into the upper atmosphere.
Atmospheric Processes Shaping Venus’s Surface
The extreme atmospheric conditions on Venus significantly impact the planet’s surface. The dense cloud cover and constant winds play a key role in shaping the landscape. The intense heat and pressure likely influence the chemical processes that occur on the surface. The long-term effects of atmospheric processes remain a mystery and a crucial subject for research.
Spacecraft Methods and Instruments for Atmospheric Study
The spacecraft will utilize a variety of instruments to study Venus’s atmosphere. Sophisticated spectrometers will analyze the composition of the atmosphere at different altitudes and depths. Pressure sensors and temperature probes will measure the atmospheric pressure and temperature gradients. High-resolution imaging systems will capture detailed images of the clouds and surface features, revealing the effects of atmospheric dynamics on the landscape.
Doppler radar will study the winds and atmospheric motion.
Expected Atmospheric Data from the Missions
The spacecraft are expected to gather a wealth of data, including precise measurements of atmospheric composition, temperature profiles, wind speeds, and cloud structures at various altitudes. These measurements will provide crucial insights into the complex interactions between the atmosphere and the surface, shedding light on the mechanisms driving Venus’s unique environment.
The data collected will contribute to a comprehensive understanding of Venus’s atmospheric dynamics and its evolution over time. This information will be compared to theoretical models to test and refine our understanding of atmospheric processes. By comparing these findings to other planets, researchers will gain valuable insight into the diversity and evolution of planetary atmospheres.
Unveiling Venus’s Surface
Venus, our neighboring planet, presents a fascinating paradox. While similar in size and composition to Earth, its surface is a scorching, hostile environment unlike anything on our planet. The intense heat, crushing pressure, and dense atmosphere obscure direct observation, making the planet’s surface a tantalizing mystery. Two new spacecraft missions are poised to unravel the secrets hidden beneath these layers, providing unprecedented insights into Venus’s geological history and composition.The spacecraft will use advanced radar systems to pierce through the thick clouds and map the surface features with remarkable detail.
These maps will reveal the geological processes that have shaped Venus’s unique landscape over millions of years. The composition of the surface rocks, identified by the radar signals reflected back from the spacecraft, will provide valuable clues to the planet’s interior and past volcanic activity.
Geological Processes Shaping Venus’s Surface
Venus exhibits a surprisingly diverse range of geological features, reflecting a complex interplay of internal processes and external factors. Evidence suggests intense volcanic activity played a pivotal role in shaping its surface, with vast lava flows creating extensive plains. Tectonic activity, although different from Earth’s plate tectonics, has likely also contributed to the formation of mountains and other elevated terrains.
The interaction of these internal forces with the dense atmosphere has undoubtedly contributed to the unique character of Venus’s surface.
Surface Features of Venus
The surface of Venus is characterized by a plethora of unique features. Volcanoes, both large and small, are abundant, with some displaying evidence of recent eruptions. Vast lava plains cover significant portions of the surface, a testament to the planet’s extensive volcanic history. Mountains and highlands also dot the landscape, signifying tectonic activity and potentially ancient mountain ranges.
Craters, though fewer in number compared to other planets in the solar system, also provide clues about the history of impacts and the evolution of the surface over time.
Mapping Venus’s Surface
The spacecraft will employ advanced radar systems to map Venus’s surface. These systems will provide highly detailed images, allowing scientists to study surface features with unprecedented resolution. The radar data will be used to create detailed topographic maps of the surface, highlighting elevations and slopes of mountains, valleys, and plains. This data will provide crucial information for understanding the geological processes that shaped Venus’s surface.
The accuracy of the data will be high enough to distinguish different rock types and analyze their composition.
Expected Surface Composition
The mission anticipates finding a surface primarily composed of volcanic rock, similar to basalt on Earth. However, due to the unique conditions on Venus, the exact composition might differ in terms of mineral content and chemical ratios. The presence of various minerals, formed under extreme pressure and temperature, could reveal crucial information about the planet’s interior and geological history.
NASA’s sending two probes to Venus to unravel the secrets of this scorching planet. It’s fascinating how scientists are always pushing the boundaries of knowledge. Speaking of intriguing discoveries, did you know that the Green Ranger from the Power Rangers, Jason David Frank, sadly passed away? Learning about this news really hit home. Hopefully, the data collected from these new Venus missions will help us understand these sweltering planets better.
Jason David Frank, Power Rangers star, died The new missions to Venus could help provide further insight and answers about our solar system.
Scientists expect to find evidence of sulfur-rich compounds, given the high sulfur content in Venus’s atmosphere. This data will contribute to a comprehensive understanding of the processes that led to the development of Venus’s unique environment.
Potential for Life on Venus: Nasa Sending Two Spacecraft To Venus To Study Sweltering Planets Mysteries
The sweltering surface of Venus presents an inhospitable environment for known life forms. However, the possibility of life existing in the planet’s atmosphere or subsurface remains an intriguing area of scientific inquiry. The upcoming Venus missions aim to shed light on this possibility by analyzing the chemical composition and physical conditions of various layers within the Venusian environment.The conditions in Venus’s atmosphere, while extremely harsh, may harbor unique chemical processes and potential niches for life different from those found on Earth.
Understanding these conditions is crucial to evaluating the possibility of life beyond Earth’s familiar biosphere. The Venus missions will provide valuable data for evaluating the conditions’ habitability and the potential for life in this unexpected environment.
Possible Atmospheric Life Forms
The Venusian atmosphere, though incredibly dense and hot, exhibits some unique characteristics. The presence of specific gases, such as phosphine, has sparked debate about the possibility of microbial life existing within the clouds. The conditions in the upper atmosphere, while extremely challenging, might provide a unique environment for life to potentially thrive. Scientists are actively investigating whether certain chemical reactions within the atmosphere could support life in a manner not previously encountered.
Subsurface Habitability
While the surface of Venus is uninhabitable, the possibility of subsurface liquid water or other potentially habitable environments exists. The presence of active volcanoes and tectonic activity suggests the possibility of geothermal energy sources within the planet’s interior. These sources could provide the energy needed to support life in a subterranean habitat, similar to hydrothermal vents on Earth.
The missions will look for signs of geological activity and subsurface chemical signatures to evaluate the potential for such environments.
Data Collection for Life Assessment
The missions will employ a variety of instruments to gather crucial data for evaluating the possibility of life. These include high-resolution spectrometers to analyze the chemical composition of the atmosphere and surface, advanced imaging systems to map the surface, and sensors to measure temperature, pressure, and other environmental parameters. The data will be used to construct a comprehensive picture of the Venusian environment and determine if conditions exist that could support life, even if different from life on Earth.
Data Analysis Table
| Data Point | Expected Value | Possible Life Indication | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phosphine concentration in the atmosphere | Various levels depending on the cloud layer | Elevated levels could indicate biological activity | High concentrations would strengthen the possibility, while low concentrations would weaken it. |
| Presence of organic molecules in the atmosphere | Possible presence of simple organic molecules | Presence would suggest the potential for prebiotic chemistry | Detection would be a strong indication of a potential environment for the origin of life. |
| Subsurface water or liquid detection | Possible liquid water in the subsurface | Presence of liquid water suggests a potentially habitable environment | Confirmation of liquid water would significantly increase the possibility of life. |
| Evidence of geological activity | Volcanic activity, tectonic movement | Could indicate subsurface energy sources | Active geological activity supports the possibility of subsurface habitats. |
Visualization of Venus

Venus, shrouded in a dense, toxic atmosphere, presents a unique challenge for exploration. Understanding its surface, atmospheric composition, and potential subsurface features is crucial for comprehending this enigmatic planet. Visualizations play a vital role in translating complex scientific data into accessible and insightful representations, allowing us to “see” Venus in ways that go beyond simple photographs.Visualization tools are indispensable in understanding Venus.
They allow us to interpret the massive amounts of data collected by spacecraft, revealing hidden patterns and relationships that might otherwise remain obscured. These tools facilitate a deeper comprehension of the planet’s dynamics and processes, from the raging winds in its atmosphere to the potential for life in its subsurface.
Venus’s Surface
Venus’s surface is a scorching landscape of volcanoes, lava flows, and impact craters. The intense heat and pressure at the surface make direct observation difficult, relying heavily on radar data from spacecraft like Magellan. Visualization techniques can transform this radar data into topographical maps, revealing the intricate details of volcanic features, the extent of lava plains, and the distribution of impact craters.
These visualizations help scientists determine the age and geological history of the surface.
NASA’s sending two spacecraft to Venus to unravel the mysteries of this scorching planet. It’s fascinating how these missions can reveal so much about our solar system. Meanwhile, keeping your online privacy safe is equally important. Tools like in app browser tracking facebook instagram privacy tool can help you control what data apps like Facebook and Instagram collect.
Ultimately, both these areas – space exploration and digital privacy – are crucial for understanding and protecting our world.
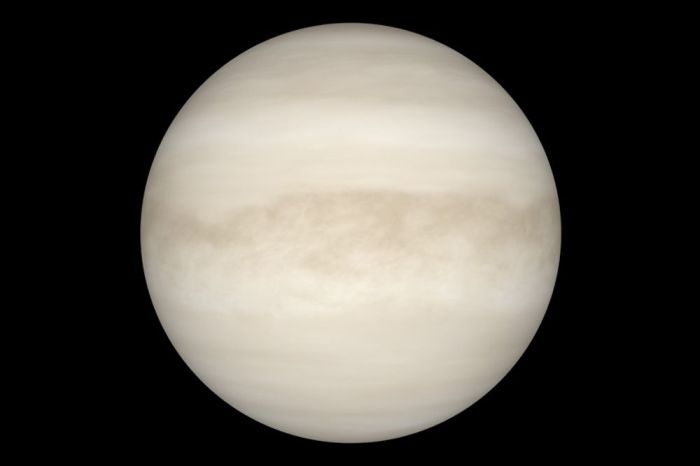
Venus’s Atmosphere
The Venusian atmosphere is a marvel of extreme conditions, a dense blanket of carbon dioxide and sulfuric acid clouds. Its unique composition and dynamic nature are responsible for the planet’s runaway greenhouse effect, creating a surface temperature hot enough to melt lead. Visualizations of atmospheric data, including temperature profiles, wind patterns, and cloud formations, can reveal the complex interactions within the atmosphere.
These visualizations can be particularly helpful in understanding the movement of clouds and the formation of atmospheric phenomena.
Venus’s Potential Subsurface
While the surface of Venus is uninhabitable, the subsurface may hold secrets about the planet’s past and potential for past or present life. Visualization techniques can be applied to seismic data and other geophysical measurements to infer the structure and composition of the subsurface. These visualizations might reveal the presence of potential water reservoirs or other subsurface features that could provide clues about the planet’s history and potential habitability.
Visualization Importance
Visualization tools are essential for extracting meaningful information from the vast amount of data collected by spacecraft. They enable scientists to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies that might otherwise remain unnoticed. For example, a visualization of temperature data across the planet could reveal localized hotspots or areas of unusually high or low pressure. By overlaying different datasets, scientists can build a more complete picture of Venus’s complex systems.
Image Caption Example: Venus’s Atmosphere
“A mesmerizing visualization of Venus’s atmosphere reveals the swirling patterns of sulfuric acid clouds. The vibrant colors represent variations in altitude and temperature, highlighting the extreme conditions of this dense atmosphere. The data, collected by [Spacecraft Name], demonstrates the dynamic nature of Venus’s weather systems, a stark contrast to the relatively calm conditions on Earth.”
Mission Timeline and Expected Outcomes
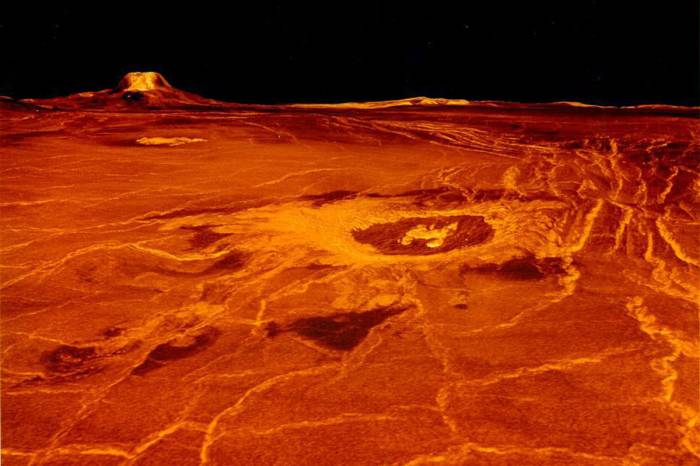
The Venus exploration missions represent a significant step forward in our understanding of this enigmatic planet. These missions will provide crucial data on Venus’s atmosphere, surface, and potential for past or present life. Understanding Venus’s extreme environment will also help us better comprehend the factors that influence planetary habitability and the processes that shape planetary evolution.
Mission Timeline
This ambitious endeavor will unfold across several distinct phases, each crucial for achieving the mission’s objectives. A phased approach allows for meticulous data collection and analysis at each stage, optimizing the return on investment in terms of scientific knowledge gained. The timeline encompasses crucial milestones, from launch and cruise phases to orbit insertion and surface exploration (if applicable).
- Phase 1: Launch and Cruise (Years 1-2): The spacecraft will embark on a journey to Venus, utilizing advanced propulsion systems for precise trajectory control. This phase will involve critical checks and calibrations of instruments, ensuring their readiness for data collection upon arrival. This period will encompass extensive checks to ensure the spacecraft and its instruments are in optimal working order. Examples of such checks include, but are not limited to, confirming the functionality of all scientific instruments, verifying the operational status of the communication systems, and performing a comprehensive review of the spacecraft’s overall performance.
- Phase 2: Arrival and Orbit Insertion (Year 2-3): The spacecraft will enter orbit around Venus, performing detailed atmospheric and surface observations. This critical stage involves precisely maneuvering the spacecraft into the desired orbit around Venus, requiring precise calculations and adjustments based on real-time data and conditions. The orbit insertion will determine the spacecraft’s observational capabilities and accessibility to different regions of the planet.
- Phase 3: Data Collection and Analysis (Years 3-5): The spacecraft will dedicate a significant amount of time to detailed data collection across various aspects of Venus’s atmosphere and surface. The mission’s duration in this phase will be critical in providing a comprehensive understanding of Venus’s environment. Data collected will include atmospheric composition, surface temperature, and geological features. The data will be analyzed by scientists worldwide, potentially leading to groundbreaking discoveries about Venus’s past, present, and future.
Expected Discoveries and Impact
The missions are expected to reveal key insights into Venus’s climate history, its geological evolution, and the potential for past or present life. By comparing Venus to Earth, scientists aim to better understand the factors influencing planetary habitability. The detailed analysis of Venus’s atmospheric processes can inform our understanding of similar processes on other planets, such as Mars, and provide critical context for future missions.
These insights will significantly advance our knowledge of planetary science.
- Atmospheric Composition and Dynamics: A deeper understanding of the atmospheric composition, dynamics, and interactions with the planet’s surface is anticipated. This could lead to new models for planetary atmospheric evolution. Understanding the mechanisms of atmospheric circulation and heat transfer is key to understanding the extreme climate of Venus.
- Surface Geology and Composition: Detailed analysis of Venus’s surface features is expected to reveal insights into its geological history. This could lead to the identification of previously unknown geological formations and the potential for past volcanic activity. Mapping and analyzing the surface geology will provide valuable data on the planet’s past and present geological processes.
- Potential for Life: The mission will investigate the possibility of past or present life on Venus, considering the possibility of extremophiles adapting to extreme conditions. Any discovery of life on Venus would have profound implications for our understanding of life’s potential to exist beyond Earth. Evidence of past or present life forms, or even microbial life, will reshape our understanding of life’s diversity and resilience.
Potential Scientific Breakthroughs
These missions have the potential to yield groundbreaking discoveries, significantly impacting our understanding of planetary science. The results may even provide a new framework for the study of atmospheric evolution on other planets.
- Improved Models of Planetary Atmospheres: The collected data will allow for the refinement of models that describe the interactions between planetary atmospheres and their surfaces. By comparing these models to data from Venus, we can improve our understanding of atmospheric dynamics and evolution.
- New Insights into Planetary Habitability: Studying Venus’s extreme environment can help us better understand the conditions that support life. Insights into Venus’s environment will shed light on the diverse range of conditions in which life might thrive. These findings will be essential for future explorations and discoveries.
- Advancements in Spacecraft Technology: The technology used in these spacecraft, from propulsion systems to advanced sensors, can be adapted for future missions to other planets. This will enable scientists to develop more robust and reliable spacecraft for exploring the cosmos.
Final Summary
NASA’s mission to Venus represents a significant leap forward in our understanding of planetary science. The detailed analysis of Venus’s atmosphere and surface, coupled with the search for potential life, will undoubtedly shape our future explorations of the solar system. The data collected by these two spacecraft will offer invaluable insights into the complexities of planetary evolution, paving the way for future missions to other intriguing worlds.
The sheer ambition and meticulous planning behind this mission are truly inspiring.