Modernize us public sector remote access with ztna 2 0 – Modernize US public sector remote access with ZTNA 2.0. This initiative tackles the challenges of remote work in government, healthcare, and education, enhancing security and accessibility while maintaining compliance. We’ll delve into the specifics of ZTNA 2.0, its advantages over traditional VPNs, and practical implementation steps for the public sector. The future of remote work in the public sector is here, and ZTNA 2.0 is poised to lead the way.
The current remote access landscape in the public sector faces significant hurdles, often sacrificing security for convenience. This is where ZTNA 2.0 shines, offering a robust, secure, and user-friendly alternative. By implementing ZTNA 2.0, the public sector can unlock a new era of remote work, streamlining operations and providing better service to citizens. We’ll explore real-world use cases and demonstrate how this technology can be tailored to meet the specific needs of various public sector organizations.
Introduction to Modernizing Public Sector Remote Access
Modernizing public sector remote access is crucial for ensuring citizen engagement, efficient service delivery, and enhanced employee productivity in today’s digital landscape. This involves a significant shift from traditional, often cumbersome, methods to more secure, flexible, and user-friendly solutions. It’s about enabling seamless access to critical resources and services for all stakeholders, from government employees and citizens to healthcare professionals and students.The current approach to remote access in many public sectors often struggles with security vulnerabilities, limited scalability, and a lack of user-friendliness.
This can lead to delays in service delivery, increased risk of data breaches, and diminished citizen satisfaction. Modernizing these systems is not just about convenience; it’s about building trust and fostering a more responsive and effective government.
Current Challenges of Remote Access in the Public Sector
Security concerns are paramount. Traditional VPN-based remote access often lacks granular control over user access, creating significant security loopholes. This exposes sensitive data to potential threats, including unauthorized access and data breaches. Limited scalability is another key challenge. Existing systems may struggle to handle a surge in remote users, impacting service delivery and responsiveness.
Moreover, the user experience can be frustrating, with cumbersome login procedures and inadequate support for diverse devices and operating systems. These challenges need to be addressed to improve the effectiveness and security of public sector operations.
Benefits of Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) 2.0 for the Public Sector
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) 2.0 offers a proactive approach to security, moving away from the traditional “trust but verify” model. Instead, ZTNA 2.0 operates on a principle of “never trust, always verify,” scrutinizing every access request, regardless of the user’s location or device. This granular control significantly reduces the attack surface, making it much harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
The improved scalability of ZTNA 2.0 solutions allows for seamless support of a growing number of remote users, ensuring that services remain responsive and accessible. Furthermore, a modern, user-friendly interface streamlines the user experience, minimizing friction and maximizing productivity.
Role of ZTNA 2.0 in Enhancing Security and Accessibility
ZTNA 2.0 plays a vital role in enhancing security and accessibility by implementing micro-segmentation, which isolates sensitive data and applications behind a virtual perimeter. This approach ensures that only authorized users and devices can access specific resources, significantly reducing the impact of a breach. Furthermore, the adaptive authentication methods of ZTNA 2.0 enable flexible access policies that are aligned with evolving security requirements.
By dynamically adjusting access privileges based on user behaviour, ZTNA 2.0 ensures that access is always aligned with the principle of least privilege.
Public Sector Use Cases for Remote Access
| Sector | Use Case | Benefits of ZTNA 2.0 |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Remote patient monitoring, telehealth consultations, secure access to medical records | Enhanced security for patient data, improved accessibility for remote consultations, efficient resource utilization |
| Education | Remote learning platforms, secure access to educational resources, online collaboration tools | Improved security for student data, greater accessibility for online learning, enhanced collaboration opportunities |
| Government Services | Citizen portals, online applications for government services, remote access to databases | Increased citizen engagement, secure access to government data, improved responsiveness and efficiency |
ZTNA 2.0’s comprehensive approach to security and accessibility allows the public sector to create more efficient, secure, and citizen-centric services. The table above illustrates how ZTNA 2.0 can be leveraged across various sectors. Improved access and security translate into significant benefits for all stakeholders.
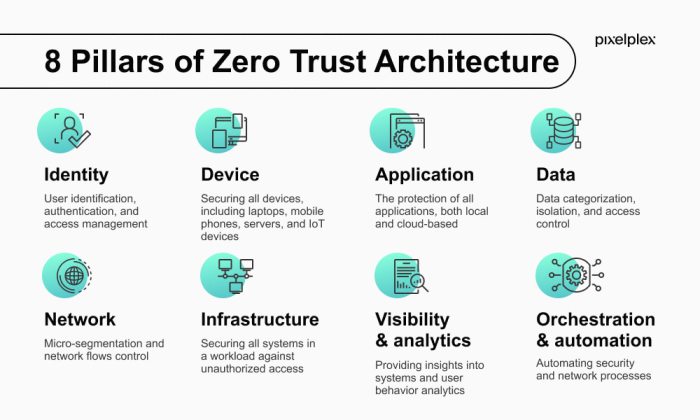
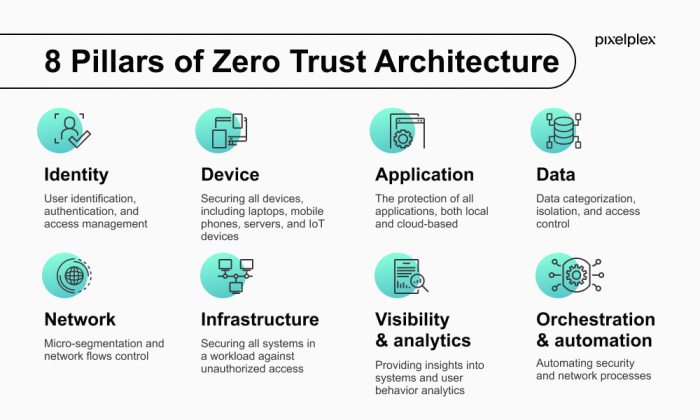
Understanding Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) 2.0
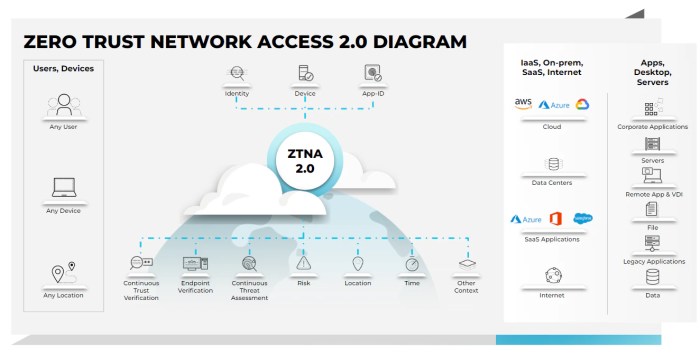
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is rapidly becoming the preferred approach for securing remote access in the public sector. ZTNA 2.0 builds upon the foundational principles of zero trust, enhancing security and manageability while addressing the evolving needs of modern organizations. This evolution is driven by the need for greater granularity in access controls, improved user experience, and enhanced visibility into network activity.
The shift towards ZTNA 2.0 reflects a broader trend in the IT security landscape, moving away from traditional, perimeter-based security models towards a more dynamic and nuanced approach.
Core Principles of ZTNA 2.0
ZTNA 2.0 is built upon the fundamental principle of “never trust, always verify.” This means that every user, device, and application is treated as a potential security risk, and access is granted only on a need-to-know basis. Access is not granted automatically based on a user’s identity or location, but rather on their specific, verified needs at a given moment.
This paradigm shift is critical in the public sector, where data security is paramount and access needs are often complex and varied.
Key Features and Functionalities of ZTNA 2.0 Solutions
ZTNA 2.0 solutions typically offer a range of advanced features, including:
- Dynamic Access Policies: Access to resources is determined based on real-time factors, such as user identity, device posture, location, and the specific application or data required. This allows for more granular and context-aware access controls, reducing the attack surface.
- Micro-segmentation: Network resources are segmented into smaller, isolated units, limiting the impact of a breach. This isolates potential vulnerabilities, preventing widespread compromise.
- Context-Aware Authentication: ZTNA 2.0 solutions employ multi-factor authentication (MFA) and other advanced authentication methods to verify user identities in dynamic contexts, adapting to changing circumstances.
- Visibility and Control: Comprehensive visibility into user and device activity provides insights into potential threats and allows for rapid response to security incidents.
- Automated Security Posture Assessment: The solution automatically assesses the security posture of users and devices, ensuring compliance with established security policies. This helps prevent malicious actors from leveraging compromised endpoints.
Comparison of ZTNA 2.0 with Traditional VPN Solutions
Traditional VPNs rely on a single, centralized connection point. They often lack the granular access controls and dynamic security policies of ZTNA 2.0. This makes ZTNA 2.0 significantly more secure and adaptable. Traditional VPNs grant broad access, while ZTNA 2.0 only allows access to the specific resources needed. This reduces the attack surface and enhances the overall security posture.
Evolution of ZTNA from Previous Generations
ZTNA has evolved significantly from its earlier iterations. Early ZTNA solutions focused primarily on securing remote access to applications. ZTNA 2.0 extends this functionality to include broader network access control, enhancing security by extending the principles of zero trust to the entire network perimeter. This more comprehensive approach reflects a growing awareness of the evolving threat landscape.
Modernizing US public sector remote access with ZTNA 2.0 is crucial for efficiency and security. While discussions around global health initiatives like the microsoft bill gates vaccine coronavirus covid are important, robust remote access solutions are vital for ensuring government services can continue uninterrupted. ZTNA 2.0 provides a secure framework to achieve this goal, ensuring critical infrastructure remains protected.
Comparison Table: ZTNA 2.0 vs. Other Remote Access Technologies
| Feature | ZTNA 2.0 | VPN | Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Security | Granular access controls, dynamic policies, micro-segmentation | Centralized connection point, less granular controls | Vulnerable to attacks if not properly secured |
| Scalability | Highly scalable, easily adaptable to changing needs | Scalability can be limited by the central connection point | Scalability can be limited, often requires dedicated servers |
| Complexity | More complex to implement initially but easier to manage long-term | Relatively simple to implement but can become complex to manage | Relatively simple to implement, but security management can be complex |
Implementing ZTNA 2.0 for Public Sector Remote Access: Modernize Us Public Sector Remote Access With Ztna 2 0
Modernizing remote access in the public sector is crucial for efficiency and security. Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) 2.0 offers a robust framework for achieving this, but its implementation requires careful planning and execution. This process involves more than just deploying new software; it necessitates a comprehensive approach that considers existing infrastructure, security postures, and risk assessments.The transition to ZTNA 2.0 is not a simple software upgrade; it demands a fundamental shift in how the public sector approaches network security.
This shift is vital to maintaining data integrity and protecting sensitive information in the face of increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. Successful implementation hinges on a meticulous understanding of existing systems and a proactive approach to potential risks.
Security Posture and Risk Assessment
A thorough security posture analysis is essential before implementing ZTNA 2.0. This involves identifying existing vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the current network architecture. A comprehensive risk assessment should pinpoint potential threats, evaluate their likelihood, and estimate their impact. This process ensures the ZTNA 2.0 solution addresses the specific security concerns of the organization, minimizing the attack surface and potential data breaches.
Thorough documentation and clear communication throughout the process are key to success.
Impact on Existing Infrastructure
The implementation of ZTNA 2.0 will likely impact existing infrastructure, potentially requiring modifications or upgrades. The extent of this impact will depend on the specific architecture and the degree of modernization already implemented. This requires careful planning to avoid disruptions to existing services. It’s crucial to assess the compatibility of existing systems with ZTNA 2.0 and develop mitigation strategies for potential conflicts.
Modernizing US public sector remote access with ZTNA 2.0 is crucial, but imagine a future where augmented reality (AR) glasses, like Meta’s Orion, become commonplace. Experiencing a glimpse into that future, I recently tried on Meta’s Orion AR glasses, a wireless taste of a neural future here. While that’s fascinating, it all points to the need for secure remote access solutions like ZTNA 2.0 to keep pace with these evolving technologies and maintain security for our public sector.
Technical Skills and Expertise
Implementing ZTNA 2.0 demands specialized skills and expertise. This includes professionals with experience in network security, cloud computing, and ZTNA technologies. A multi-disciplinary team comprising network engineers, security architects, and system administrators is essential for successful deployment. Outsourcing specific tasks to vendors with specialized expertise can also be a strategic option, depending on the resources available. Clearly defining roles and responsibilities for each team member is crucial for efficient project management.
Integration with Existing Systems
A step-by-step procedure for integrating ZTNA 2.0 with existing systems is vital for a smooth transition. This involves careful planning, thorough testing, and meticulous execution.
- Assessment and Planning: A detailed inventory of existing systems and applications is necessary to determine compatibility with ZTNA 2.0. This includes identifying access points and network configurations to understand the potential impact on current operations.
- Phased Implementation: Deploying ZTNA 2.0 in phases allows for thorough testing and validation at each step. This approach minimizes disruptions to ongoing operations and provides opportunities to adjust strategies based on real-world feedback.
- Security Testing and Validation: Rigorous security testing is essential to ensure that the integrated ZTNA 2.0 solution meets security standards and effectively mitigates potential vulnerabilities.
- User Training and Support: Training users on new access procedures and providing ongoing support are crucial for successful adoption. This step involves developing comprehensive documentation and establishing channels for user inquiries and assistance.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Continuous monitoring and evaluation are necessary to assess the effectiveness of the ZTNA 2.0 implementation and identify areas for improvement.
Security and Compliance in ZTNA 2.0 Deployments
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) 2.0 is revolutionizing remote access security for the public sector. Its layered approach to authentication and authorization significantly strengthens defenses against cyber threats, while simultaneously complying with stringent data protection regulations. This approach ensures that only authorized users can access specific resources, minimizing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.ZTNA 2.0 offers a robust framework for securing sensitive public sector data, adapting to the evolving threat landscape.
By implementing strict access controls and leveraging advanced security protocols, public sector organizations can significantly reduce the attack surface and maintain compliance with critical regulations.
Security Benefits of ZTNA 2.0 for Public Sector Data
ZTNA 2.0 enhances public sector data security by meticulously controlling access based on the principle of least privilege. This prevents unauthorized individuals from gaining access to sensitive information, even if they have legitimate credentials to other systems. By limiting access to only the resources needed for their tasks, ZTNA 2.0 drastically reduces the potential impact of a security breach.
This is particularly crucial in the public sector, where data breaches can have severe consequences for citizens and the integrity of government operations.
Compliance Requirements for Public Sector Remote Access
Public sector remote access must adhere to strict compliance requirements, often dictated by federal, state, or local regulations. These regulations often mandate specific security measures to protect sensitive data, such as personally identifiable information (PII). Examples include HIPAA for healthcare data, FERPA for educational records, and GDPR for EU citizens’ data. Meeting these requirements is crucial for maintaining public trust and avoiding costly penalties.
Examples of How ZTNA 2.0 Addresses Data Breaches and Unauthorized Access
ZTNA 2.0 actively mitigates the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access through dynamic access policies. Instead of granting blanket access, ZTNA 2.0 authenticates and authorizes users on a per-application and per-resource basis. This granular control significantly reduces the attack surface. For instance, a ZTNA 2.0 implementation could restrict access to financial data only to authorized personnel with the proper credentials and device posture.
The Role of Multi-Factor Authentication in ZTNA 2.0
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a cornerstone of ZTNA 2.0. It strengthens security by requiring multiple forms of verification to confirm a user’s identity. This prevents unauthorized access even if a user’s credentials are compromised. Typical MFA methods include passwords, security tokens, and biometric scans. This layered approach provides an essential layer of defense against sophisticated attacks.
Security Protocols Supported by ZTNA 2.0, Modernize us public sector remote access with ztna 2 0
ZTNA 2.0 supports a range of security protocols to enhance data protection and ensure secure remote access. This robust approach ensures a high level of protection against potential threats.
| Protocol | Description |
|---|---|
| Secure Socket Layer (SSL)/Transport Layer Security (TLS) | Provides encrypted communication channels between users and applications. |
| Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) | Ensures secure data transmission across networks by encrypting packets. |
| Secure Shell (SSH) | Provides secure remote access to servers and applications. |
| OAuth 2.0 | Provides secure authorization for applications. |
User Experience and Adoption in Public Sector Remote Access
Modernizing public sector remote access with Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) 2.0 requires a user-centric approach. A seamless and intuitive user experience is paramount to ensuring widespread adoption and maximizing the benefits of this technology. Ignoring user needs and preferences can lead to frustration, low utilization rates, and ultimately, failure to achieve the desired outcomes.ZTNA 2.0’s potential for improving public sector efficiency and accessibility is significant.
However, the success of this transition hinges on the public sector’s ability to craft a user experience that’s not only secure but also user-friendly and readily adopted. This involves careful consideration of training, accessibility, and successful adoption strategies.
Importance of User-Friendly Interfaces in ZTNA 2.0
A user-friendly interface is crucial for ZTNA 2.0 implementation. Intuitive design and clear navigation are essential for public sector employees to easily access resources and services. Complex interfaces can lead to confusion and errors, hindering productivity and potentially creating security risks. A well-designed interface should be visually appealing, consistent, and provide clear feedback to the user. This enhances the overall user experience and encourages adoption.
Best Practices for Training Public Sector Employees on ZTNA 2.0
Comprehensive training programs are vital for successful ZTNA 2.0 adoption. Training should cover the functionality of the new system, security protocols, and best practices for using the ZTNA 2.0 platform. Interactive training modules, hands-on workshops, and readily available online resources can facilitate effective learning. The training program should address specific roles and responsibilities within the public sector, tailoring the content to the unique needs of each department.
It’s important to provide ongoing support and resources to employees after the initial training.
Modernizing US public sector remote access with ZTNA 2.0 is crucial for security and efficiency. Imagine accessing sensitive data from anywhere, anytime, with the added security of zero trust. This is incredibly valuable, especially considering the potential of playing all games on Playstation Now for $25 the entire year play all games playstation now 25 entire year.
Ultimately, a strong remote access system like ZTNA 2.0 is essential for a secure and modern government.
Impact of Accessibility Features on User Adoption
Accessibility features are essential for ensuring that ZTNA 2.0 is usable by all public sector employees, regardless of their abilities. This includes features such as alternative text for images, keyboard navigation, screen reader compatibility, and adjustable font sizes. Implementing these features not only fulfills legal requirements but also fosters inclusivity and broader adoption across the workforce. This approach ensures that all employees can access the system efficiently and safely.
Examples of Successful User Adoption Strategies in Public Sector Remote Access
Successful user adoption strategies often involve a combination of factors, including clear communication, phased implementation, and ongoing feedback mechanisms. For example, organizations that have successfully implemented remote access solutions have utilized communication campaigns to educate employees, provided ongoing support, and gathered feedback to refine the system. They have implemented user feedback mechanisms to ensure continuous improvement.
Features that Improve the User Experience
| Feature | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Intuitive Navigation | Clear and logical pathways through the ZTNA 2.0 platform. | Reduces user frustration and improves efficiency. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Simplification | Streamlined MFA processes, eliminating unnecessary steps. | Increases user satisfaction and reduces security risks. |
| Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) | Granting access based on employee roles and responsibilities. | Improves security and streamlines access to necessary resources. |
| Comprehensive Documentation | Easy-to-understand manuals and FAQs. | Reduces the need for extensive support calls. |
| Accessibility Features | Support for diverse needs (screen readers, keyboard navigation). | Enhances inclusivity and ensures all users can effectively access the platform. |
Future Trends and Innovations in Public Sector Remote Access
The public sector is rapidly adopting remote work, driven by the need for agility, cost-effectiveness, and improved citizen service delivery. This shift necessitates a robust and secure remote access infrastructure, and Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) 2.0 is emerging as a key enabler. However, the future of remote access extends beyond current ZTNA capabilities, demanding innovation and adaptation to evolving needs.
Emerging Trends in Public Sector Remote Access Technologies
The public sector is increasingly leveraging advanced technologies to enhance remote access security and user experience. Cloud-based solutions, improved mobile device management, and advancements in biometric authentication are becoming integral parts of modern remote access strategies. These technologies promise increased efficiency and reduced operational costs while maintaining the highest levels of security. Furthermore, the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices into public sector operations presents both opportunities and challenges for remote access, demanding careful consideration of security protocols and data privacy concerns.
Potential Impact of AI and Machine Learning on ZTNA 2.0
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are poised to significantly enhance ZTNA 2.0 capabilities. AI-powered threat detection systems can proactively identify and mitigate potential security risks in real time, improving the overall security posture of remote access environments. ML algorithms can also personalize user experiences, optimizing access based on individual user profiles and activity patterns. This personalization improves efficiency and security, ensuring that users have appropriate access rights tailored to their needs.
For example, AI-driven anomaly detection can identify unusual access patterns that might indicate a security breach, allowing for rapid response and containment.
Forecast of the Future of Remote Work in the Public Sector
Remote work in the public sector is likely to become more prevalent and integrated into daily operations. Hybrid work models will become increasingly common, balancing the advantages of remote work with the benefits of in-person collaboration. This transition will require robust remote access solutions that can seamlessly support both remote and in-person workstyles. This adaptability is crucial for ensuring continuity and effectiveness across all public sector operations.
How ZTNA 2.0 Supports Evolving Public Sector Needs
ZTNA 2.0’s granular access controls and dynamic policies are well-suited to the evolving security needs of the public sector. The ability to tailor access permissions based on user role, location, and device type allows for a highly customized security approach, adapting to new threats and regulatory compliance demands. Furthermore, ZTNA 2.0’s focus on least privilege access significantly reduces the attack surface, minimizing the potential damage from a security breach.
Examples of Innovative Remote Access Solutions in the Public Sector
Several public sector organizations are pioneering innovative remote access solutions. These include leveraging blockchain technology for secure data sharing and identity management, implementing AI-driven threat detection systems to improve security posture, and adopting multi-factor authentication methods to enhance user security. One example is a city government that has successfully deployed a ZTNA solution to allow its employees to access critical systems remotely while maintaining strict compliance with data privacy regulations.
Another example involves a state agency using AI to predict and prevent potential security threats, proactively mitigating potential risks. This innovative approach not only enhances security but also streamlines operations and improves citizen service delivery.
Closing Summary
In conclusion, modernizing US public sector remote access with ZTNA 2.0 is not just a technological upgrade; it’s a strategic shift towards a more secure, efficient, and accessible future. We’ve examined the challenges, explored the benefits of ZTNA 2.0, and Artikeld the steps for implementation. From enhancing security to improving user experience, this comprehensive approach ensures a smooth transition to a more agile and citizen-centric public sector.
The future of work in the public sector is now more secure and efficient than ever before, thanks to the power of ZTNA 2.0.