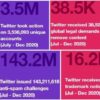
Grindr GDPR data sharing complaint advertising mopub match group okcupid tinder are hot topics right now. These apps handle user data in various ways, sometimes raising privacy concerns. From the collection of personal information to the partnerships with advertising platforms like Mopub and Match Group, the practices of these dating apps are under scrutiny. We’ll explore how these apps share data, potential GDPR violations, and the impact on users.
This article delves into the complexities surrounding data sharing and privacy in the realm of dating apps, analyzing the practices of Grindr, OkCupid, Tinder, and others. It also examines the role of advertising platforms and the potential consequences of non-compliance with GDPR regulations. Furthermore, it examines user perspectives and potential best practices for these apps.
Data Sharing Practices in Dating Apps: Grindr Gdpr Data Sharing Complaint Advertising Mopub Match Group Okcupid Tinder
Dating apps have become ubiquitous, connecting millions worldwide. However, the data collection and sharing practices of these platforms raise significant privacy concerns, especially regarding user expectations of personal information handling. Understanding how these apps manage user data is crucial for informed consent and protecting personal privacy.
Data Collection Practices of Dating Apps
Dating apps, like Grindr, OkCupid, and Tinder, meticulously collect vast amounts of user data. This information goes beyond basic profile details, encompassing a wide range of personal and usage information. These platforms often leverage this data for various purposes, including targeted advertising, enhancing user experience, and providing matched connections. The extent of data collected and shared can significantly impact user privacy.
Types of Data Collected
Dating apps gather diverse data categories. Personally Identifiable Information (PII) includes user names, email addresses, phone numbers, and location data. Usage data encompasses activity logs, such as swipes, messages exchanged, and interactions with profiles. These apps frequently collect information on user preferences, interests, and even financial details associated with in-app purchases. The combination of these data points paints a detailed picture of individual users, which can be exploited if not handled responsibly.
Recent complaints about Grindr, OkCupid, and Tinder regarding GDPR data sharing and advertising practices via platforms like MoPub and Match Group are raising some interesting questions. It’s fascinating how these apps handle user data, and I’m finding myself increasingly interested in how these complex systems work. For instance, how does the way Google Docs integrates via its app embeds, APIs, chips, and canvas relate to the user data handling in these dating apps?
google docs app embeds api chips canvas provides some interesting insights. Ultimately, these data privacy concerns surrounding dating apps remain a critical area for future discussion and scrutiny.
Data Sharing Practices and Potential GDPR Violations, Grindr gdpr data sharing complaint advertising mopub match group okcupid tinder
These apps often share user data with third-party partners, including advertising networks and data analytics companies. For example, Grindr may share user location data with advertising platforms to tailor ads. OkCupid might share user interests with recommendation engines to improve matching accuracy. Tinder could share swipe data with other apps for advertising purposes. These practices raise concerns about potential GDPR violations if adequate consent isn’t obtained or if data security measures are insufficient.
Data breaches or misuse of user information can lead to severe consequences.
Comparison of Data Sharing Policies
| App Name | Data Types Collected | Data Sharing Partners | GDPR Compliance Assessment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grindr | PII (name, email, location, etc.), usage data (swipes, messages, etc.), preferences, financial data | Advertising networks, data analytics companies, potentially other apps | Potentially problematic due to lack of transparency and specifics on data sharing practices. Requires thorough review of the fine print. |
| OkCupid | PII (name, email, location, etc.), usage data (swipes, messages, etc.), preferences, interests | Recommendation engines, advertising networks, data analytics companies | Potentially problematic due to lack of transparency and specifics on data sharing practices. Requires thorough review of the fine print. |
| Tinder | PII (name, email, location, etc.), usage data (swipes, messages, etc.), preferences, interests | Advertising networks, data analytics companies, potentially other apps | Potentially problematic due to lack of transparency and specifics on data sharing practices. Requires thorough review of the fine print. |
| Mopub | Data from third-party apps, including dating apps (user data), usage data | Advertising networks, advertisers, potentially other data brokers | Potentially problematic due to lack of transparency and specifics on data sharing practices. Requires thorough review of the fine print. |
“Transparency and user consent are crucial elements of GDPR compliance. Dating apps must be explicit about what data they collect, how it’s used, and with whom it’s shared.”
GDPR Complaints and Enforcement

Dating apps, with their vast user bases and intricate data collection practices, are increasingly facing scrutiny under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Users are becoming more aware of their rights and are actively utilizing GDPR mechanisms to challenge perceived violations. This scrutiny has led to a rise in complaints and a need for these apps to strengthen their compliance measures.
Common Types of GDPR Complaints
Dating apps often face complaints related to insufficient transparency regarding data collection and usage. Users frequently express concerns about the lack of clear information on how their personal data is processed, shared, and stored. Another significant area of complaint centers around the lack of user control over their data. This includes concerns about the ability to access, rectify, or erase personal data, as well as the lack of mechanisms for users to opt-out of data sharing.
Finally, complaints arise from the inadequate security measures implemented by the apps to protect user data from unauthorized access or breaches.
Frequent GDPR Violations in Dating Apps
A frequent violation concerns the lack of explicit and informed consent for data processing. Dating apps often collect extensive personal data, but the process for obtaining user consent for its use may be unclear or insufficient. Another recurring issue involves the inappropriate sharing of user data with third-party entities, such as advertising networks. Without clear consent, this practice can violate user rights.
A third recurring violation concerns the lack of adequate data security measures. If a data breach occurs, the app may be held liable for the damage caused to users.
Whew, the dating app drama surrounding GDPR data sharing complaints, particularly with Grindr, OkCupid, Tinder, and Match Group, is intense. It’s making me wonder if my phone’s privacy settings are even worth it. Luckily, there’s some tech excitement to distract from it all – Android 15 beta 4 is here! Here’s how to grab the latest beta and potentially improve my privacy settings a bit, even if it’s just to keep my phone updated.
All this data sharing talk is a bit much though, right? I’m still trying to figure out what I can do to avoid my dating app info ending up in a data breach.
Enforcement Mechanisms by Authorities
Data protection authorities, such as the Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) in the UK, actively investigate complaints regarding GDPR violations. These investigations involve examining the app’s data collection and processing practices, ensuring compliance with GDPR principles, and assessing whether the app has taken sufficient steps to protect user data. The authorities often issue recommendations or directives to apps, requiring them to rectify the identified violations.
Furthermore, if significant violations are found, the authorities can impose significant penalties.
Potential Consequences of GDPR Violations
| Violation Type | Potential Consequences | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Lack of informed consent | Significant fines, reputational damage, legal action | Failure to properly inform users about data sharing practices. |
| Inappropriate data sharing | Fines, user data breaches, reputational damage | Sharing user data with third parties without explicit consent. |
| Inadequate data security | Data breaches, significant fines, legal action, loss of user trust | Insufficient measures to protect user data from unauthorized access or breaches. |
| Failure to comply with access requests | Fines, legal action, reputational damage | Inability to provide users with access to their personal data as requested. |
Advertising and Data Collection
Dating apps thrive on attracting users and keeping them engaged. A significant part of this strategy involves targeted advertising, a process that relies heavily on the data collected from users. This data, often shared with third-party platforms, fuels the personalized experiences and ads we encounter within these apps. Understanding how this data flow works is crucial for navigating the digital dating landscape and making informed choices about privacy.
Advertising Platform Integration
Dating apps frequently partner with advertising platforms like MoPub to display ads relevant to users. These platforms act as intermediaries, connecting advertisers with app users. The process typically involves collecting user data, such as location, age, interests, and activity within the app. This data is then used to create detailed user profiles, allowing advertisers to tailor their messages and offers to specific demographics and preferences.
Data Sharing and Targeted Advertising
The connection between data sharing and targeted advertising is direct. Dating apps share user data with advertising platforms to enable precise targeting. For example, a user who frequently searches for “hiking” and “nature” might see ads for outdoor gear or hiking trails. This personalization, while potentially convenient, raises concerns about the extent and use of collected information.
Match Group’s Role
Match Group, the parent company of many prominent dating apps, plays a pivotal role in this advertising ecosystem. They manage the data flow between their apps and advertising platforms, influencing the types of ads users see. Their data practices have a significant impact on the user experience and the privacy implications of targeted advertising within their suite of apps.
Comparison of Advertising Practices
| App | Advertising Methods | Data Used for Targeting | Potential Privacy Concerns |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grindr | Display ads, sponsored content, in-app promotions | Location, sexual orientation, interests, app activity | Potential for discriminatory targeting based on sexual orientation, data misuse, and lack of transparency in data sharing practices. |
| OkCupid | Display ads, sponsored content, partnerships with related services | Demographics, interests, search history, app activity | Potential for misrepresentation of user interests, misuse of data for non-dating purposes, and lack of control over personalized recommendations. |
| Tinder | Display ads, sponsored content, in-app promotions, partner integrations | Location, age, gender, interests, app activity, swipe data | Potential for biased match suggestions, data misuse by advertisers, and lack of clarity on how swipe data is used for targeting. |
| Mopub | Provides the ad platform and technology for ad serving | Data shared by apps, including user demographics and app activity | Potential for lack of control over how data is used by advertisers, insufficient transparency on data handling, and potential for data breaches. |
User Impact and Concerns
Dating apps, while popular, often collect and share vast amounts of user data. This practice, while sometimes presented as beneficial for matching and personalized experiences, raises significant concerns about user privacy and security. The potential for misuse of this data, combined with the increasing sophistication of cyber threats, has led to a growing unease among users regarding their personal information.The impact of data sharing on user behavior and trust is undeniable.
Users might become hesitant to share personal details or engage fully with the platform, impacting their overall experience and potentially limiting the app’s ability to effectively serve their needs. Furthermore, negative public perception surrounding data privacy breaches can significantly harm the reputation and market position of these companies.
Potential Negative Impacts on User Privacy and Security
Data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive user information are significant risks associated with data sharing practices. Compromised data can lead to identity theft, financial fraud, and harassment. For instance, leaked geolocation data could expose users to stalking or other safety concerns. This is particularly critical for vulnerable user groups.
User Concerns Regarding Data Privacy and Security
Users often express concerns about how their data is being collected, processed, and shared. These concerns stem from the lack of transparency in data sharing agreements and the fear of misuse. A lack of control over personal information can lead to distrust and anxiety about the safety of their sensitive data. Furthermore, the perceived lack of accountability for misuse of data fuels these concerns.
Impact on User Behavior and Trust
Data sharing practices can significantly impact user behavior and trust. Users may become more cautious about sharing personal information, limiting the amount of data they provide to dating apps. This reduced sharing can lead to less accurate matching and personalized experiences. Moreover, users might actively seek out platforms with stronger privacy protections. A decrease in user engagement, caused by mistrust, could also affect the app’s overall profitability and market position.
Recent complaints about Grindr, OkCupid, and other dating apps regarding GDPR data sharing and advertising platforms like MoPub and Match Group are raising some interesting questions. The constant stream of data requests and how these platforms handle user privacy is definitely a hot topic. Meanwhile, I’ve been checking out the Google Nest Audio smart speaker assistant; its price, specs, and features are really intriguing.
Ultimately, these data privacy concerns surrounding dating apps are likely to remain a significant issue for some time, especially with the current regulatory landscape.
Public Perception of Dating Apps Regarding Data Privacy and Security
Public perception of dating apps regarding data privacy and security is a critical factor. Negative experiences and publicized data breaches can damage public trust and lead to a decline in user numbers. The perception of these apps as reliable and trustworthy is vital for maintaining a strong user base. Public awareness campaigns highlighting data security and privacy practices can help improve public perception.
Industry Best Practices and Recommendations
The dating app industry faces significant challenges in balancing user privacy with the need for effective advertising and data collection. Maintaining user trust while adhering to regulations like GDPR requires a robust and transparent approach to data handling. This necessitates a shift towards proactive privacy measures and a commitment to user consent, rather than simply reacting to complaints.
Best Practices for Data Handling and User Privacy
Dating apps must prioritize data minimization, collecting only the necessary information for their services. This includes limiting the types of data collected and securely storing it. Transparent data policies, readily accessible to users, are crucial for building trust. These policies should clearly Artikel how data is used, shared, and protected.
Recommendations for Improving Data Sharing Policies and User Privacy Protections
- Implement a tiered consent system, allowing users granular control over the data they share. For example, users should be able to specify which data points are shared with advertisers and for what purposes. This would provide users with a level of control that they do not currently have.
- Develop clear and concise data policies that are easy for users to understand. Avoid technical jargon and provide examples of how the data is used. The policies should be written in a user-friendly language, explaining the various data points in a manner that is readily understandable.
- Implement robust data security measures to protect user data from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. This includes employing encryption techniques and regularly assessing security vulnerabilities. Periodic security audits should be conducted to ensure the ongoing protection of user data.
- Provide users with clear and concise information on how their data is being used by third-party partners, such as advertising networks. Users should be informed about the specific data points being shared and the purposes for which they are used. This transparency will build trust and allow users to make informed decisions.
- Establish a clear and accessible process for users to exercise their rights under GDPR, such as the right to access, rectify, erase, restrict, object, and data portability. Provide clear instructions on how users can submit requests and the timeframe for processing these requests. This will demonstrate that the company values user control over their data.
Importance of Transparency and User Consent in Data Handling
Transparency in data handling practices is paramount. Users need to understand how their data is being used, shared, and protected. This understanding fosters trust and empowers users to make informed decisions about their personal information. Genuine user consent is essential. It must be freely given, specific, informed, and unambiguous.
This requires clear communication about the purpose of data collection and the potential consequences of not consenting. Users should be given the option to opt out of data sharing with third parties at any time.
Ideal Data Handling Process for a Dating App
| Step | Action | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Data Collection | Collect only necessary data, with clear user consent. |
| 2 | Data Storage | Store data securely, using encryption and access controls. |
| 3 | Data Use | Use data only for stated purposes, with user consent. |
| 4 | Data Sharing | Share data only with explicit user consent and with clear guidelines for third-party partners. |
| 5 | Data Security | Regularly assess and improve data security measures to protect user data from breaches. |
| 6 | User Rights | Implement a clear process for users to exercise their GDPR rights (access, rectification, erasure, etc.). |
| 7 | Auditing | Conduct regular audits to ensure compliance with GDPR and best practices. |
Comparison of App Features and Privacy Policies
Dating apps have become ubiquitous, offering a wide array of features to connect users. However, this richness of functionality often comes with complexities in data handling and privacy policies. Understanding how these apps collect, use, and share user data is crucial for informed decision-making. This section dives into the diverse features and nuanced privacy policies of various popular dating apps.Different features in these apps can influence how user data is shared and potentially impact user privacy concerns.
Features like location services, advanced search filters, and in-app messaging have direct implications on the types of data collected and its subsequent use. Understanding these features and their relationship to data sharing is key to assessing the level of privacy protection offered by each app.
App Feature Comparison
The features offered by different dating apps vary significantly. Some apps prioritize location-based matching, while others focus on detailed profiles and interest-based algorithms. The extent of data collected and shared often correlates with the complexity and scope of the app’s functionalities. For example, apps emphasizing location-based services inherently collect more location data compared to those that rely solely on profile information.
- Location Services: Some apps, like Grindr and OkCupid, heavily rely on location-based matching, collecting precise location data for matching users. This can be a crucial feature for users seeking local connections but also raises significant privacy concerns regarding the accuracy and extent of location sharing. Other apps might offer less granular location services, relying primarily on broader geographical areas for matching.
- Advanced Search Filters: The availability and complexity of search filters significantly influence the amount of data collected and used. Apps with extensive search filters, such as OkCupid and Tinder, collect and process user data based on various criteria (age, gender, sexual orientation, interests, and other attributes). This allows for targeted matching but also means more user data is collected and analyzed.
- In-App Messaging: Most dating apps include messaging features, which collect data on communication patterns. This data can range from the frequency of messages exchanged to the content of the messages themselves. The privacy policies of apps need to clearly Artikel how this communication data is handled, stored, and potentially shared.
Privacy Policy Differences
The differences in privacy policies across various dating apps are substantial. Some apps are more transparent about data collection practices, while others provide less detailed information. This lack of transparency can raise concerns about the extent to which user data is being used and shared. A thorough examination of the privacy policies is necessary to assess the level of protection offered to users.
| App Name | Key Privacy Policy Points | Areas for Improvement |
|---|---|---|
| Grindr | Provides information on data collection for location-based matching and user profiles. | Could offer more granular control over location data sharing. |
| MoPub | Details advertising and data collection practices, highlighting third-party ad providers. | Needs to clarify how user data is used in relation to targeted advertising. |
| Match Group (Tinder, OkCupid) | Offers details on data collection for profile matching and user interactions. | Needs to specify the use of data collected for targeted advertising and potentially improve transparency on data sharing with third parties. |
| Tinder | Provides information on data collection for matching and user profiles. | Could be more explicit about the extent of location data collected and used. |
| OkCupid | Explains data collection for matching and user profiles, including interest-based matching. | Could offer more detailed information on data sharing with third-party partners. |
Final Summary

In conclusion, the data practices of dating apps like Grindr, OkCupid, and Tinder are a significant issue. Concerns about GDPR compliance, advertising practices, and the potential impact on user privacy and security demand attention. The apps need to prioritize transparency, user consent, and robust data handling procedures to maintain user trust and avoid potential legal repercussions. Ultimately, a shift towards user-centric data policies is crucial for the future of these apps.