Google plans more visual snackable search with videos AI report says, hinting at a significant shift in how we interact with search. This isn’t just about adding pictures; it’s about integrating videos and AI to deliver more immediate, digestible information. Imagine searching for a recipe and instantly seeing a short video tutorial, or finding a product by visually identifying its image.
This new approach promises to revolutionize search, but what are the potential benefits and drawbacks? Let’s explore.
The report suggests Google is moving towards a more visual, user-friendly search experience. This evolution leverages AI to analyze images and videos, enabling quicker and more accurate results. The integration of AI is crucial for processing this wealth of visual data. This change has the potential to transform user interaction with search, offering faster, more intuitive ways to find information.
Google’s Vision for Visual Search
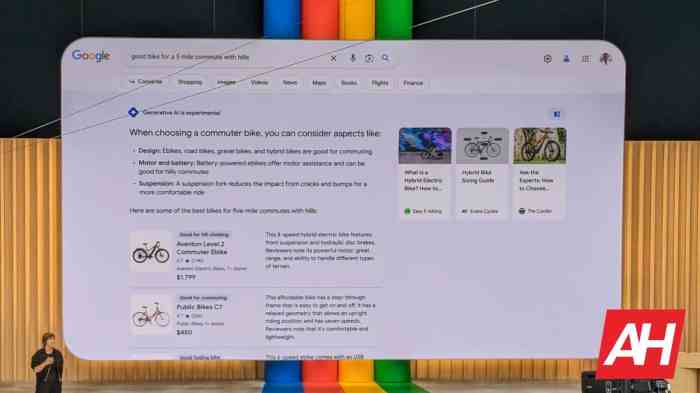
Google is reportedly planning a significant overhaul of its search engine, incorporating more visual elements, particularly videos, into its search results. This shift reflects a broader trend in how people interact with information online, moving beyond text-based searches to encompass a richer, more visually engaging experience. The move signifies Google’s commitment to evolving its search technology to meet the changing demands of modern users.This evolution in search functionality promises a more intuitive and comprehensive way to access information.
By integrating visual media, Google aims to provide users with a more holistic understanding of search queries, going beyond simple text matches and encompassing the visual context associated with the query. This change has the potential to revolutionize how we find and process information online.
Google’s Reported Plans for Visual Search
Google’s reported plans involve incorporating videos and other visual content directly into search results. This approach aims to enhance the user experience by providing a more immediate and comprehensive understanding of the subject matter. The inclusion of visual elements will likely improve the relevance and context of search results, leading to a more efficient and satisfying search process for users.
Potential Benefits of Incorporating Videos, Google plans more visual snackable search with videos ai report says
Integrating videos into search results offers several advantages. Users can instantly grasp concepts, see processes demonstrated, and gain a more nuanced understanding of topics. This is particularly beneficial for complex subjects or those requiring visual demonstrations, such as tutorials, product demonstrations, or explanations of technical processes. Videos can also help users make more informed decisions, as they provide a more immersive and detailed view of the subject matter.
Impact on User Experience and Search Behavior
The inclusion of videos in search results is expected to significantly alter user behavior. Users will likely spend more time engaging with search results, as visual content provides a more engaging and informative experience. This could lead to a shift in search patterns, with users actively seeking out video-rich results to gain a deeper understanding of queries. This will be particularly true for educational purposes and for understanding the process or procedure of something.
Examples of Visual Search in Other Search Engines
Several search engines are already incorporating visual search features. For example, Pinterest’s visual search allows users to search for similar images, finding related products or articles based on visual input. Similarly, Google Lens allows users to identify objects and places in images, providing contextual information. These examples demonstrate the increasing importance of visual search and the potential for integrating these features into Google’s core search experience.
Role of AI in Visual Search
Artificial intelligence plays a critical role in enabling visual search functionalities. AI algorithms are used to analyze images and videos, extract relevant information, and identify connections between visual content and user queries. The ability of AI to process and interpret visual data is crucial to the effectiveness of visual search, enabling systems to understand complex relationships and contextual information.
Visual Search Results: Types, Benefits, and Drawbacks
| Type of Visual Search Result | Benefits | Potential Drawbacks | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Image Recognition | Quickly identifies objects, places, or people in images; aids in finding similar items or related information. | May not accurately identify objects in complex or poorly lit images; could lead to irrelevant results if the image is ambiguous. | Searching for a specific type of flower based on a picture. |
| Video Search | Provides demonstrations, tutorials, or explanations of topics; allows for a more immersive understanding. | Videos might be low quality, inaccurate, or irrelevant to the query; could be a time-consuming way to search. | Searching for how to assemble a piece of furniture. |
| Interactive Visualizations | Provides dynamic representations of data or concepts; enhances understanding and comprehension. | Interactive elements might not always be accessible or intuitive for all users; technical issues could hinder the user experience. | Searching for information on the stock market and viewing charts. |
| 3D Models | Provides a detailed view of objects, allowing users to rotate and examine them from various angles. | The availability of 3D models might be limited for certain products or concepts; the loading time of the model could affect the user experience. | Searching for information about a new car and viewing its 3D model. |
AI’s Role in Visual Search
Google’s push towards more visual, snackable search highlights the increasing importance of AI in processing and interpreting visual information. This shift reflects a growing user preference for visual content and the need for sophisticated tools to extract meaningful data from images and videos. AI is crucial to unlocking the potential of this new search paradigm, enabling users to find what they need more quickly and effectively.AI is expected to play a pivotal role in analyzing visual content for search results, moving beyond simple matching to encompass complex image and video understanding.
This involves tasks such as object recognition, scene understanding, and even sentiment analysis within visual media. AI algorithms are trained to identify objects, actions, and relationships within images and videos, allowing for highly accurate and contextually relevant search results.
AI Techniques in Visual Search
A variety of AI techniques are employed in visual search, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are prominent in object recognition and image classification, allowing the system to identify objects, people, or scenes within an image. These models are trained on massive datasets of labeled images, enabling them to learn patterns and features associated with specific objects or concepts.
Another important technique is Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) for video analysis. RNNs excel at understanding temporal relationships within video sequences, which is crucial for recognizing actions, events, and narratives. These models process the sequence of frames in a video, understanding the movement and context of the visual data. Beyond these core techniques, more sophisticated models, like transformers, are also being investigated to improve accuracy and efficiency in visual search, especially for more complex tasks like scene understanding and relationship extraction.
Google’s apparently planning more visual search results, with videos, according to an AI report. This shift towards more engaging visual content is definitely interesting, and could potentially change the way we interact with search. Meanwhile, if you’re in the market for some new earbuds, checking out the amazon echo buds 2 features price release date might be a good idea.
But back to Google’s visual search plans, this could lead to a more immersive and informative online experience, making searching even easier and more enjoyable.
Challenges and Limitations of AI in Visual Search
Despite the advancements, using AI for visual search presents certain challenges. One key limitation is the inherent ambiguity in visual data. Images and videos can be ambiguous, with multiple interpretations possible for a single image. AI models may misinterpret or misclassify ambiguous content. Another challenge is the need for massive datasets to train the models accurately.
This training data often needs meticulous labeling and annotation to ensure that the AI understands the intended meaning of the visual data. The complexity of the human visual system is another hurdle. Capturing the nuances of human perception and interpretation in an AI model is still a significant challenge. The models may struggle to grasp subtle differences or context that humans readily understand.
Effectiveness of Different AI Models
Different AI models exhibit varying degrees of effectiveness in extracting information from images and videos. CNNs excel at object recognition, performing well in scenarios where identifying specific objects is the primary task. However, for more complex tasks, such as understanding relationships between objects or interpreting dynamic scenes, more sophisticated models like RNNs or transformers are often required. The choice of model depends heavily on the specific application and the nature of the visual data being analyzed.
The performance of each model is often evaluated on benchmarks and datasets, providing quantifiable comparisons.
Data Requirements for AI Models
Accurate visual search necessitates substantial training data. This data should be comprehensive and representative of the diverse range of images and videos that the search engine will encounter. It must encompass a broad range of visual content, including different viewpoints, lighting conditions, and variations in object appearances. The data should also include accurate labels and annotations to ensure that the AI models learn the correct associations between visual features and their corresponding meanings.
The quality and quantity of the training data significantly influence the performance of the visual search system.
Comparison of AI Models
| AI Model Type | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) | Excellent at object recognition, image classification, and feature extraction. Relatively efficient for simpler tasks. | Struggles with complex relationships, context, and dynamic scenes. May misinterpret ambiguous content. |
| Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) | Effective at understanding temporal relationships in video sequences. Captures actions, events, and narratives. | Can be computationally intensive, especially for long video sequences. May struggle with complex scene understanding. |
| Transformers | Potentially superior at understanding context and relationships between objects in images and videos. Can handle complex tasks like scene understanding. | Often require substantial computational resources and data. Still under development for visual search applications. |
Impact on Existing Search Functionality: Google Plans More Visual Snackable Search With Videos Ai Report Says
Google’s foray into visual search, fueled by advancements in AI, promises a significant shift in how we interact with information. This evolution raises crucial questions about the future of text-based search and the potential for a blended, multimodal approach. The integration of visual data into the search engine ecosystem will undoubtedly reshape how we find and process information.The current text-based search paradigm, while established, often falls short in handling complex visual queries.
For instance, identifying a specific architectural style, recognizing a rare plant, or understanding a historical event through visual cues can be cumbersome and less precise with text alone. Visual search aims to address these limitations, offering a more intuitive and direct path to retrieving information.
Impact on Text-Based Search Methods
Text-based search will likely remain a crucial component of the overall search experience. Visual search will augment, not replace, text search. Users will likely combine text queries with visual cues to refine and personalize their search results. For example, a user searching for “Italian restaurants in Rome” might supplement this text query with a picture of a specific dish or architectural style to narrow the results to restaurants that fit their specific tastes or preferences.
Google’s apparently planning more visual search results, with videos, according to an AI report. This shift towards snackable video content is interesting, and reminds me of how games like explore wasteland your phone farlight 84 makers afk arena offer quick, engaging gameplay experiences. It seems like Google is trying to make search more visually appealing and interactive, aligning with the trend of bite-sized content.
It’ll be interesting to see how this plays out in the future of search.
Potential for a Hybrid Search Approach
The future of search likely lies in a hybrid model that seamlessly blends text and visual inputs. Users could input both text descriptions and visual elements, allowing for more nuanced and accurate results. This hybrid approach can significantly improve the precision of search results by leveraging the strengths of both modalities. Imagine a user searching for “vintage cars from the 1960s.” Adding a picture of a specific car model would significantly refine the search, directing the user towards similar vintage vehicles.
Comparison of Visual and Text Search for Specific Use Cases
| Use Case Scenarios | Advantages of Visual Search versus Text Search |
|---|---|
| Identifying a specific object in a cluttered image (e.g., finding a particular piece of furniture in a cluttered room) | Visual search can quickly isolate the desired object, even if it’s partially hidden or obscured. Text search might struggle with such nuanced queries. |
| Finding similar products (e.g., identifying alternative products with similar features) | Visual search can identify products with similar visual characteristics, while text search relies on matching. This is particularly valuable for users unfamiliar with specific product names or descriptions. |
| Locating information from historical or vintage images | Visual search can analyze the image’s content, offering contextual information. Text search might struggle with deciphering the meaning or context of historical images. |
| Retrieving images from video | Visual search offers the ability to retrieve specific moments from videos based on visual cues, like a specific action or object. Text search might struggle with extracting such nuanced information from video. |
Integration with Existing Search Features
Google’s image recognition and video tagging capabilities will play a pivotal role in the integration of visual search. Visual search results could seamlessly integrate with existing search features. For example, an image of a product might be displayed alongside detailed product information, links to related items, and user reviews. A video clip showing a recipe could automatically identify the ingredients and provide links to their corresponding products.
This would provide a richer and more comprehensive search experience.
User Experience Considerations
Google’s planned visual search enhancements, powered by AI, promise a significant leap in user experience. These advancements will not only improve how users interact with search but also reshape how information is discovered and understood. However, successful implementation hinges on careful consideration of potential user experiences, pain points, and the design of intuitive interfaces.
Potential User Experience Improvements
Visual search can revolutionize information retrieval by allowing users to search using images instead of text. This opens doors to discovering products, identifying objects, and understanding visual concepts. Users can now upload a picture of a flower and instantly find its name and care instructions. This capability extends to finding similar products, comparing options, and locating specific items within larger images.
Improved accuracy and speed in identifying items and locations will streamline tasks and enhance user satisfaction.
Potential Issues and User Concerns
While visual search holds immense potential, several concerns must be addressed. Users may encounter difficulties with image quality, ambiguity in objects, or inconsistencies in image recognition. Images with low resolution or poor lighting might lead to inaccurate results. Complex or cluttered images could also cause difficulties. Furthermore, users may be hesitant about the privacy implications of sharing images with search engines.
Concerns about data security and potential misuse of user-uploaded images are valid and should be proactively addressed during the development phase.
Design Considerations for Intuitive Visual Search Interfaces
Intuitive interfaces are crucial for successful visual search adoption. The interface should provide clear instructions, feedback, and multiple options for input. A simple, clean design, with clear labeling of image upload areas, search filters, and results display, is paramount. Users should be able to refine their search using tools like color, shape, size, or texture. Additionally, the interface should support zooming and cropping to enhance precision in image-based queries.
Google’s planning more visual search, with videos apparently taking center stage, according to an AI report. This shift towards more engaging visual content is super interesting, especially when you consider the trend of “smartphone but make it art” – like, what if phones were masterpieces of design and functionality? That sort of aesthetic thinking could actually inspire the next generation of visual search experiences, and potentially lead to even more innovative search features, further enhancing the user experience with Google’s visual search.
smartphone but make it art It’s a fascinating evolution of how we interact with information online, all driven by AI advancements and a desire for more immersive, visual experiences.
Effective error handling is essential to guide users through the process when encountering problems.
Examples of Successful Visual Search Interfaces
Several platforms have successfully integrated visual search features. Pinterest’s visual discovery platform excels at providing relevant visual search results and allowing users to create boards based on visual cues. Similarly, Google Lens offers a practical visual search solution, allowing users to identify objects and translate text within images. Learning from these examples and addressing their strengths will help shape a user-friendly visual search experience.
Addressing User Frustrations with Visual Search Features
To alleviate user frustrations, developers should prioritize a comprehensive testing phase. Thorough user testing, involving diverse user groups, can identify potential pain points and design improvements. Addressing issues early in the development cycle can minimize negative user experiences and ensure that the new features enhance the overall search experience. Providing clear and concise feedback messages during the search process, along with suggestions for refining queries, is crucial.
User Experience Analysis and Proposed Solutions
| User Group | Expected Reaction | Potential Pain Points | Proposed Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Search Novice | Initial hesitation, need for clear instructions | Difficulty understanding search parameters, inaccurate results | Intuitive interface, step-by-step guidance, clear feedback messages |
| Experienced Search Users | Expectation of high accuracy and speed | Inaccurate results, slow response time, limited search options | Advanced search filters, enhanced image recognition, real-time feedback |
| Users with Specific Needs | Desire for tailored results | Limited accessibility options, inability to refine search by specific attributes | Customizable filters, support for diverse image types, improved accessibility features |
| Privacy-Conscious Users | Concerns about data privacy | Data security issues, lack of transparency about data usage | Clear privacy policy, secure image handling, robust data encryption |
Market Implications and Trends
Google’s foray into visual search promises a paradigm shift, impacting various industries and sectors in profound ways. The ability to search by image rather than text will reshape how consumers interact with information, driving innovation and potentially altering the competitive landscape. This shift will necessitate adaptation from businesses and reshape how users engage with digital content.Visual search technology, as it matures, will likely impact industries ranging from e-commerce and retail to education and healthcare.
This shift is already underway, with early adopters and innovators proactively incorporating visual search into their strategies.
Potential Market Impact on Industries
Visual search has the potential to revolutionize numerous sectors. E-commerce will benefit from more accurate and efficient product discovery. Retailers can leverage visual search to provide detailed product information, enhance customer experience, and improve inventory management. In education, visual search can aid in identifying and interpreting complex diagrams, historical artifacts, or scientific images, enriching the learning process.
Healthcare professionals may find visual search useful in identifying medical imagery, enhancing diagnostics, and streamlining research.
Adaptations by Companies to Visual Search Trends
Numerous companies are already implementing visual search strategies. E-commerce platforms are integrating image-based search tools to enable customers to find products quickly and easily. Retailers are using visual search to enhance in-store experiences, allowing customers to scan products and access information instantly. Education platforms are exploring ways to integrate visual search into learning materials to enhance student engagement and knowledge retention.
These early adopters are experiencing increased customer engagement and efficiency.
Competitive Pressures from Google’s Initiatives
Google’s visual search initiatives will undoubtedly create significant competitive pressures for other search engines and image-based platforms. Companies will need to adapt their search algorithms and user interfaces to stay competitive in this evolving landscape. The integration of AI and machine learning will be crucial for maintaining a leading edge.
Influence on User Interaction with Websites and Applications
Visual search will profoundly affect how users interact with websites and applications. Users will expect a more intuitive and image-based approach to information retrieval. Websites need to be optimized for visual search to maintain visibility and engagement. Applications will need to integrate visual search capabilities to stay relevant in the future.
Future Trends in Visual Search Technology
Future trends in visual search technology point towards more sophisticated AI-powered systems. The technology will likely become more accurate and versatile, enabling the recognition of more complex objects and scenes. Augmented reality (AR) integration is a strong possibility, allowing users to interact with visual search results in a three-dimensional space. The development of personalized visual search experiences tailored to individual user preferences will also be a significant future trend.
Comparison of Google’s Visual Search Strategy with Competitors
| Feature | Competitor A | Competitor B | |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI Integration | High, utilizing advanced machine learning models | Moderate, relying on existing image recognition technologies | Low, relying on -based search primarily |
| Image Recognition Accuracy | High, with continuous improvement | Moderate, with room for improvement | Low, often misidentifying objects |
| User Interface Design | Intuitive and user-friendly, focusing on simplicity | Complex and cluttered, lacking in visual appeal | Traditional and non-intuitive, not adapted to visual search |
| Scalability | High, supporting large volumes of images and queries | Moderate, potentially struggling with large datasets | Low, limiting the scope of visual search capabilities |
Technical Implementation and Infrastructure
Google’s ambitious vision for visual search necessitates a robust technical foundation. The sheer volume of visual data, from images and videos to intricate metadata, demands innovative solutions for storage, processing, and retrieval. This section delves into the key technical considerations and infrastructure requirements for achieving this ambitious goal.
Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
The foundation of any robust visual search system lies in the acquisition and meticulous preprocessing of visual data. This involves diverse sources, including user uploads, web crawling, and partnerships with content providers. Raw visual data must be transformed into a format suitable for efficient indexing and querying. This often includes image resizing, format conversion, and extraction of relevant features like color histograms, object detection, and scene recognition.
These features form the basis for similarity comparisons during search queries. Effective preprocessing minimizes the computational burden during search and enhances the accuracy of results.
Feature Extraction and Representation
A critical aspect of visual search is the ability to represent complex visual content in a manner that allows for effective similarity comparisons. Deep learning models, particularly Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), are employed to extract robust and discriminative visual features. These features capture nuanced aspects of images, such as object shapes, textures, and relationships, enabling the system to understand the context of the image.
These extracted features are then encoded into a numerical representation that facilitates efficient similarity searches. This process ensures that the system can identify images with similar visual characteristics, even if they differ in lighting, orientation, or background.
Indexing and Retrieval
Efficient indexing and retrieval are crucial for fast response times. Modern indexing techniques, often combined with vector databases, are employed to store and organize the extracted visual features. These databases are optimized for high-dimensional similarity searches, enabling the system to quickly retrieve relevant images based on user queries. Advanced indexing methods, such as inverted indexes and approximate nearest neighbor search algorithms, ensure rapid retrieval of images matching the user’s visual query.
Scalability and Cloud Computing
The sheer scale of visual data necessitates a robust and scalable infrastructure. Cloud computing platforms play a vital role in this aspect, providing flexible and dynamic resources that can adapt to fluctuating data volumes and user demands. Google’s extensive cloud infrastructure, including Google Cloud Platform (GCP), allows for the deployment of massive-scale computing resources for handling image processing and storage.
The use of distributed systems and parallel processing enables the system to handle a massive influx of images and queries concurrently. The inherent scalability of cloud infrastructure is critical for handling the exponential growth of visual data.
Technical Implementation and Infrastructure Analysis
| Technology Used | Associated Costs | Scalability Concerns ||—|—|—|| Deep Learning Models (CNNs) | High initial investment in specialized hardware and expertise | Model training and maintenance require significant resources || Cloud Computing Platforms (GCP) | Pay-as-you-go model, variable costs depending on usage | Reliance on third-party infrastructure, potential latency issues in geographically dispersed deployments || Vector Databases | Costs depend on the specific database and storage needs | Potential performance bottlenecks with very large datasets || Distributed Systems and Parallel Processing | Increased infrastructure costs but potential for significant efficiency gains | Complex to manage and coordinate, requires specialized expertise |
Ending Remarks

Google’s planned visual search overhaul, driven by AI, could significantly impact user experience and market trends. The potential for faster, more engaging search results is exciting, but challenges like data privacy and algorithm bias need careful consideration. How users adapt to this new paradigm remains to be seen, but the shift towards visual search is undeniably here. Will Google succeed in creating a truly revolutionary search experience?
The future will tell.




