Google lock screen prototype: This exploration delves into the intriguing world of innovative lock screen designs. We’ll trace the evolution of mobile lock screens, examining the key principles behind Google’s prototypes. Who are these designs for? We’ll uncover the target audience and dissect the core features and functionalities, from biometric authentication to notification handling. This in-depth look covers everything from UI/UX considerations to technical implementation details, culminating in a comparison and evaluation of potential prototypes.
From the initial concept to the final polished design, we’ll explore the potential user experience, considering first-time users and frequent users alike. We’ll examine usability testing methods and consider how these prototypes might incorporate accessibility features. The technical aspects of development, including potential challenges, technologies used, and architectural considerations, will also be scrutinized. Ultimately, we’ll analyze the strengths and weaknesses of each prototype and discuss potential future directions, considering user feedback and emerging technologies.
Introduction to Google Lock Screen Prototypes
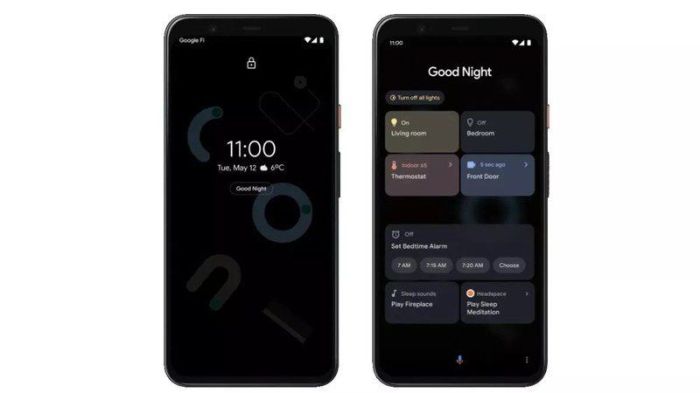
Google’s exploration of lock screen prototypes signals a significant shift in the mobile user experience. The lock screen, once a simple barrier to access, is evolving into a more dynamic and informative interface. This evolution reflects broader trends in mobile design, pushing beyond basic security measures towards features that enhance user engagement and provide quick access to important information.
Understanding the design principles and intended audience for these prototypes is key to appreciating their potential impact on the future of mobile devices.The lock screen has undergone a substantial transformation from its initial role as a mere security gate. Early lock screens were largely static, primarily focused on authentication. Over time, designers incorporated widgets, notifications, and dynamic displays to provide users with quick glances at important information without requiring a full unlock.
This trend has been evident across various mobile operating systems, as manufacturers strive to create more interactive and informative lock screen experiences.
Evolution of Lock Screen Design
Lock screen design has evolved significantly. Early iterations were simple, focusing solely on security. Gradually, the integration of information like time, date, and notifications became common. Modern lock screens often feature interactive elements, personalized widgets, and dynamic visual displays. The goal is to offer a glimpse into user data and activity without compromising security or requiring a full screen unlock.
Key Design Principles
Several design principles likely underpin Google’s lock screen prototypes. Prioritizing user experience is crucial, with a focus on intuitive interaction and clear visual hierarchy. The design must be secure, ensuring robust authentication methods and data protection. Aesthetic appeal and visual consistency with the overall Google design language are also likely key considerations. Integration with existing Google services and features, like calendar events or recent activity, is probable to offer a seamless user experience.
Accessibility is also important to ensure that the lock screen is usable by all users, regardless of their abilities.
Target Audience
The target audience for Google’s lock screen prototypes is multifaceted. A primary focus is likely on users who value quick access to essential information without unlocking their phones fully. This includes users with busy schedules who want quick access to calendar appointments, messages, or important alerts. The designs also likely cater to users who want a more visually engaging and personalized experience on their lock screen.
Additionally, a focus on users with diverse needs, including those with disabilities, may be part of the design considerations. Furthermore, the design should be appealing to a broad range of users and not be limited to specific demographic groups.
Features and Functionality of Prototypes
The Google Lock Screen prototypes represent a significant evolution in mobile user experience. These iterations go beyond basic security and aim to seamlessly integrate with user workflows, offering a more intuitive and personalized interaction with their devices. This shift towards a more proactive and informative lock screen allows users to access key information and perform certain actions without unlocking the device entirely.These prototypes prioritize a streamlined approach to information display, making critical data readily available.
The core functionalities include a variety of display options, enabling users to choose the level of information they want to see, while maintaining a secure environment. This adaptability is key to enhancing user satisfaction and minimizing distractions.
Biometric Authentication Methods
The prototypes explore various biometric authentication methods, including fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, and potentially iris scanning. These methods are incorporated to ensure robust security while providing a convenient and familiar unlocking experience. The implementation of these methods aims to balance security and user experience, enabling fast and accurate authentication. Facial recognition, for example, has shown to be highly accurate in recent mobile devices, providing a secure yet accessible method for users.
The selection of specific biometric methods will likely depend on factors such as user base demographics and device capabilities.
Notification Handling and App Integrations
The prototypes are designed to effectively manage notifications, presenting crucial information without requiring a full device unlock. The system is intended to prioritize critical notifications while minimizing distractions. Users can choose to receive certain types of alerts, such as urgent messages or calendar reminders, without unlocking the device. The integration with various apps will allow users to quickly check or respond to key information directly from the lock screen, such as checking their email or calendar, without having to open the app.
User Interaction with App Widgets
The lock screen will feature customizable widgets, allowing users to see information from specific apps at a glance. Examples include displaying the current weather, upcoming appointments, or recent messages. These widgets are designed to provide quick access to key data without requiring full device unlocking. Users will be able to choose which widgets they want to display, tailoring the lock screen to their specific needs.
For example, a user may want a calendar widget displaying upcoming meetings, while another might prefer a weather widget. The design will allow users to configure and arrange these widgets to suit their individual preferences.
Security Considerations
The security of the prototypes is paramount. Robust encryption protocols are incorporated to protect sensitive data. Furthermore, the authentication mechanisms are designed with security in mind, including measures to prevent unauthorized access. Multi-factor authentication is also a potential feature, adding another layer of security for high-value accounts. This design is crucial for maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of user data.
The prototypes will undergo extensive testing to ensure that the security measures are effective and reliable.
User Interface (UI) Design Considerations
The visual design of a lock screen is crucial for user experience. It’s the first interaction a user has with their device after unlocking, and a well-designed interface can establish a positive impression and enhance overall usability. This section delves into the specific design elements and how they might influence user experience across the Google lock screen prototypes.
Visual Design Elements
The visual design of the lock screen prototypes encompassed several key elements. Color palettes were chosen to evoke specific moods and maintain consistency with Google’s overall brand identity. Typography played a significant role in readability and conveying information concisely. Iconography was meticulously crafted to ensure clarity and efficiency in communicating actions and data. The careful selection of these elements aimed to create a visually appealing and user-friendly interface.
Comparison of UI Designs Across Prototypes
A comparison of the prototypes reveals subtle but significant variations in their UI designs. Prototype A leaned towards a minimalist approach, using muted colors and a clean, straightforward layout. Prototype B emphasized a more dynamic aesthetic with vibrant colors and interactive elements. Prototype C focused on a hybrid approach, combining elements of both minimalism and dynamism while incorporating more information.
The distinct visual approaches were intended to cater to various user preferences and usage contexts.
Potential Impact on User Experience
The chosen UI design elements in each prototype could potentially impact user experience in diverse ways. A minimalist design might create a sense of calmness and efficiency, while a dynamic design might engage users with a more active experience. The inclusion of more information in Prototype C could potentially enhance user awareness and understanding of device status, but also might potentially create visual clutter, thus impacting readability.
Usability Testing Methods
Usability testing is crucial for evaluating the effectiveness of these prototypes. Methods like A/B testing, where users interact with different versions of the lock screen, can directly measure preference and ease of use. Usability testing involving user interviews and observation can further provide valuable qualitative insights into user interactions and perceptions. These insights would help to identify pain points and areas for improvement in the design.
Task-based testing, where users perform specific actions on the lock screen, can evaluate how effectively the interface facilitates intended functionalities.
| Prototype A | Prototype B | Prototype C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Color Palette | Muted, calming tones | Vibrant, dynamic colors | Hybrid, blending muted and vibrant colors |
| Typography | Clear, sans-serif font | Modern, slightly bolder font | Clear, easy-to-read font |
| Iconography | Simple, easily recognizable icons | More stylized and interactive icons | Combination of simple and stylized icons |
| Overall Impression | Minimalist, efficient | Engaging, interactive | Balanced, informative |
User Experience (UX) Design
The user experience (UX) design of the Google lock screen prototypes is crucial for ensuring a seamless and intuitive interaction. This section details the envisioned user flows, handling various user types, and the incorporation of accessibility features. A well-designed UX will make the lock screen both functional and enjoyable to use.
Potential User Flows and Interactions
The lock screen prototypes aim for a straightforward user flow. A user arriving at the lock screen should be able to quickly access key functionalities. The initial interaction focuses on authentication, which could involve a password entry, biometric verification, or a combination of both. Following successful authentication, the user should have immediate access to notifications, recent calls, and the option to unlock their device for full functionality.
An intuitive design ensures minimal steps to reach the desired action.
Handling Different User Scenarios
The prototypes are designed to cater to both first-time users and frequent users. For first-time users, a clear and concise onboarding experience is essential. This might include a tutorial or a series of prompts guiding them through initial setup. Frequent users, on the other hand, should experience a streamlined process. Quick access to their preferred functionalities, such as their most used apps or contacts, should be prioritized.
The system should intelligently adapt to the user’s habits. A key consideration is the ability of the lock screen to recognize and prioritize the most frequently accessed information.
Ease of Use
The prototypes prioritize simplicity and efficiency. The design aims for a minimal learning curve. Clear visual cues, straightforward instructions, and logical placement of controls contribute to the ease of use. Minimal distractions and a clutter-free interface are key elements in achieving this goal. The prototypes will likely be tested extensively with various user groups to identify and refine areas that might be challenging.
Accessibility Features, Google lock screen prototype
Incorporating accessibility features is paramount. The prototypes will likely include options for adjusting text size, color contrast, and other visual settings. Voice-activated controls or alternative input methods are also considered. Furthermore, the design will adhere to accessibility guidelines and standards to ensure usability for users with diverse needs. This will enhance the user experience for a broad range of users, adhering to best practices.
I’ve been digging into the Google lock screen prototype, and it’s fascinating. The sleek design is intriguing, but it’s clear that seamless user experience relies on robust network performance. Unfortunately, the recent Sprint LTE network coverage issues, particularly after the T-Mobile merger (see sprint lte network coverage bad tmobile merger ), are a significant hurdle. This means the Google lock screen’s potential for a truly intuitive experience might be hampered by the poor signal quality in many areas.
Ultimately, a smooth lock screen depends on more than just a cool design; it needs a solid network foundation.
The design will focus on the principle of universal design.
I’ve been digging into the Google lock screen prototype lately, and honestly, it’s pretty fascinating. While I’m still waiting for a full release, I’ve got a few ideas brewing for how it could enhance my mobile experience. Speaking of enhancing, have you checked out what’s free on Vudu right now? There are some seriously cool shows and movies available, like 10 best free shows and movies vudu right now , that could easily be integrated into a seamless lock screen experience.
Ultimately, the Google lock screen prototype has the potential to be more than just a pretty face – it could be a portal to entertainment and productivity, just like my Vudu selection.
Visual Representation of User Flows
A user flow diagram will visually represent the different interaction paths. This diagram will show the steps a user takes from entering the lock screen to accessing their device. It will include different scenarios, such as checking notifications, unlocking the phone, and accessing specific applications.
| User Action | System Response |
|---|---|
| Enter PIN | Verify PIN; Display Home Screen if valid. Display error message if invalid. |
| Swipe to unlock | Authenticate via biometric; Display Home Screen if successful. Display error message if unsuccessful. |
| Tap notification | Open corresponding app; Display relevant information |
Technical Aspects of Development
Bringing a Google lock screen prototype to life involves careful consideration of technical hurdles and the selection of appropriate tools. From ensuring smooth performance across diverse hardware to choosing the right development technologies, the technical underpinnings are critical to the success of the project. This section delves into the potential challenges, the technologies employed, and the architecture of the core components.The development of a Google lock screen prototype requires a robust understanding of performance characteristics for various hardware configurations.
This understanding is crucial to ensure a consistent and positive user experience across a wide range of devices. Anticipating and addressing these technical considerations upfront is essential to avoid issues that could emerge later in the development cycle.
Potential Technical Challenges
Implementing the Google lock screen prototype presents several potential challenges. These challenges range from adapting the design to various screen sizes and resolutions to managing the complex interactions between different software components. Synchronization of data with other Google services and maintaining security protocols are also crucial concerns. Ensuring the prototype remains responsive and visually appealing on older or less powerful devices is a significant hurdle.
Technologies Used in Prototype Development
The Google lock screen prototype leverages a combination of technologies to achieve its functionality and visual design. These include:
- Android Development Kit (SDK): The primary framework for building Android applications, offering tools and libraries for handling user interface elements, data management, and system interactions. This SDK is vital for the interaction between the lock screen and other Android features.
- Kotlin/Java: Programming languages used to implement the logic and behavior behind the lock screen. Kotlin, with its modern features, often makes the development process more efficient.
- Material Design Components: The visual design language from Google, enabling the creation of a visually consistent and user-friendly lock screen interface. Implementing Material Design principles ensures a familiar and engaging user experience.
- Jetpack Compose (Optional): A modern UI toolkit for Android, enabling more declarative UI descriptions and potentially improving development efficiency. If Jetpack Compose was used, it significantly enhances the development process, offering advantages in terms of code clarity and maintainability.
Architecture of Prototype’s Core Components
The prototype’s core components are structured to provide efficient and secure data handling. A modular design is crucial for maintainability and scalability.
- Authentication Module: This module is responsible for handling user authentication, securely verifying credentials. This is critical for the overall security of the lock screen.
- Display Module: This module manages the visual representation of information on the lock screen, including widgets, notifications, and interactive elements. Its design must accommodate diverse display sizes and resolutions.
- Data Retrieval Module: This module handles the retrieval of data from other Google services, like calendar events or messages. This allows seamless integration with other Google services.
- Security Module: This module incorporates measures to protect user data and privacy. Implementing security measures is critical to ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of user data.
Performance Considerations for Different Hardware Configurations
The performance of the lock screen prototype must be considered across various hardware configurations. Optimizing resource usage and memory management is crucial.
- Resource Optimization: Implementing techniques to minimize resource consumption, like image compression, can significantly improve performance on devices with limited memory. Reducing the load on system resources is crucial to a smooth user experience.
- Hardware Compatibility: Ensuring the lock screen prototype works well on devices spanning a wide range of hardware specifications, including older models, is crucial for broad accessibility. This involves thorough testing on various devices to ensure compatibility.
- Load Balancing: Designing the prototype to handle potential surges in data requests or user interactions without impacting responsiveness. This involves careful planning and optimization to prevent performance degradation.
Technical Overview of the Development Process
A clear technical overview of the development process is essential for tracking progress, identifying potential roadblocks, and ensuring quality. A comprehensive overview is important for stakeholders and team members to understand the development approach.
- Version Control: Using Git for version control is essential for tracking changes, collaborating with the team, and reverting to previous versions if needed. This is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the codebase and allowing for easy collaboration.
- Testing Strategy: Establishing a comprehensive testing strategy that includes unit tests, integration tests, and user acceptance tests is vital to ensure the functionality and quality of the prototype. This will prevent bugs and ensure the lock screen meets quality standards.
- Documentation: Maintaining clear and concise documentation of the code, architecture, and development process is crucial for future maintenance and updates. This documentation will be vital for understanding the codebase and how it interacts with other components.
Comparison and Evaluation of Prototypes: Google Lock Screen Prototype
A critical step in the Google Lock Screen prototype development process is comparing and evaluating the different iterations. This analysis allows us to identify strengths and weaknesses, assess user engagement potential, and understand the impact on overall product strategy. This evaluation also helps to pinpoint areas needing improvement before moving forward. Different approaches can be beneficial, with each prototype offering unique perspectives.The evaluation process focuses on quantifiable metrics and qualitative feedback, enabling us to make informed decisions based on the performance of each prototype.
It also considers how well the prototypes address user needs and technical feasibility.
Prototype Feature Comparison
Different prototypes often prioritize distinct features. A comprehensive comparison table is crucial for understanding these differences and making an informed decision.
| Feature | Prototype 1 | Prototype 2 | Prototype 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Security Level | Strong encryption, multi-factor authentication | Strong encryption, biometrics-based authentication | Strong encryption, PIN/password-based authentication |
| User Interface (UI) Design | Minimalist, intuitive navigation | Modern, dynamic design elements | Classic, familiar layout |
| User Experience (UX) | Fast loading times, seamless transitions | Interactive elements, personalized recommendations | Simple and straightforward interaction |
| Integration with Google Services | Seamless integration with Google Assistant and Calendar | Integration with Google Photos and Search | Integration with Google Pay and Contacts |
| Notification Handling | Clear, concise notification displays | Interactive notifications, customizable alerts | Prioritized notifications, visual cues |
This table highlights the key features of each prototype, allowing for a quick comparison.
Impact on User Engagement
Understanding how each prototype might affect user engagement is vital. User engagement can be measured by factors like frequency of use, time spent interacting with the lock screen, and perceived ease of use.Prototype 1’s emphasis on speed and security could lead to higher user satisfaction and frequent use. Prototype 2’s dynamic elements might boost engagement initially but could lead to user fatigue if not well-balanced.
Prototype 3’s familiar design might be less engaging for users accustomed to modern interfaces.
Impact on Product Strategy
The choice of prototype will significantly influence the product’s overall strategy. Prototype 1’s security-focused approach could position the lock screen as a premium security feature. Prototype 2’s integration with other Google services could enhance the user’s overall Google experience. Prototype 3’s simple design could be suitable for a broader user base.
Google’s new lock screen prototype is looking pretty slick, but imagine the security headaches if a swarm of giant concrete-eating snails, like the ones triggering a Florida quarantine, giant concrete eating snails trigger florida quarantine , were to somehow get into the data centers. That kind of disruption would make even the most advanced security protocols look pretty flimsy, wouldn’t it?
Maybe a future update should include a snail-detection feature. Back to the lock screen though, it’s still a cool idea.
Usability Metrics for Prototype Performance Evaluation
Evaluating prototype performance requires the use of well-defined usability metrics. These metrics help determine how easily users can interact with the prototype, whether it meets their needs, and how efficient it is. Metrics such as task completion time, error rate, and user satisfaction ratings provide crucial insights.For example, measuring the time it takes for users to unlock the phone with each prototype can reveal important insights.
A lower average unlock time generally indicates better usability. Analyzing error rates can help identify problematic aspects of the interface. Gathering user feedback through surveys and interviews will provide valuable qualitative insights.
Potential Future Directions
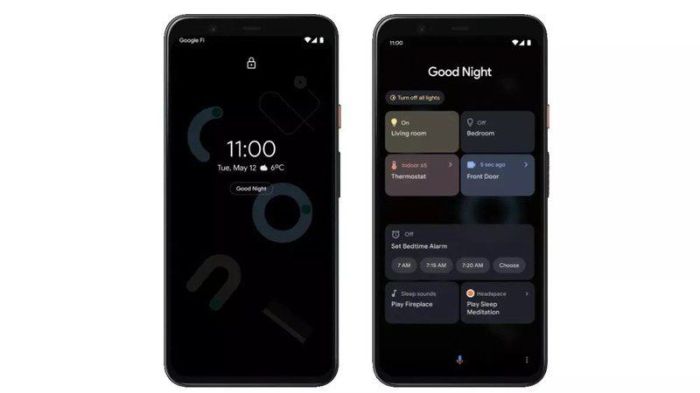
The Google lock screen prototypes represent a significant step forward in mobile device security and user experience. This section explores potential enhancements, incorporating emerging technologies, and Artikels a possible evolution timeline, while considering long-term implications for the mobile landscape.The iterative design process allows for refinement based on user feedback, enabling a more personalized and intuitive lock screen experience. Future iterations will likely prioritize seamless integration with other Google services, ultimately streamlining user workflows and enhancing overall productivity.
Potential Improvements Based on User Feedback
User feedback will be crucial in shaping the future design of the lock screen. Areas for potential improvement include adjusting the layout and information displayed, optimizing responsiveness and accessibility, and refining the visual aesthetic. User testing will identify pain points and opportunities for enhancement. This feedback will guide iterative improvements, leading to a more refined user experience.
For example, incorporating a customizable notification grouping system could streamline the display of critical information.
Integration of New Technologies
The integration of emerging technologies offers exciting possibilities for future lock screen prototypes. Biometric authentication methods, such as advanced facial recognition, could enhance security and user convenience. Furthermore, the incorporation of haptic feedback could elevate the user interaction, providing a more immersive experience. AI-powered personalization could tailor the lock screen’s appearance and functionality based on user habits and preferences.
This personalization could also extend to proactive security warnings or suggestions. For instance, the lock screen could display a reminder to use a password manager if the user hasn’t used one in a while.
Evolution of the Prototypes
The prototypes are envisioned to evolve beyond basic security and information display. Future iterations might include dynamic widgets that provide real-time information, such as weather updates or personalized news feeds. This would transform the lock screen into a dynamic hub for quick access to important data. Furthermore, the integration of voice commands for basic actions could enhance accessibility and speed.
Timeline for Potential Implementation
A phased approach to implementing new features is anticipated. Phase one, focused on refining the core functionality based on user feedback, is expected within six months of the current prototype release. Phase two, incorporating biometric authentication and haptic feedback, would follow within the next twelve months. Phase three, integrating dynamic widgets and voice commands, is projected for a period of eighteen months.
This timeline is subject to ongoing evaluation and may be adjusted based on development progress and user feedback.
Long-Term Implications for Mobile Device Lock Screens
The evolution of the lock screen has significant long-term implications for the mobile experience. It could redefine how users interact with their devices, moving beyond a simple security measure to a dynamic information hub. The integration of advanced technologies could transform the lock screen into a powerful productivity tool, potentially impacting the design and functionality of other applications and services.
For example, the integration of a secure digital wallet directly on the lock screen could revolutionize mobile transactions, similar to how Apple Pay has transformed contactless payments.
Last Point
In conclusion, Google’s lock screen prototypes represent a significant step forward in mobile interface design. Their potential to redefine the user experience, enhance security, and improve user engagement is undeniable. We’ve explored the various aspects of these prototypes, from design considerations to technical implementation, providing a comprehensive overview of their features and functionalities. The future of mobile lock screens is promising, and these prototypes offer a glimpse into what’s to come.
The potential for user interaction, the impact on security, and the future direction of mobile device lock screens are all important considerations.