Google Android 12 trash bin recover lost deleted files – a frustrating experience for many. This guide dives deep into understanding Android 12’s file system, exploring various methods to retrieve those accidentally deleted files. We’ll cover common scenarios, recovery tools, and preventative measures to safeguard your data in the future.
From understanding Android 12’s storage mechanisms to practical steps for recovery, this comprehensive guide equips you with the knowledge and tools to navigate the complexities of file loss on your Android 12 device. We’ll cover internal and external storage, different deletion types, and the limitations of each recovery method.
Understanding Android 12’s File System

Android 12, like its predecessors, relies on a robust file system to manage data storage and retrieval. Understanding how this system functions is crucial for anyone working with Android devices, especially when dealing with lost or deleted files. This exploration dives into the intricacies of Android 12’s file system, encompassing internal and external storage, deletion mechanisms, and the implications for recovery efforts.The Android file system, while seemingly straightforward, presents nuances that significantly impact file recovery.
Understanding these nuances is key to maximizing recovery chances. The different storage locations, deletion methods, and file system structures all play a critical role in the process.
Ever lost a crucial file on your Android 12? Luckily, recovering deleted files from the trash bin is often possible. But while you’re out exploring nature, wouldn’t it be great to have your phone securely mounted on your bike? Check out this awesome bike mount for 50% off – perfect for capturing those epic trail memories, and keeping your phone safe from spills and drops, so you can focus on your next photo ops.
Regardless, knowing how to recover those lost files in the Android 12 trash bin is always a good idea.
Internal Storage Locations
Android 12, like previous versions, employs a hierarchical structure for internal storage. This structure is crucial for organizing files and applications efficiently. The primary location is often the `/data` directory, which contains user data and application files. Applications are typically assigned specific directories within this area, facilitating efficient data management. Understanding these directory paths is critical for targeted file recovery.
External Storage Locations
External storage, often represented by removable SD cards or other external storage devices, presents a separate storage hierarchy. This external storage is frequently mounted as a separate file system. Android 12’s handling of external storage is designed for compatibility with various formats and devices, ensuring seamless integration. The mounting process and file structure on external storage can influence recovery procedures.
File Deletion Mechanisms
Android 12, like its predecessors, employs different mechanisms for deleting files. Immediate deletion involves the immediate removal of file entries from the directory. However, the actual data may not be erased immediately. Delayed deletion is a mechanism where file entries are marked for deletion but the data remains on the storage device until overwritten. This distinction is crucial in recovery efforts.
Delayed deletion allows for potential recovery if the data hasn’t been overwritten.
Ever lost a crucial file on your Android 12 device? Don’t despair, the trash bin might hold the answer. While recovering deleted files from your phone’s storage can be tricky, exploring methods like checking the Android 12 trash bin is worth a shot. Recent discussions about privacy concerns with messaging apps like Facebook Messenger, especially in the context of the recent Kansas abortion ruling, highlight the importance of data security.
However, understanding how to effectively recover lost files on your phone is a different issue entirely, which brings us back to the importance of the Android 12 trash bin. You can explore more on this topic by reading about facebook messenger encryption abortion kansas for a different perspective.
Immediate Deletion
Immediate deletion is a straightforward process where the file entry is removed from the directory immediately. This means the file’s metadata, including its name and location, is no longer accessible. This can potentially make the file more difficult to recover. However, the actual data on the storage device may still remain, depending on the storage device’s characteristics.
Delayed Deletion
Delayed deletion, on the other hand, marks a file for deletion but doesn’t immediately erase the data from the storage device. This is often a temporary step before the data is permanently overwritten. This delayed erasure is a critical aspect of data recovery as the actual data is preserved until overwritten.
File System Structures
Android 12, like its predecessors, uses a variety of file system structures, including ext4 for internal storage and others for external storage. The specifics of the file system structure play a role in the recovery process. Different file systems handle data differently, impacting recovery strategies.
Implications for File Recovery
The file system configurations significantly influence the potential for file recovery. Understanding the deletion mechanisms (immediate or delayed) and the specific file system used for the storage location is crucial. For instance, immediate deletion presents fewer recovery options than delayed deletion. Moreover, different file systems might have different characteristics in terms of data preservation after deletion.
Methods for Lost File Recovery: Google Android 12 Trash Bin Recover Lost Deleted Files
Recovering lost files on Android 12 can be challenging, but understanding the various scenarios and available methods can significantly improve your chances of retrieval. This section delves into common file loss situations and detailed approaches to recovering deleted files, ranging from simple recovery methods to more complex techniques. Factors such as the deletion method and the nature of the device’s storage play crucial roles in the success of recovery efforts.The path to file recovery involves careful consideration of the circumstances surrounding the loss.
Knowing how a file was deleted—whether intentionally, accidentally, or due to a system malfunction—is vital for choosing the most appropriate recovery technique. Furthermore, understanding the limitations of each method is essential for setting realistic expectations.
Common Scenarios of File Loss
Accidental deletion is a frequent cause of lost files. Users often delete files unintentionally, either by mistaking them for other files or by performing an action that results in unintended deletion. Corrupted storage or software malfunctions can also lead to data loss. Improper device shutdown, insufficient storage space, or even physical damage to the device can cause file loss.
Additionally, third-party applications or system updates can sometimes result in data corruption or deletion.
Methods for Recovering Lost Files
Several methods can be employed to recover lost files on Android 12. The effectiveness of each method depends on the specific circumstances surrounding the loss.
- Using Recovery Tools: Specialized data recovery software designed for Android devices can potentially recover lost files. These tools often employ sophisticated algorithms to scan storage devices for deleted or hidden files. However, their success depends on the extent of data modification or deletion and the type of storage used. Some tools are able to recover files even after the Recycle Bin is emptied.
An example is Recuva, which is capable of recovering lost files from various storage media, including Android devices. It can recover files deleted from the Recycle Bin as well as files deleted from the primary storage space.
- Using Cloud Backups: If your files were backed up to a cloud storage service (like Google Drive, Dropbox, or OneDrive), you may be able to restore them from the backup. This method is highly effective if the backup was recent and the file was not overwritten. However, cloud backups may not always capture every file or folder, especially those modified frequently or in real-time.
Also, restoring from a cloud backup can sometimes lead to version conflicts or overwriting of existing files.
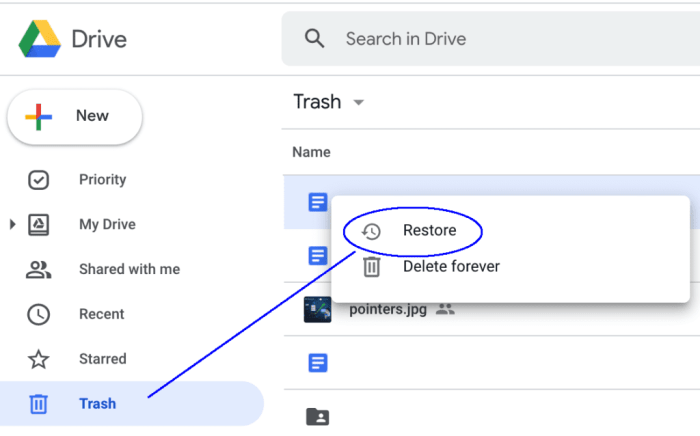
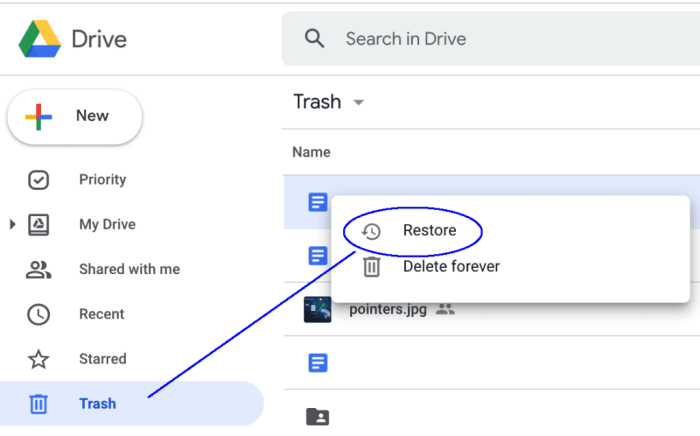
- Using the Recycle Bin (if applicable): Android 12 devices often include a Recycle Bin feature. Files moved to the Recycle Bin can be recovered if the Recycle Bin hasn’t been emptied. The availability and functionality of the Recycle Bin vary depending on the device manufacturer and the specific settings. Recovery from the Recycle Bin is usually straightforward and doesn’t require any additional software.
- Using File Managers: Some file managers may offer options to recover recently deleted files. These features often rely on the device’s internal mechanisms to retrieve files that have been recently deleted, similar to the Recycle Bin approach. The success rate is often limited by the time elapsed since the deletion and the file system’s internal state. The effectiveness is not guaranteed.
- Recovering from a System Image Backup: A system image backup, if available, can be used to restore the entire system, including the lost files. This method is typically employed when the device is severely damaged or unusable. However, restoring from a system image backup can be a time-consuming process and might not preserve any changes made after the last backup.
Limitations of File Recovery Methods
Each file recovery method has limitations. No method guarantees the recovery of all lost files. The success of recovery depends on various factors, including the type of file loss, the storage medium’s integrity, and the specific circumstances surrounding the loss.
- Recovery Tools: Recovery tools may not be able to recover files if the storage has been significantly altered or corrupted. Their effectiveness depends on the software’s ability to find deleted or hidden files. The method may not work on all types of storage media, especially those with complex or unusual file structures.
- Cloud Backups: Cloud backups may not capture all files, especially those modified frequently or created after the last backup. Also, restored files may overwrite existing files with the same name. Moreover, cloud backups might be limited by storage space, and the security of the cloud service provider.
- Recycle Bin: The Recycle Bin might not be present on all devices or may not be properly configured, rendering recovery impossible. Emptying the Recycle Bin permanently removes the files, making recovery impossible. The time limit for recovery from the Recycle Bin varies by device manufacturer and model.
- File Managers: The effectiveness of file manager recovery tools is limited and may not be successful if the files are severely damaged or overwritten. File managers’ recovery features often rely on temporary storage mechanisms, so the recovery is not always guaranteed.
- System Image Backup: System image backups may not be readily available or might not contain the desired files. Restoring from a system image backup is a complex process that might not work on all devices.
Tools and Techniques for Recovery
Recovering lost files on an Android 12 device can be a challenging but often surmountable task. Understanding the intricacies of Android’s file system and employing appropriate recovery tools are crucial steps in this process. This section delves into the various tools and techniques available, guiding you through the steps to potentially retrieve your deleted data.File recovery tools are not always guaranteed to restore files, particularly if the data has been overwritten.
Success hinges on the extent of the data’s alteration and the quality of the recovery software. Different tools cater to various needs and file types, making careful selection crucial.
Comparison of File Recovery Tools
Several tools facilitate Android file recovery. Choosing the right one depends on factors like supported file types, features, ease of use, and cost.
| Tool Name | Supported File Types | Features | Ease of Use | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disk Drill | Wide range, including documents, images, videos, and audio | Advanced scanning, preview, selective recovery | Generally user-friendly, with intuitive interface | Subscription-based, with varying tiers |
| Recuva | Extensive range of file types | Easy-to-navigate interface, supports various storage devices | Straightforward to use, even for beginners | Free version available with limitations, paid versions offer more features |
| Stellar Data Recovery | Broad support for common file formats | Provides options for different recovery scenarios | Generally user-friendly, with clear instructions | Subscription-based, with various tiers |
| EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard | Vast support for data types | Allows data recovery from different storage devices | User-friendly interface, with clear instructions | Subscription-based, with various tiers |
Steps for Using Disk Drill
Disk Drill is a widely recognized tool for file recovery. Its comprehensive features and user-friendly interface make it a popular choice.The following steps Artikel how to use Disk Drill for recovering files from internal storage:
- Download and install Disk Drill on your computer.
- Connect your Android device to the computer using a USB cable.
- Launch Disk Drill and select “Recover Files”.
- Choose the storage location of the deleted files (e.g., internal storage). Select the appropriate drive/partition.
- Disk Drill will scan the selected drive for lost files. This process may take time depending on the size of the drive and the number of files.
- Preview the recovered files to ensure they are the ones you need.
- Select the files to recover and click “Recover”.
- Choose a location on your computer to save the recovered files.
File Recovery Options by File Type
The success of recovering specific file types can vary depending on factors like the file’s format, the extent of data loss, and the tool used.
| File Type | Recovery Method | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Images (JPEG, PNG) | Using specialized file recovery software like Disk Drill or Recuva | Generally high, especially if the file hasn’t been overwritten |
| Documents (Word, Excel, PDF) | Using file recovery software that supports document formats | Moderate to high, depending on the extent of damage |
| Videos (MP4, AVI) | Using file recovery software | Moderate to high, depending on the extent of damage |
| Audio (MP3, WAV) | Using file recovery software | Moderate to high, depending on the extent of damage |
Prevention of Data Loss
Protecting your precious Android 12 files is crucial. Accidental deletions, system crashes, or even device loss can lead to irreversible data loss. Proactive measures are essential to mitigate these risks. This section Artikels key preventative strategies to safeguard your valuable information.Regular backups are vital to avoid the devastating consequences of data loss. Implementing robust backup procedures and understanding the role of cloud storage can significantly reduce the likelihood of losing important files.
Importance of Regular Backups
Regular backups are a cornerstone of data protection. They create a safe copy of your files, allowing you to restore them in case of data loss. This proactive approach ensures you don’t lose precious memories, important documents, or critical applications. The frequency of backups should be tailored to your needs and the sensitivity of the data being backed up.
Role of Cloud Storage
Cloud storage services, such as Google Drive, provide a secure and accessible off-site repository for your data. This remote storage mitigates the risk of data loss due to local device issues, such as hardware failure or accidental damage. The cloud acts as a failsafe, ensuring your data remains accessible even if your physical device is compromised.
Backing Up Files on Android 12
Backing up your files using Google Drive or another cloud service is straightforward. The following steps provide a clear guide:
- Enabling Backup on Android 12: Ensure that the automatic backup feature in your chosen cloud service is enabled on your Android 12 device. This is usually a setting within the app itself.
- Choosing Files to Back Up: Select the files and folders you want to back up. You can choose specific folders or enable automatic backup of all new files.
- Connecting to Wi-Fi: Cloud backups generally work best when connected to a stable Wi-Fi network to ensure efficient data transfer.
- Monitoring Backup Progress: Keep an eye on the backup progress to ensure successful completion. Some services provide notifications or visual cues to indicate the status.
- Verification: After the backup is complete, verify the backup’s contents to ensure they have been successfully transferred to the cloud.
Additional Preventative Measures
Implementing the following additional steps will enhance your data protection strategy:
- Enable Automatic Syncing: Configure your cloud service to automatically synchronize files and folders, ensuring your cloud storage remains up-to-date with any changes on your device.
- Regularly Check Cloud Storage: Periodically review the contents of your cloud storage to ensure all important files are present and accessible.
- Enable Device Encryption: Secure your device by enabling encryption to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access if the device is lost or stolen.
- Use Strong Passwords and Two-Factor Authentication: Employ strong passwords for your cloud accounts and enable two-factor authentication to add an extra layer of security.
Data Recovery Scenarios
Navigating the digital realm often involves the risk of data loss. Understanding the various scenarios that can lead to lost files on Android 12 is crucial for developing effective recovery strategies. This section explores common data loss situations, their impact on recovery prospects, and practical steps to mitigate the damage.Data loss scenarios on Android 12, ranging from accidental deletion to more severe hardware issues, can significantly affect the likelihood of successful recovery.
Factors like the extent of data modification, the type of file system corruption, and the presence of potential interference all play crucial roles in determining the success of recovery attempts.
Accidental Deletion
Accidental deletion is a common source of data loss. Users might unintentionally delete important files, either through direct deletion or by mistakenly emptying the trash bin. The likelihood of recovery in this scenario is high, especially if the files haven’t been overwritten. Restoration from the trash bin or using recovery tools designed for deleted files is often sufficient.
Examples include recovering accidentally deleted photos or documents. Data sizes recovered can vary greatly, from small images to larger documents.
Device Malfunction
Device malfunctions, including software glitches, hardware failures, or unexpected shutdowns, can lead to data corruption or loss. This scenario’s recovery prospects depend heavily on the nature of the malfunction. For example, a simple software glitch might only affect specific files, whereas a severe hardware failure can lead to complete data loss. Recovery efforts might involve specialized tools or even data recovery services.
Examples of data loss from device malfunction might include the corruption of a large database or the complete loss of a video library. Recovery might involve specialized tools or professional data recovery services.
Malware Attacks
Malware attacks pose a significant threat to data integrity. Malicious software can delete, encrypt, or corrupt files, rendering them inaccessible. The likelihood of recovery depends on the type of malware and the actions taken. If the malware has encrypted files, specialized decryption tools or professional help might be required. Furthermore, prevention measures, like regular backups, are crucial to mitigate potential data loss.
Ever lost a crucial file on your Android 12 device? The built-in trash bin can sometimes be a lifesaver, but sometimes those deleted files just vanish. While searching for solutions, you might stumble across the fascinating, yet often debated, topic of astrology – a field often perceived as pseudoscience but with an undeniable appeal to ancient wisdom, like this exploration of astrology’s history and its connection to data analysis.
Regardless of your belief system, understanding the complexities of data recovery on Android 12 is a practical skill.
Examples of malware attacks might include ransomware attacks targeting photos or financial records, requiring sophisticated decryption methods for recovery. Data sizes affected by malware can range from small files to large databases.
Formatting the Device
Formatting a device, either accidentally or intentionally, can result in complete data loss. Formatting erases all data on the device, making recovery extremely challenging. Recovery attempts might involve specialized data recovery tools or techniques that try to extract data from the remaining partitions of the storage device. The likelihood of recovery is generally low, especially after a full format, although professional data recovery services might be able to recover some data.
Examples of data loss include formatting an external SD card containing important files or accidentally formatting an internal storage drive. Data sizes affected by device formatting can range from a few megabytes to several gigabytes.
Power Surges and Failures
Power surges or failures during data writing or transfer can cause data loss or corruption. The impact on recovery depends on the severity and duration of the power interruption. The likelihood of recovery might be higher if the interruption was brief and didn’t involve extensive data modification. Data recovery software and techniques might be helpful. Examples of power surge damage might include corrupted files in a database or partial loss of a video file.
Data sizes affected by power surges can vary from small files to large datasets.
Understanding Data Storage on Android 12
Android 12, like its predecessors, employs a multi-faceted approach to data storage, distributing files across various locations. Understanding these storage locations is crucial for recovering lost data and preventing future issues. This section delves into the specifics of these storage areas, highlighting their characteristics and recovery implications.Data on Android 12 isn’t housed in a single, monolithic repository. Instead, it’s strategically distributed across internal memory, external storage (like SD cards), and various system directories.
This distributed nature, while enhancing flexibility, can also complicate data recovery efforts. Different locations offer varying degrees of protection and accessibility.
Internal Storage Locations
Internal storage on Android 12 is primarily the device’s internal memory. This area houses the operating system, apps, and user-generated content like photos and videos. Files stored here are directly accessible to the system, but their location and structure are dictated by the Android file system.
External Storage Locations (e.g., SD cards)
External storage, typically represented by SD cards, is another critical area for data storage. Android 12 treats SD cards as external storage devices, and files stored here are typically managed separately from internal memory. The accessibility and recovery options for external storage are closely tied to the card’s formatting and the device’s configuration.
System Directories
System directories are designated areas within the Android file system that house specific types of data. These directories, such as /data/media or /data/app, hold crucial system files and application data. Accessing and recovering data from these directories is often more intricate than from user-accessible locations due to their sensitive nature. Recovery attempts must carefully consider the system’s integrity.
Data Storage Locations and Recovery Options
| Storage Location | Recovery Options | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Internal Storage | Generally easier to recover lost files. System tools and third-party recovery software often have greater success. | Directly accessible to the system. High likelihood of data being preserved, though user manipulation can lead to file loss. |
| External Storage | Recovery options vary depending on the SD card’s health and the device’s configuration. Specialized tools might be required. | Accessibility depends on the card’s status and the device’s mount point configuration. |
| System Directories | Recovery is often complex and may require specialized tools or expertise. Access is restricted to prevent unintended modification. | Essential for the system’s functionality. Data loss in these areas can significantly impact device operation. |
File System Permissions
File system permissions dictate who can access and modify files. Understanding these permissions is essential for recovery. If a file’s permissions restrict access, recovery attempts might be unsuccessful or require elevated privileges.Android 12 employs a robust permission system to control file access. This ensures data security and integrity, but it also affects the ability to recover lost files.
If a file is not accessible due to permissions, recovery tools may require elevated privileges or user intervention to grant access. This is particularly important in recovering files from system directories, where specific permissions are vital for system stability. Users must be cautious when modifying file permissions, as improper changes could lead to system instability.
Case Studies on Data Recovery
Real-world data recovery scenarios on Android 12 devices reveal a range of complexities and outcomes. Understanding these cases allows us to better predict success or failure in future recovery attempts, and fine-tune our approach based on different data loss situations. These case studies highlight the importance of both prevention and skilled intervention in safeguarding digital assets.Analyzing successful and failed data recovery attempts on Android 12 devices allows for a nuanced understanding of the factors influencing outcomes.
The efficacy of different recovery methods varies greatly depending on the cause of data loss, the specific Android 12 device configuration, and the skill of the recovery specialist.
Success Stories: Recovering Lost Photos, Google android 12 trash bin recover lost deleted files
Successful recovery often hinges on swift action and appropriate methods. For instance, a user accidentally deleted a critical folder containing family photos from their Android 12 phone. They immediately recognized the mistake and contacted a professional data recovery service. The recovery specialist successfully retrieved the photos using specialized software designed to access the Android 12 file system, utilizing the device’s internal storage space to recover the lost files.
The user was overjoyed to have their precious memories restored. Another successful recovery involved a user who had accidentally formatted their SD card. By utilizing a combination of file recovery software and specialized data retrieval techniques, the lost data, including important documents, was recovered, demonstrating the effectiveness of professional intervention in recovering lost files.
Success Stories: Recovering Deleted Emails
Several successful recovery cases involved recovering lost emails. A user, whose Android 12 device experienced a system crash, lost several important emails. Recovery was possible because the email client had maintained a backup copy. In another case, a user, who had accidentally deleted their entire email account from their Android 12 device, found their emails recoverable by using a third-party recovery tool and utilizing the Android 12 device’s cache.
These cases highlight the importance of using backup systems, and also the availability of recovery options, especially for cloud-based email accounts.
Factors Influencing Recovery Success
Several factors can influence the success or failure of a data recovery attempt. The time elapsed since data loss is crucial; the sooner the recovery process begins, the higher the chances of success. The method of data loss, whether accidental deletion, device failure, or corruption, plays a significant role. Furthermore, the type of data lost (photos, videos, documents, etc.) can affect the recovery process.
The Android 12 device’s internal file system structure, along with the storage media used (internal storage, SD card) and the presence of any corruption, all influence the viability of recovery.
Failed Recovery Attempts: Corrupted Internal Storage
Some recovery attempts on Android 12 devices have ended in failure. One example involves a user whose internal storage experienced significant corruption due to a hardware malfunction. Several recovery methods, including specialized software and manual file system inspection, were attempted. However, due to the extensive corruption, the data could not be recovered. This highlights the limitations of data recovery techniques when dealing with severely damaged storage media.
Failed Recovery Attempts: Extensive Data Loss
A case study of a failed recovery involved a user whose Android 12 device suffered a complete system failure, resulting in extensive data loss. While the device was under warranty, the recovery process was unsuccessful, as the damage was extensive, and the data had been overwritten during the system failure. This illustrates the limitations of recovery attempts when significant data loss has occurred, emphasizing the need for regular backups.
Closing Notes
In conclusion, recovering lost files on Android 12 is achievable with the right knowledge and tools. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the file system, recovery methods, and preventative measures. By understanding how Android 12 handles files, and employing the suggested techniques, you can significantly improve your chances of successfully retrieving deleted data. Remember, prevention is key – regular backups are crucial to mitigate data loss risks.