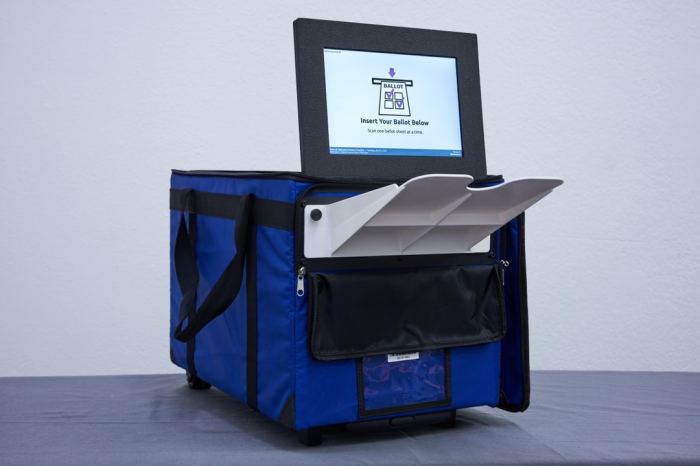
Election software maker remote access voting machine is a rapidly evolving field, promising to revolutionize how we cast our votes. This technology offers the potential for increased accessibility and enhanced security, but also presents new challenges. From the historical context of remote voting to the practical considerations of software implementation and security, this exploration delves into the complexities of this innovative approach to elections.
The core components of such a system, including software security protocols, voter registration and authentication procedures, and the user experience, are critically examined. This analysis considers the legal and regulatory frameworks surrounding remote voting, and explores the emerging trends in the field, providing insights into the future of this evolving technology.
Introduction to Remote Access Voting Machines: Election Software Maker Remote Access Voting Machine
Remote access voting, a paradigm shift in election administration, offers voters a new level of convenience and flexibility. This method of casting ballots expands the traditional in-person voting experience to include various digital platforms. It allows individuals to participate in elections regardless of location, time constraints, or physical limitations.This innovative approach to voting presents significant implications for election integrity and accessibility.
Understanding the historical context, different types of systems, and the potential benefits and drawbacks is crucial for informed public discourse. This exploration will delve into the fundamental concept, historical evolution, various types, and a comparative analysis with traditional voting methods.
Fundamental Concept of Remote Access Voting Machines
Remote access voting encompasses the use of electronic technologies to enable voters to cast ballots from a distance. This technology facilitates voting via the internet, mobile devices, or dedicated kiosks. It is designed to enhance voter participation and accessibility, particularly for individuals who face geographical barriers or other limitations.
Historical Overview of Remote Voting Technologies
Early forms of remote voting can be traced back to mail-in ballots. The introduction of online voting platforms marked a significant advancement in remote voting technology, though these systems faced challenges related to security and accessibility. Recent innovations focus on mobile voting apps, providing a more user-friendly and accessible experience.
Different Types of Remote Access Voting Systems
Various remote access voting systems exist, each employing unique technologies and approaches. Mail-in ballots, while a long-standing practice, are considered a form of remote voting. More recent developments include online voting portals, which allow voters to cast ballots via the internet, and mobile applications that provide voters with a more convenient method to cast their vote. The choice of system often depends on factors such as technological infrastructure, voter access, and security requirements.
Comparison of Remote Access Voting with Traditional In-Person Voting
Traditional in-person voting is a well-established practice with established procedures. Remote access voting, however, presents a more flexible alternative. It potentially broadens voter participation, especially for individuals with mobility issues or those living in remote areas. The key difference lies in the location of the voting process. In-person voting occurs at a designated polling place, while remote voting allows the voter to participate from a remote location.
Potential Benefits of Remote Access Voting
Remote access voting offers numerous potential advantages, including increased voter turnout, particularly among those who face barriers to traditional in-person voting. It can also enhance voter convenience, allowing individuals to vote at times and locations that suit their schedules. Improved accessibility is another key benefit, catering to voters with disabilities or those in geographically isolated areas.
Potential Risks and Challenges of Remote Access Voting
Despite its potential benefits, remote access voting presents certain challenges. Security concerns are paramount, and ensuring the integrity of the voting process is crucial. The potential for voter fraud and manipulation is a major concern, which needs careful consideration and robust security measures. Technical glitches and accessibility issues for voters unfamiliar with technology also need careful planning.
Comparison of Different Remote Voting Methods
| Voting Method | Description | Accessibility | Security | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mail-in Ballots | Ballots sent by mail to voters. | Relatively accessible, requires a mailing system. | Potentially vulnerable to tampering or loss in transit. | Moderate. |
| Online Voting | Voting via secure internet portals. | Accessible to those with internet access. | Requires robust security measures to prevent hacking and fraud. | High, due to infrastructure and security needs. |
| Mobile Voting | Voting through mobile applications. | Highly accessible to those with mobile devices and internet access. | Requires strong encryption and secure mobile infrastructure. | Moderate to High, depending on the platform. |
This table highlights the key differences between various remote voting methods, illustrating the trade-offs between accessibility, security, and cost.
Software for Remote Access Voting Machines
Remote access voting, while offering convenience and potentially increased accessibility, demands robust software to ensure the integrity and security of the entire process. This software must address critical aspects of voter authentication, data management, and security to prevent fraud and maintain public trust in the election outcome. The software must also consider the technical requirements and legal frameworks for remote voting in different jurisdictions.The core function of this software is to facilitate secure and verifiable remote voting.
This involves a complex interplay of authentication protocols, data encryption, and audit trails to protect against tampering and ensure the accuracy of the election results. Careful attention to detail in software design is paramount to maintaining the integrity of the entire remote voting process.
Election software makers are increasingly incorporating remote access into voting machines, which raises some interesting security questions. Speaking of interesting, did you know that the Ninja Foodi air fryer is on sale for $224, a discount of $106? Check out the deal here. Regardless of the latest kitchen gadget deals, the security implications of remote voting systems are a critical issue for election integrity.
Key Components of Election Software
This software encompasses several critical components that work together to facilitate a secure and reliable remote voting experience. These include modules for voter registration, authentication, ballot creation, ballot casting, and result tabulation. Each module is meticulously designed to safeguard sensitive information and ensure data integrity.
Security Protocols in Remote Access Voting Software
Robust security protocols are essential to protect against various threats in remote voting systems. These protocols include encryption of data transmitted between the voter’s device and the voting server, multi-factor authentication, and secure storage of voter data. Implementing these protocols is crucial for maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of the voting process.
Data Integrity and Confidentiality Procedures
Ensuring data integrity and confidentiality in remote voting requires a multi-layered approach. This involves using cryptographic hashing algorithms to verify the integrity of data, encrypting sensitive information, implementing access controls, and establishing audit trails to track all actions within the system. These procedures guarantee that the election results accurately reflect the will of the voters.
Voter Registration and Authentication
The software must incorporate a secure system for voter registration and authentication. This system should use robust methods to verify voter identity, ensuring that only eligible voters can participate in the election. This may include linking to state voter databases or implementing unique identifiers and multi-factor authentication.
Election software makers offering remote access voting machines raise some serious questions, especially considering the recent spotlight on government surveillance. Instances like the FBI’s surveillance following the Orlando shooting and the Senate Republicans’ push for National Security Letters, as detailed in this article , highlight the need for transparency and robust security measures in any system handling sensitive data.
This all underscores the critical need for independent audits and rigorous security protocols in election software, especially regarding remote access voting machines.
Software Features
| Feature | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| User Interface | Intuitive and user-friendly design for voters, administrators, and election officials. | Facilitates smooth and efficient use of the software by all parties. |
| Security Features | Encryption, multi-factor authentication, and access controls to protect data from unauthorized access and manipulation. | Crucial for safeguarding voter information and maintaining the integrity of the election. |
| Data Management | Secure storage, retrieval, and processing of voter information, ballot data, and election results. | Ensures the accurate and reliable handling of all data throughout the election process. |
| Audit Trails | Comprehensive records of all actions taken within the system, including voter activity and administrative tasks. | Provides a crucial mechanism for verification and accountability, enabling transparency and traceability. |
Comparison of Election Software Platforms
Different platforms offer varying functionalities and features. Some platforms may specialize in specific aspects of remote voting, such as ballot creation or voter authentication, while others provide a comprehensive suite of tools. A careful evaluation of the needs and requirements of the election is crucial in selecting the appropriate platform.
Implementation and Maintenance Steps
Implementing and maintaining remote voting software requires a phased approach. This includes careful planning, thorough testing, stakeholder training, and ongoing maintenance to ensure the system functions reliably and securely.
Security Considerations in Remote Access Voting
Remote access voting, while offering potential benefits like increased accessibility, introduces unique security challenges. Protecting the integrity of the election process is paramount, and understanding these vulnerabilities is crucial for building robust systems. The security of remote voting hinges on the implementation of strong safeguards and rigorous testing throughout the development lifecycle.Security in remote voting systems is not merely about preventing hacking attempts; it’s about ensuring the entire process, from voter authentication to vote tabulation, is secure and trustworthy.
This requires a multifaceted approach that addresses potential vulnerabilities at each stage of the voting process.
Vulnerabilities of Remote Access Voting Systems
Remote access voting systems, due to their reliance on networked infrastructure, are susceptible to a range of cyberattacks. Compromised servers, malicious software, and social engineering tactics can all jeopardize the security of the entire system. Weak authentication protocols, insufficient encryption, and inadequate access controls can also leave the system vulnerable. Moreover, a lack of comprehensive testing can introduce unforeseen vulnerabilities.
Security Measures to Protect Against Cyberattacks
Robust security measures are essential to mitigate the risks associated with remote access voting. These measures encompass the entire system, from the voter interface to the vote counting process. Implementing strong encryption, secure communication channels, and multi-factor authentication is crucial. Regular penetration testing and vulnerability assessments are vital for identifying and addressing potential weaknesses.
Potential Vulnerabilities in Remote Voting Software
Potential vulnerabilities in remote voting software can range from insecure coding practices to flaws in the system’s architecture. These vulnerabilities can be exploited to manipulate votes, disrupt the voting process, or gain unauthorized access to sensitive voter information. For instance, insufficient input validation can lead to injection attacks, while poorly designed authentication mechanisms can be easily bypassed. In addition, insufficient logging and monitoring can make it difficult to detect and respond to malicious activities.
Importance of Encryption and Secure Communication Channels
Encryption is fundamental to secure remote voting. End-to-end encryption of communication channels ensures that only authorized parties can access voter data. Using secure protocols like TLS/SSL is vital for encrypting data transmitted between the voter’s device and the voting server. This prevents eavesdropping and tampering with transmitted data. Furthermore, encryption of stored voter data protects against unauthorized access and modification.
Verifying Voter Identity During Remote Voting
Robust voter identification is crucial to prevent fraudulent voting. Multi-factor authentication, incorporating biometrics or one-time passwords, can significantly enhance the verification process. This approach makes it more difficult for unauthorized individuals to impersonate voters. Maintaining voter registration databases securely and implementing a strong voter authentication system are critical components of this process.
Auditing and Monitoring Remote Voting Activities
Auditing and monitoring are critical for detecting anomalies and ensuring transparency. Comprehensive logs of all voting activities, including user authentication attempts, vote submissions, and system errors, provide valuable insights into the system’s behavior. Regular reviews of these logs can reveal potential security breaches or irregularities. Transparent auditing mechanisms help to build public trust in the integrity of the election.
Summary of Security Protocols and Their Effectiveness
| Security Protocol | Effectiveness | Description |
|---|---|---|
| TLS/SSL | High | Provides secure communication channels by encrypting data transmitted between the voter’s device and the voting server. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication | High | Adds an extra layer of security by requiring multiple forms of verification, such as passwords and biometric data. |
| End-to-End Encryption | High | Encrypts data from the voter’s device to the voting server, ensuring only authorized parties can access it. |
| Regular Penetration Testing | High | Simulates real-world attacks to identify and address vulnerabilities in the system. |
| Robust Voter Registration Database | Medium | Maintains a secure database of registered voters, minimizing the risk of voter impersonation. |
Voter Experience and Usability

Remote access voting, while offering significant advantages, hinges on a seamless and user-friendly experience. A well-designed interface and clear instructions are paramount to ensuring voter confidence and participation. This section dives into the crucial aspects of voter experience, focusing on usability, accessibility, and the overall voting process.
User Interface Design for Remote Voting
A user-friendly interface is essential for remote voting. The design should prioritize clarity, intuitive navigation, and minimal steps. Visual cues, such as progress indicators and tooltips, should guide voters through the process. Clear instructions and concise language should be employed to avoid confusion. Form fields should be self-, with appropriate input validation to prevent errors.
The interface should also adapt to different screen sizes and devices, ensuring a consistent experience across various platforms. For example, a responsive design would be crucial for ensuring compatibility with smartphones, tablets, and desktop computers.
Accessibility Features for Voters with Disabilities
Ensuring accessibility is critical for inclusivity. The remote voting system should comply with accessibility standards, such as WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines). This includes features like adjustable font sizes, screen reader compatibility, and keyboard navigation. Alternative text descriptions for images and interactive elements are necessary. Captions for audio and video components, if present, are also vital.
Furthermore, options for verbal or text-based assistance should be provided. Color contrast and alternative input methods, such as voice recognition, should also be considered.
Steps Involved in Using Remote Access Voting Machines
The voting process should be straightforward and well-documented. Voters should be guided through each step with clear instructions and visual cues. Detailed steps, illustrated by visual aids, will help voters navigate the process confidently. A step-by-step guide would greatly assist voters in comprehending each phase of the remote voting process. Simple language and illustrations will further aid in the comprehension of the process.
Importance of Voter Education and Training Materials
Voter education and training materials are crucial to ensure a smooth transition to remote voting. Clear and concise tutorials, FAQs, and instructional videos are vital. These materials should be readily available and accessible on the system’s website or through other channels. Detailed instructions should be provided on how to register, log in, and cast their vote. The training materials should address common concerns and questions that voters might have.
Examples of User-Friendly Interfaces for Remote Voting Systems
Numerous user-friendly interfaces are available for remote voting systems. One example is a system that uses a visually appealing design with clear icons and concise text. Another approach is a system that provides step-by-step instructions with interactive elements to guide voters. The use of progress bars and tooltips will help voters track their progress and understand each step of the process.
A good example of an interface would have a simple, clean layout with large buttons and clear text. Simple language, intuitive navigation, and a clear visual representation of each step are crucial elements.
Strategies for Addressing Potential User Issues and Concerns
Strategies for addressing potential user issues and concerns should include proactive measures. Providing multiple channels of support, such as phone, email, and live chat, is crucial. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) and troubleshooting guides should be readily available. A dedicated help desk or support team will aid voters in navigating any challenges. A robust system for monitoring user activity and detecting potential problems will ensure quick resolution of any issues.
Addressing potential issues proactively, through a robust help system and user feedback mechanisms, will greatly contribute to voter satisfaction.
Election software makers are increasingly offering remote access voting machines, which raises interesting security questions. For instance, how does this new technology affect voter privacy and data security? A related concern, especially with the proliferation of location tracking, is managing your digital footprint, like clearing your Google Maps location history timeline. Thankfully, there are ways to do this easily, check out this guide on deleting your Google Maps location history timeline.
Ultimately, secure remote voting hinges on robust software and transparent protocols, ensuring trust in the election process.
Table: Steps for Using a Remote Voting System
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| Registration | Create an account with the system, providing necessary information. |
| Login | Enter credentials to access the voting platform. |
| Voting | Select candidates and cast your ballot securely. |
| Confirmation | Review and confirm your ballot before submitting. |
Legal and Regulatory Frameworks
Navigating the legal landscape surrounding remote voting is crucial for the integrity and security of elections. Different jurisdictions have varying regulations, and a deep understanding of these legal frameworks is essential for election software developers and administrators to ensure compliance. Failure to adhere to these rules could lead to significant penalties and jeopardize the legitimacy of the election process.A robust legal framework for remote voting must address crucial elements, including voter identification, authentication, ballot secrecy, and the security of the entire voting system.
This ensures that remote voting is as secure and trustworthy as traditional in-person voting, fostering public confidence in the election process.
Legal Requirements for Remote Voting
Establishing clear legal requirements for remote voting is vital to maintaining public trust and the integrity of the election process. These regulations typically address voter registration, authentication, ballot security, and the use of secure communication channels. Different jurisdictions often have specific requirements concerning voter verification methods, which can vary widely. Strict adherence to these standards is critical to avoid legal challenges and maintain the integrity of the electoral process.
Laws Governing Election Software
Regulations governing election software are designed to ensure the reliability, security, and transparency of the voting process. These laws often mandate that the software undergo rigorous testing and certification processes. Furthermore, they may specify requirements for the storage, access, and handling of sensitive voter data. Software developers must be acutely aware of these regulations and must adhere to strict compliance standards to maintain the security and integrity of the election.
Standards and Guidelines for Secure Remote Voting
Ensuring secure remote voting requires adhering to stringent standards and guidelines. These guidelines often involve encryption protocols for data transmission, robust authentication mechanisms for voter identification, and comprehensive audit trails to track all actions within the system. Specific industry standards and best practices in cryptography and security are also often incorporated into the legal frameworks.
Examples of Jurisdictions’ Policies on Remote Voting
Different jurisdictions have adopted diverse approaches to remote voting, reflecting varying political and technological considerations. Some jurisdictions may permit remote voting only for specific demographics or under certain conditions, while others have established comprehensive policies covering all aspects of the process. For example, some states might require a higher level of voter authentication compared to others. Understanding these variations is critical for compliance.
Procedures for Compliance with Legal Requirements, Election software maker remote access voting machine
Establishing and adhering to specific procedures for compliance with legal requirements is crucial. This involves meticulously documenting every step of the software development process, ensuring compliance with all applicable regulations, and maintaining detailed records of all system updates and changes. These procedures must be clearly Artikeld, understood, and consistently followed by all stakeholders involved in the election process.
Legal Implications of Using Remote Access Voting
Using remote access voting machines carries legal implications. These implications must be thoroughly assessed and addressed by election authorities and software developers. Potentially, these could include liabilities related to security breaches, data privacy violations, and allegations of voter fraud. Careful planning and proactive measures are necessary to mitigate these risks.
Table of Legal Frameworks and Requirements
| Country/Region | Key Legal Framework | Voter Authentication | Data Security |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | State election laws | Varying requirements, including photo ID | Specific regulations regarding data storage and handling |
| European Union | EU data protection regulations | Strong emphasis on data privacy | Strict compliance with GDPR and other relevant regulations |
| Canada | Provincial election laws | Provincial-specific requirements for voter identification | Provincial data protection regulations |
| Australia | Federal and state election laws | Strict voter identification and verification | National security standards for election data |
Emerging Trends and Future Directions

Remote voting, once a niche application, is rapidly evolving. New technologies and innovative approaches are transforming how elections are conducted, offering potential improvements in accessibility, security, and voter participation. This shift necessitates a careful understanding of the emerging trends and potential future developments in election software.
Emerging Trends in Remote Voting Technologies
Several key trends are shaping the future of remote voting. Blockchain technology, for example, is being explored for enhancing the security and transparency of election processes. Biometric authentication is also gaining traction, offering a more secure way to verify voter identity. The use of mobile-first platforms and innovative user interfaces is enabling more convenient and user-friendly remote voting experiences.
These trends, combined with the increasing availability of high-speed internet access, are making remote voting more accessible to a broader population.
Innovative Approaches to Remote Voting
One innovative approach is the development of secure, online voting platforms that leverage advanced encryption techniques. These platforms often integrate with existing voter registration databases, streamlining the process and reducing the potential for fraud. Another example is the use of mobile applications for remote voting, enabling voters to cast their ballots from anywhere with a smartphone or tablet.
Furthermore, some jurisdictions are experimenting with hybrid models that combine in-person and remote voting options, catering to diverse needs and preferences.
Potential Impact of New Technologies on Election Software
Advancements in technology will necessitate modifications to election software. Software will need to incorporate robust security measures to protect against cyber threats and ensure the integrity of the voting process. New technologies will also demand improvements in user interfaces, making remote voting accessible and intuitive for all voters. Furthermore, the integration of new authentication methods like biometrics will require changes in existing voter registration and authentication protocols.
Advancements in Technology to Improve Remote Voting Systems
Advancements in technology can dramatically improve remote voting systems. Increased bandwidth and faster internet connections can improve the speed and reliability of remote voting processes. More sophisticated fraud detection algorithms can identify and mitigate potential irregularities. Additionally, enhanced encryption protocols can bolster the security of remote voting systems, preventing unauthorized access and manipulation.
Future Developments in Election Software
Future election software will likely incorporate artificial intelligence (AI) for tasks like detecting anomalies and preventing fraud. This technology could analyze voter patterns and identify potential threats in real-time. Moreover, the development of more user-friendly interfaces tailored for specific demographics will improve voter experience and engagement.
Implications of These Developments for Election Administration
The advancements in remote voting technology will require significant changes in election administration practices. Training programs for election officials will be crucial to ensure proper implementation and operation of new systems. Furthermore, the adoption of new technologies will necessitate adjustments to existing legal frameworks and regulations governing elections.
Potential Future Advancements and Benefits
| Potential Future Advancement | Potential Benefit |
|---|---|
| Blockchain-based voting systems | Enhanced security and transparency, reduced risk of fraud |
| Biometric authentication | Increased voter verification accuracy, enhanced security |
| AI-powered fraud detection | Real-time identification of potential irregularities, reduced risk of manipulation |
| Mobile-first voting platforms | Increased accessibility and convenience for voters, broader participation |
| Hybrid in-person/remote voting models | Flexibility for voters, enhanced voter participation |
Final Review
In conclusion, remote access voting, facilitated by specialized software, offers exciting possibilities for broader voter participation. However, navigating the complexities of security, usability, and legal compliance is crucial for successful implementation. This comprehensive overview highlights the multifaceted challenges and opportunities inherent in this rapidly advancing technology.