Curved displays practical or used just looks? This exploration dives deep into the world of curved screens, examining their design considerations, user experience, practical applications, aesthetic impact, technical limitations, and future trends. Are they more than just a pretty face, or do they offer tangible benefits beyond the visual appeal? Let’s unpack it.
From gaming to general use, we’ll compare curved displays to traditional flat screens, analyzing their strengths and weaknesses across various factors like viewing angles and visual immersion. We’ll also consider user feedback, ergonomic concerns, and specific use cases to determine if the curve is worth the hype.
Display Design Considerations
Curved displays have captivated the tech world, promising immersive experiences. While the initial novelty has faded, the underlying design considerations continue to shape the evolution of these screens. This exploration delves into the intricacies of curved displays, comparing them to traditional flat screens and analyzing their applications and challenges.Curved displays offer a unique visual experience, particularly in scenarios where immersion and user interaction are crucial.
Their shape can be tailored to enhance the user’s perception of depth and space, making them ideal for various applications, including gaming, media consumption, and general use. Understanding the nuances of their design and manufacturing is crucial for evaluating their true potential.
Types of Curved Displays
Curved displays come in various forms, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The most common types include displays with gentle curves, often found in consumer electronics, and those with more pronounced curvatures, frequently seen in specialized applications like automotive displays. The gentle curves often provide a more natural viewing experience, while the pronounced curves may offer more extreme immersion, but potentially at the cost of visual distortion.
Understanding these differences is crucial for choosing the right type of curved display for a particular use case.
Physical Design Characteristics
Curved displays differ significantly from flat displays in their physical design. The curvature of the screen affects the way light is reflected and projected, leading to varying viewing angles and visual experiences. Flat displays, with their uniform surface, provide a consistent viewing experience across all angles. Curved displays, however, can enhance the perception of depth and immersion, but this is often at the cost of potential distortion in peripheral vision.
The manufacturing processes for curved displays are also more complex than those for flat displays, adding to the cost implications.
Applications and Benefits
Curved displays hold potential for various applications. In gaming, they can create a more immersive environment, drawing the user into the game’s world. Media consumption, like watching movies or playing videos, can benefit from the enhanced depth and field of view. Even in general use, the curved shape can contribute to a more visually engaging experience. For example, curved monitors in offices or homes can subtly guide the user’s gaze and enhance visual perception.
Honestly, are curved displays truly practical, or are they just a stylish gimmick? While some argue their aesthetic appeal is undeniable, the utility of a curved screen in everyday use is often debated. It’s a similar debate to the one surrounding the recent Twitter lawsuit filed by Ken Paxton, the Texas AG, investigating content moderation practices. Are these legal battles genuinely about protecting free speech or are they a distraction?
Ultimately, whether a curved display is a practical investment or just a flashy purchase depends on individual needs and preferences. Ultimately, the twitter ken paxton texas ag lawsuit content moderation probe highlights how the tech industry faces scrutiny, just like the value of curved screens.
However, the visual effects are not always universally appreciated, and the cost may not justify the perceived benefits in all applications.
Manufacturing Challenges and Cost Implications
Manufacturing curved displays presents unique challenges compared to flat displays. The curved shape necessitates specialized manufacturing techniques and materials. The increased complexity in production often translates to higher costs. Furthermore, maintaining consistency in curvature across large production runs can be challenging. Durability is also a concern, as the curved shape can potentially make the display more susceptible to damage.
The initial investment in equipment and expertise can significantly impact the overall cost, impacting the affordability for some users.
Comparison of Curved and Flat Displays
| Feature | Curved Display | Flat Display |
|---|---|---|
| Viewing Angle | May offer a more focused, immersive viewing experience from a central point, potentially with some distortion at the edges. | Consistent viewing experience across all angles. |
| Resolution | Resolution is similar to flat displays of the same size. | Resolution is similar to curved displays of the same size. |
| Visual Immersion | Potentially higher visual immersion due to the curved shape, but not universally appreciated. | Standard visual experience, not typically designed for extreme immersion. |
User Experience and Perception
Curved displays are no longer a novelty; they’re becoming increasingly prevalent in various devices. Understanding how this curved design impacts user experience and perception is crucial for designers and manufacturers. This section delves into the psychological and ergonomic considerations associated with curved screens, comparing them to their flat counterparts.The curvature of a display subtly alters the user’s visual experience, influencing not only how they perceive the screen but also their overall engagement with the device.
This effect is multifaceted, involving both visual comfort and psychological responses to the design element. Beyond aesthetics, understanding the impact of curvature on user engagement and perceived usability is essential.
Impact on Visual Perception
The curved shape of a display can alter the perceived size and depth of the content. Users might experience a sense of immersion or a more enveloping visual field, particularly with wider curved displays. This is often compared to the experience of watching a movie in a curved cinema screen. The curvature can also affect the perceived distance to the content, leading to a more engaging and immersive experience.
Honestly, curved displays – are they truly practical, or just a visual gimmick? I’ve been pondering this lately, especially since I’ve been really enjoying my new DJI Air 2S. DJI Air 2S is the drone landscape photographers should buy for incredible shots, and the compact size is a game-changer. Maybe curved displays are a bit of a “look” thing, and the practical benefits are still up in the air.
Still, I’m not sure how much of a practical difference it really makes.
Conversely, the curvature can introduce distortions or inconsistencies in the display’s appearance, depending on the viewing angle and content.
Psychological Impact on User Engagement
Curved screens have been linked to increased user engagement in some studies. The immersive nature of the curved design can encourage users to spend more time interacting with the display. This is especially true in applications like gaming, where the sense of being enveloped in the virtual world can be a significant factor. However, this increased engagement is not universally positive, and some users might find the curvature distracting or overwhelming.
User Feedback Comparison
User feedback on curved versus flat displays varies significantly across different applications and user groups. In gaming, many users report a more immersive and engaging experience with curved displays, often describing a sense of being closer to the action. In productivity applications, however, the feedback is more mixed. Some users appreciate the curved design for its visual appeal and perceived spaciousness, while others find it distracting or problematic for tasks requiring precise detail.
Ergonomic Considerations
Potential ergonomic considerations with curved displays relate to how the user interacts with the device. For instance, the curvature might affect the natural posture of the user. Sustained use of a curved display may lead to neck strain or discomfort if not used in conjunction with ergonomic accessories. Additionally, the curve may affect the visual alignment of the display with the user’s eyes.
The user should be positioned at an appropriate distance to minimize visual strain and maintain proper posture.
Perceived Advantages and Disadvantages of Curved Displays
| Aspect | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|
| Immersion | Users report increased engagement and a sense of being enveloped in the content, particularly in gaming and entertainment. | Distraction or discomfort in some users, especially those performing tasks requiring precise detail or fine-grained work. |
| Visual Appeal | Aesthetically pleasing design, perceived spaciousness, and enhanced visual appeal compared to flat screens. | Potential for visual distortion or inconsistencies depending on the viewing angle and content. |
| Ergonomics | Potential for improved visual comfort and posture if used correctly with ergonomic support. | Potential for neck strain or discomfort with sustained use if not used in conjunction with ergonomic adjustments. |
| Engagement | Increased user engagement in some applications, especially those requiring immersive experiences like gaming. | Potential for reduced efficiency in productivity tasks that require high precision. |
Practical Applications and Use Cases: Curved Displays Practical Or Used Just Looks
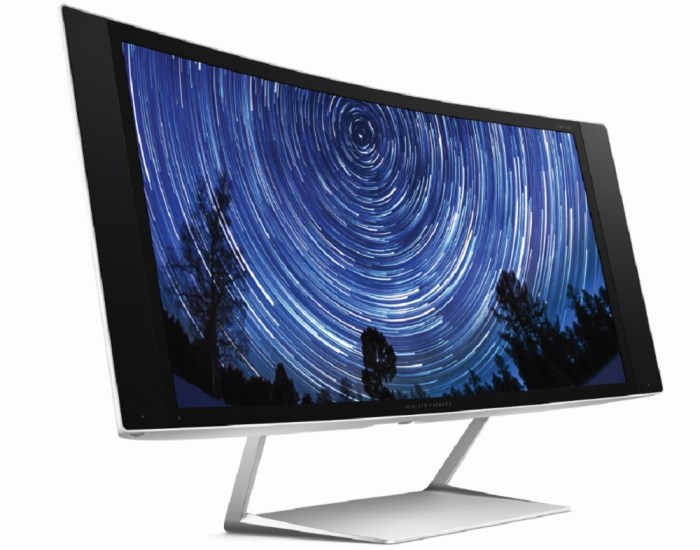

Beyond the captivating curves and sleek aesthetics, curved displays offer a wealth of practical advantages in various industries. Their unique form factor allows for a more immersive and user-friendly experience, making them ideal for specific applications that go beyond mere visual appeal. This section delves into the real-world applications of curved displays, examining their use in automotive, healthcare, and entertainment sectors.Curved displays, unlike their flat counterparts, can adapt to the natural curvature of the human eye and the user’s field of view.
This results in a more comfortable and engaging interaction. By carefully designing the curve, manufacturers can enhance the user’s immersion and comprehension of information presented on the display. This approach can translate into a more intuitive and enjoyable user experience in diverse applications.
Automotive Applications
Curved displays in vehicles are increasingly common. Their seamless integration into dashboards and infotainment systems allows for a more intuitive and visually appealing presentation of driving-related information. Drivers can access vital data like speed, navigation directions, and entertainment options with greater clarity and ease of use. The curves can also contribute to a more ergonomic and comfortable driving experience.
For example, a curved display in a car’s dashboard can provide a more natural and engaging view of navigation data, compared to a series of flat screens, making it easier for the driver to process information while keeping their eyes on the road.
Healthcare Applications
In healthcare settings, curved displays offer advantages for medical imaging and patient monitoring. Curved screens can provide a more comprehensive view of medical data, facilitating better diagnostics and treatment plans. For instance, a curved display can be used to display a patient’s vital signs and medical history in a holistic way, making it easier for doctors to monitor and interpret the data.
A larger curved display can accommodate a more comprehensive overview of a patient’s medical records, improving efficiency and accuracy.
Entertainment Applications
Curved displays enhance the immersive quality of entertainment experiences. In home theaters, curved screens provide a more cinematic viewing experience, mimicking the wider field of view that is often associated with large movie theaters. The curved shape allows for a more expansive visual field, creating a sense of greater immersion in movies and games. Game consoles and virtual reality (VR) headsets are examples of entertainment devices that are already using curved displays to enhance user experience.
Potential Scenarios for Curved Displays
A curved display could offer significant advantages in several situations:
- Immersive Gaming Experiences: A curved display can provide a more realistic and engaging gaming experience by creating a wider field of view and a more natural visual perspective. This can significantly impact the user’s experience, as they feel more enveloped in the game environment.
- Interactive Digital Signage: In public spaces, a curved display can create a more engaging and immersive experience for viewers, displaying information in a more visually appealing and dynamic way. This could be particularly effective in museums or interactive kiosks.
- Architectural Design Visualization: Architects and designers can utilize curved displays to showcase their designs in a realistic and immersive manner. The curvature of the display can better represent the three-dimensional nature of the project and facilitate easier interaction with the design.
- Retail Environments: Curved displays can create a more engaging and immersive shopping experience for customers. They can showcase products from different angles and offer a more interactive and captivating presentation.
Industries Likely to Adopt Curved Displays
The adoption of curved displays is likely to be strongest in sectors where visual immersion and user experience are paramount:
- Automotive Industry: The automotive industry is rapidly integrating curved displays for enhanced driver information systems and infotainment.
- Entertainment Industry: The entertainment industry benefits from curved displays’ ability to improve viewing experiences for home theaters and gaming systems.
- Healthcare Industry: Medical imaging and patient monitoring systems are increasingly utilizing curved displays to improve data visualization and clinical workflows.
- Retail Industry: Retailers are adopting curved displays to create engaging and immersive shopping experiences.
Aesthetic Considerations

Curved displays are no longer a futuristic novelty; they’re increasingly integrated into various products and spaces. Their aesthetic impact extends beyond simple visual appeal, influencing the overall design language and user experience. Understanding how curvature shapes perception and how it’s effectively implemented is crucial for designers aiming to create compelling and engaging products.Curved displays introduce a dynamic element to product design.
The organic curves can soften sharp edges, creating a more welcoming and user-friendly interface. Furthermore, the curvature can be used strategically to direct the user’s gaze and highlight specific areas within the interface, thus enhancing usability. This interplay between form and function is critical in contemporary design.
Impact on Product Design
The curvature of a display significantly alters the perceived size and shape of the screen. A curved display can make a smaller screen appear larger, and its flowing contours can seamlessly integrate into a product’s design. For example, a curved smartphone screen can give the impression of a more immersive experience, drawing the user into the content. Conversely, a curved display on a large screen can visually expand the viewing area, making the entire space appear more engaging.
Successful Design Implementations
Numerous examples showcase the successful integration of curved displays. Samsung’s curved monitors, for instance, offer a wider viewing angle and a more immersive experience, particularly useful for multitasking. In automotive design, curved displays in dashboards can seamlessly integrate with the car’s overall aesthetic, creating a cohesive and sophisticated design language. Moreover, curved TVs can create a more immersive home theater experience, drawing the viewer into the content.
Impact of Curvature on Perceived Size and Shape
The curvature of a display affects how its size and shape are perceived. A curved display can visually expand the apparent area, making a smaller screen seem larger, a key consideration in devices with limited space. The curvature can also influence the perceived depth and three-dimensionality of the display, further enhancing its aesthetic impact.
Role of Curvature in Enhancing Visual Appeal
Curvature can significantly enhance the visual appeal of a device or environment. The flowing lines and smooth transitions of a curved display can create a more organic and inviting design, as opposed to the angular, rigid aesthetics of traditional flat displays. This visual fluidity can subtly influence the user’s perception of the product or space, creating a more engaging experience.
Different Design Styles Incorporating Curved Displays
| Design Style | Description | Example Image |
|---|---|---|
| Minimalist | Sleek, uncluttered design with clean lines and a focus on the display’s curvature as the primary aesthetic element. | (Imagine a smartphone with a subtle, elegant curve, with minimal bezels, showcasing the curvature of the screen as the key design element. The background could be a neutral color, highlighting the curvature.) |
| Organic | Embrace natural forms and flowing lines, incorporating the curvature of the display to create a harmonious and aesthetically pleasing design. | (Envision a tablet with a smooth, rounded back, featuring a curved display seamlessly integrated into the design. The materials used might be soft-touch or have a matte finish, emphasizing the organic form.) |
| Futuristic | Bold, innovative designs that use the curvature of the display as a key element to create a modern and futuristic impression. | (Picture a gaming console with a highly curved display and vibrant colors, with the curvature emphasizing a futuristic design language. The materials could be glossy or reflective, highlighting the advanced aesthetic.) |
Technical Specifications and Limitations
Curved displays, while visually appealing, come with a set of unique technical challenges. Understanding these specifications and limitations is crucial for anyone considering incorporating them into their designs or products. From resolution and refresh rate to manufacturing complexities, the journey into the world of curved displays involves a multifaceted approach.Curved displays are not simply flat screens bent into a shape.
Their manufacturing and performance characteristics differ significantly from their flat counterparts, introducing specific hurdles in terms of image quality, uniformity, and overall cost-effectiveness. These technical constraints must be carefully evaluated alongside the aesthetic advantages to ensure a well-rounded and practical design.
Resolution and Refresh Rate
Curved displays, like their flat counterparts, utilize pixels to create images. Resolution, measured in pixels per inch (PPI), dictates the level of detail visible on the screen. Higher resolution translates to sharper images and greater visual clarity. Refresh rate, measured in Hertz (Hz), indicates how many times per second the screen’s image is updated. A higher refresh rate reduces motion blur, especially important for gaming and video playback.
The relationship between these two factors plays a critical role in the overall user experience.
Response Time
Response time, measured in milliseconds (ms), is the time it takes for a pixel to change from one color to another. A faster response time is vital for smooth image transitions, reducing motion blur and ghosting effects, particularly in fast-paced content like action movies or video games. Lower response times are generally preferable, though they often come with trade-offs in other technical specifications.
Honestly, are curved displays truly practical, or are they just a cool aesthetic? It’s a question that’s been debated for years. Meanwhile, companies like Lyft are focusing on more sustainable practices, like using recycled redwood materials for their batteries in their e-bikes and scooters, which is a fantastic step forward in the green tech revolution. lyft redwood materials battery recycle ebike scooter initiatives like this are inspiring.
Regardless, I still find myself wondering if the curves on those new phones are genuinely better than the standard flat design or just a trendy gimmick.
Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing process for curved displays differs significantly from that of flat displays. Producing a curved screen involves more complex and often more costly procedures. For instance, the glass substrate for curved displays needs to be meticulously shaped and held to precise tolerances during the production phase. The production processes require specialized equipment and techniques to ensure consistency across the entire display surface, leading to higher manufacturing costs.
Comparison with Flat Displays
Flat displays employ simpler manufacturing techniques. The glass substrates are easier to produce and manipulate, resulting in lower production costs. The manufacturing process for flat screens typically involves simpler steps and less complex equipment. This difference in production processes often translates into cost differences between the two types of displays.
Future Advancements
Advancements in display technology hold the promise of addressing some of the current limitations of curved displays. Improvements in material science and manufacturing techniques could potentially reduce manufacturing costs and improve the uniformity of curved displays. Furthermore, advancements in flexible display technology could lead to even more innovative and customizable curved displays in the future.
Technical Specifications Table
| Display Type | Resolution | Refresh Rate | Response Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| OLED Curved | 4K (3840 x 2160) | 120Hz | 0.1ms |
| LCD Curved | 1440p (2560 x 1440) | 144Hz | 4ms |
| Micro-LED Curved | 8K (7680 x 4320) | 240Hz | 0.01ms |
Market Trends and Future Prospects
Curved displays, once a novelty, are now finding their place in the broader technological landscape. Their adoption rate is influenced by various factors, including evolving consumer preferences, technological advancements, and market competition. Understanding these trends is crucial for predicting the future of curved displays and their impact on different sectors.
Current Market Trends
The current market for curved displays shows a mixed trend. While adoption hasn’t reached the explosive levels some initially predicted, a consistent, albeit slow, growth continues in specific segments. This suggests a gradual integration rather than a complete rejection of the technology. Factors driving this ongoing interest include the desire for immersive experiences, particularly in gaming and entertainment, and the ability of curved screens to enhance visual comfort in certain viewing scenarios.
Factors Driving Interest
Several factors are fueling the sustained interest in curved displays. Immersive experiences are a key driver, as curved screens can create a more enveloping and realistic visual field, particularly in gaming and virtual reality applications. Additionally, some users find curved screens more comfortable for prolonged viewing, especially in environments where the screen is positioned at an angle. These benefits are particularly attractive to specific user demographics, including gamers and those who frequently use their devices for entertainment.
Future Potential
The future of curved displays likely lies in niche applications and specialized markets. While mass market adoption might not be imminent, their integration into specific industries is possible. Consider curved displays in automotive dashboards, for instance, or interactive retail displays. Their use in medical imaging or specialized scientific instruments is also a plausible future development.
Popularity Comparison
Comparing curved and flat displays reveals a fascinating dynamic across demographics. Younger demographics, particularly those heavily involved in gaming, show a stronger preference for curved displays. They are drawn to the enhanced immersion and visual comfort they provide. Older demographics, however, often favor flat displays, prioritizing familiarity and perceived ease of use. This suggests a strong correlation between user experience and specific user demographics.
Growth Projections, Curved displays practical or used just looks
| Region | Projected Growth | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|
| North America | Moderate growth (5-7% CAGR) | Strong gaming market, increasing demand for immersive experiences. |
| Asia Pacific | Significant growth (8-10% CAGR) | Rising disposable incomes, increasing smartphone and display penetration. |
| Europe | Steady growth (3-5% CAGR) | Established consumer base, increasing demand for high-end displays. |
| Latin America | Moderate growth (4-6% CAGR) | Growing middle class, increasing adoption of technology. |
The table above illustrates projected growth for curved displays in different regions. Growth rates are expected to vary, driven by factors specific to each region, such as economic conditions, technological adoption rates, and consumer preferences. These projections are based on current market trends and expert estimates.
Last Point
In conclusion, the question of curved displays practical or used just looks depends largely on individual needs and priorities. While aesthetics play a role, the practical benefits, such as enhanced immersion and ergonomics in specific applications, can’t be ignored. The future of curved displays hinges on ongoing advancements in technology and market demand, making it a compelling area to watch.