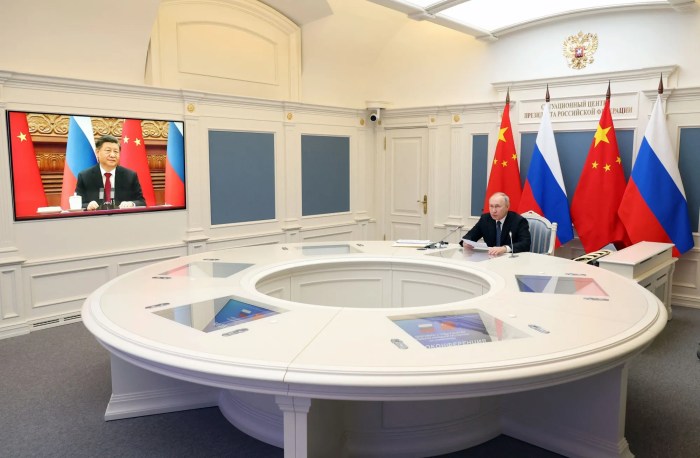
Commerce departments new rule hacking tools china russia is sparking global debate. This new regulation aims to address the growing threat of malicious hacking tools originating from China and Russia, impacting international commerce. The rule Artikels specific provisions targeting these tools, intending to enhance trade security and deter malicious actors. This complex issue has the potential to reshape global trade relationships and spur innovation in cybersecurity.
The new rule, a significant development in international trade, delves into the intricacies of hacking tools used by both China and Russia. It not only describes the tools themselves but also analyzes their potential applications and misuses. The document is a comprehensive study of the implications for both countries, including potential disruptions to supply chains and the impact on specific sectors like technology and manufacturing.
Implications for China and Russia

The recent implementation of new commerce regulations targeting hacking tools originating from China and Russia marks a significant shift in global trade dynamics. This proactive measure aims to mitigate the risks associated with malicious cyber activity, potentially impacting both nations’ economic and geopolitical landscapes. The response and adaptation strategies of these two major powers will be crucial in determining the long-term effects.The new rules, while ostensibly focused on countering malicious cyber activity, are likely to have cascading effects on legitimate trade relationships and technological advancement.
The potential for misinterpretation and unintended consequences underscores the need for careful consideration and clear communication between the involved parties.
Potential Impacts on Chinese Commerce
China’s robust technological sector and manufacturing base are heavily reliant on international trade. Any restrictions on the export or import of hacking tools, especially if broadly defined, could significantly impact specific industries. The Chinese government might respond by implementing alternative strategies to maintain its technological competitiveness, including developing domestic solutions and fostering partnerships with countries that are not subject to the same restrictions.
This could potentially lead to a shift in the global technological landscape, with long-term consequences for innovation and trade.
Potential Impacts on Russian Commerce
Russia’s economy is more closely tied to its energy sector and defense industry, making its response potentially different. Russia might seek alternative markets and partners for its defense and technology sectors, potentially leading to more strategic alliances with countries less affected by these restrictions. The impact on Russia’s technological capabilities could be significant, especially in the realm of cybersecurity and defense-related technologies.
Furthermore, the potential for sanctions and countermeasures by Russia should not be underestimated.
Comparison of Likely Responses
China, with its vast market and diversified economy, is likely to adopt a more pragmatic approach, focusing on finding alternative avenues for trade and technological advancement. Russia, due to its more concentrated economy and geopolitical tensions, might adopt a more assertive stance, potentially prioritizing national security interests and challenging the new regulations. The divergence in their responses will shape the future of global trade and technological cooperation.
Potential Economic Repercussions
The new rules could lead to a reduction in trade volume and a shift in investment patterns between China, Russia, and other nations. The impact on specific sectors, such as technology and defense, is expected to be significant. The overall economic repercussions could be substantial, potentially leading to decreased global trade and a more fragmented global economy. Historical precedents, like trade wars and sanctions, demonstrate the unpredictable and sometimes damaging outcomes of such regulatory actions.
Commerce departments are cracking down on the use of hacking tools, particularly from China and Russia. This new rule highlights a growing concern about cyber threats. Interestingly, this trend seems mirrored in the innovative world of music, where projects like Elvis interpolation vergecast, exploring the future of music, elvis interpolation vergecast future of music , are pushing the boundaries of sound.
Ultimately, these security measures are necessary to protect against sophisticated attacks in the digital landscape.
Potential Disruptions to Supply Chains and Trade Relationships
Disruptions to existing supply chains, particularly those involving Chinese and Russian companies, are a potential outcome. The need for alternative suppliers and revised trade agreements will be crucial. This could result in delays, increased costs, and decreased efficiency across various industries. Supply chain resilience will be tested as companies adapt to these changes.
Potential Impacts on Specific Sectors
| Sector | China | Russia |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Reduced access to certain foreign technologies, increased investment in domestic alternatives, potential shift in global tech dominance. | Increased reliance on domestic tech development, potential loss of access to foreign expertise and equipment, possible redirection of resources to alternative partnerships. |
| Defense | Potential for increased domestic production, search for alternative partners for advanced military technologies. | Potential for increased reliance on domestic production and technology development, search for alternative markets for military equipment and expertise. |
| Manufacturing | Potential for relocation of manufacturing facilities, increased focus on domestic production and supply chains. | Potential for relocation of manufacturing to other countries, emphasis on developing domestic manufacturing and supply chains. |
| Energy | Potential for increased focus on renewable energy and diversification of energy sources. | Potential for increased reliance on alternative energy sources, possible re-evaluation of energy exports and dependence. |
Examination of Hacking Tools: Commerce Departments New Rule Hacking Tools China Russia
This section delves into the specifics of the hacking tools targeted by the new commerce department rule. Understanding the types of tools, their development methodologies, and potential misuse is crucial for comprehending the implications of this regulation. The goal is to illuminate the complexities of these tools and how they can be used for both malicious and unintentional harm.The new rule encompasses a broad range of tools, from sophisticated exploits to readily available scripts.
The tools’ capabilities vary greatly, ranging from basic reconnaissance probes to advanced penetration testing frameworks. This diverse range necessitates a detailed understanding of each tool type and its potential application. This detailed examination aids in predicting and mitigating the risks associated with their use.
Types of Hacking Tools Covered
The new rule addresses a wide spectrum of hacking tools, encompassing various categories designed for different stages of a cyberattack. This includes network scanning tools, vulnerability exploit kits, password cracking software, and malicious code injection frameworks. Sophisticated tools like reverse engineering frameworks and custom malware development platforms are also covered. This breadth of coverage reflects the evolving nature of cyber threats.
Methods of Development and Deployment
The development and deployment of these tools can range from amateur scripting to sophisticated, professional-grade coding projects. Open-source tools often undergo modifications and customization, making them potentially more dangerous. The availability of readily available hacking tools online significantly lowers the barrier to entry for malicious actors. This makes it crucial for companies to prioritize robust security measures.
Many tools are built using established programming languages, allowing for further modification and customization.
Potential for Misuse and Unintended Consequences
Misuse of these tools can lead to a variety of damaging outcomes, from data breaches and financial losses to reputational damage. Unintended consequences might include accidental harm to legitimate systems or unintended side effects of tool usage. This is especially true for advanced tools that require a deeper understanding of the target systems. Careful consideration and rigorous testing are crucial to mitigate such risks.
Table of Hacking Tools and Potential Applications
| Tool Type | Description | Potential Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Network Scanners | Identify vulnerabilities in networks by probing systems and services. | Reconnaissance, identifying open ports, discovering potential entry points. |
| Vulnerability Exploit Kits | Pre-packaged tools for exploiting known vulnerabilities in software. | Automated attacks, quickly exploiting weaknesses across multiple systems. |
| Password Cracking Software | Attempt to decipher passwords through brute-force or dictionary attacks. | Gaining unauthorized access to accounts, networks, and systems. |
| Malware Injection Frameworks | Enable the creation and deployment of malicious software. | Deploying viruses, Trojans, ransomware, or other malicious programs. |
| Reverse Engineering Frameworks | Enable analysis of existing software to identify vulnerabilities or create new exploits. | Developing custom exploits, analyzing security flaws in existing software. |
International Trade and Security Concerns
The newly established rules regarding hacking tools, specifically targeting China and Russia, introduce significant complexities into the global trade landscape. These regulations, while aimed at bolstering cybersecurity, inevitably affect the flow of goods and services across borders, demanding careful consideration of their potential consequences. Navigating the intricacies of international relations and enforcement becomes paramount in ensuring the effective implementation of these rules.The new rules represent a significant shift in the approach to global trade security.
Previously, cybersecurity concerns were often addressed on a case-by-case basis, lacking a unified framework. This new approach, by explicitly targeting specific countries, underscores a growing recognition of the interconnectedness of cybersecurity and international trade. This shift, however, necessitates a thorough examination of its implications on various aspects of international relations.
Connection to Global Trade Security
The connection between the new rule and global trade security is multifaceted. The rules aim to deter the use of malicious software in commercial transactions and supply chains, protecting sensitive data and intellectual property. By establishing clear guidelines, the intent is to foster a more secure environment for international trade. This, in turn, fosters trust and encourages cooperation among trading partners.
Implications for International Relations and Cooperation
The new rules’ impact on international relations is considerable. Countries that are targeted by these regulations may view them as discriminatory, potentially leading to retaliatory actions. The establishment of a common understanding of cybersecurity threats and vulnerabilities, however, is a crucial element for fostering international cooperation. Maintaining open communication channels between nations is paramount in mitigating potential conflicts and ensuring a smooth implementation of the new rules.
Countries may adjust their export controls for technology and services related to hacking tools to comply with the new regulations.
Potential Risks and Challenges Related to Enforcement and Compliance
Enforcing these new rules globally presents significant challenges. Varying legal systems and interpretations of the rules create potential for inconsistencies in enforcement. Effective international cooperation is vital to establish a consistent framework and address the complexity of jurisdiction across borders. Difficulties in attribution, establishing the origin of malicious software, will be a key challenge for enforcement. This may lead to uncertainty and disputes among trading partners.
Possible Scenarios of Non-Compliance and Subsequent Consequences
Non-compliance with the new rules can result in several consequences, ranging from economic sanctions to trade restrictions. For instance, companies that utilize hacking tools developed in non-compliant countries may face import restrictions, affecting their ability to conduct business internationally. These repercussions can be severe, impacting the financial health and global competitiveness of affected nations. The specific sanctions and restrictions would be determined by the severity and extent of non-compliance.
International Perspectives on the New Rule
| Country/Region | Potential Perspective |
|---|---|
| United States | Likely to support the new rule as it aligns with their national security interests and aims to protect their companies from malicious attacks. |
| China | May view the rule as discriminatory and a potential impediment to their technological advancement and economic growth. They may retaliate with similar restrictions on U.S. exports. |
| Russia | Similar to China, likely to perceive the rule as targeting their interests and may respond with countermeasures, such as restricting access to certain technologies or initiating legal challenges. |
| European Union | Likely to adopt a nuanced perspective, balancing the need for cybersecurity with concerns about trade disruption and economic consequences. |
Potential for Technological Advancement
The new rule regarding hacking tools, particularly those originating from China and Russia, presents a unique opportunity for technological advancement in commerce. While the immediate concern is security, the proactive measures required to mitigate the threat can stimulate innovation across various sectors. This proactive response, fostering a competitive environment for advanced security solutions, can yield significant returns.The rule, by forcing a heightened awareness and investment in cybersecurity, creates a powerful impetus for innovation.
The potential for a surge in research and development (R&D) is substantial, leading to advancements in not just defensive technologies but also offensive security measures. This dynamic will propel the entire technological landscape forward.
Influence on Technological Advancement in Commerce
The rule’s primary impact is on the acceleration of cybersecurity innovation. Companies will be compelled to develop and deploy advanced defensive measures, leading to stronger encryption protocols, more sophisticated intrusion detection systems, and improved incident response mechanisms. This, in turn, creates a demand for skilled cybersecurity professionals, fueling growth in the related industry.
Potential for Innovation in Cybersecurity and Anti-Hacking Technologies, Commerce departments new rule hacking tools china russia
The heightened threat of sophisticated attacks will stimulate innovation in several critical areas. For example, machine learning algorithms can be further developed to detect subtle anomalies in network traffic indicative of hacking attempts. Advanced encryption techniques and quantum-resistant cryptography will become more prevalent, enhancing data security. The need to develop resilient systems capable of withstanding sophisticated attacks will foster the development of technologies that are more adaptable and less susceptible to exploits.
Examples of Driving Research and Development
The rule can drive specific research and development efforts. For example, the need for more robust authentication methods beyond passwords will incentivize research into biometrics, behavioral biometrics, and other advanced authentication technologies. The need to secure the supply chain of critical infrastructure will spur development of secure and tamper-proof hardware and software. Moreover, the requirement to develop tools for ethical hacking and penetration testing will necessitate the development of specialized tools and training programs.
Table: New Technologies and Countermeasures
| Area of Development | Potential New Technologies | Countermeasures |
|---|---|---|
| Encryption | Quantum-resistant cryptography, homomorphic encryption | Enhanced encryption standards, more robust decryption keys |
| Network Security | Advanced intrusion detection systems, machine learning-based threat detection, anomaly detection | Continuous monitoring, automated response systems |
| Incident Response | Automated incident response tools, predictive security models, real-time threat intelligence | Proactive security measures, enhanced incident response teams |
| Supply Chain Security | Secure hardware and software, blockchain-based supply chain management | Robust verification systems, enhanced auditing procedures |
| Authentication | Behavioral biometrics, multi-factor authentication, Zero Trust models | Enhanced authentication protocols, access control improvements |
Enforcement and Compliance Strategies
Navigating the complex landscape of international trade requires robust enforcement mechanisms to deter malicious actors and ensure compliance with new regulations regarding hacking tools. Effective enforcement strategies are crucial for maintaining a secure and predictable trading environment. This section delves into potential enforcement mechanisms, compliance challenges, and the potential for international cooperation.
Potential Enforcement Mechanisms
The new rules necessitate a multi-faceted approach to enforcement, combining proactive measures with reactive responses. This includes enhanced intelligence gathering to identify and track suspicious activity related to the use of hacking tools. International cooperation plays a vital role in this process. Effective mechanisms also involve the establishment of dedicated investigative teams equipped with advanced analytical capabilities to quickly identify and analyze potential violations.
Penalties for non-compliance should be clearly defined and proportionate to the severity of the offense. This will help deter future instances of malicious activity. Furthermore, transparent reporting mechanisms are essential to track the effectiveness of enforcement efforts and identify areas needing improvement.
Compliance Challenges for International Businesses
Businesses operating across international borders face significant challenges in complying with the new rules. The varying legal frameworks and enforcement standards across countries create a complex compliance environment. Understanding and adhering to the specific requirements of each jurisdiction is crucial, but often necessitates significant resources for legal expertise and compliance personnel. Furthermore, the rapid evolution of technology makes it challenging for companies to stay abreast of emerging threats and adapt their security practices accordingly.
Commerce departments are cracking down on hacking tools originating from China and Russia, which is a critical issue for global security. This focus on cybersecurity dovetails with recent Microsoft news events, including their advancements in gaming, cloud computing, and Windows, which are all critical for a robust digital ecosystem. These technological developments, showcased in resources like microsoft news events gaming cloud windows , highlight the importance of staying ahead of cyber threats.
Ultimately, the commerce department’s new rules will hopefully make it harder for these countries to use hacking tools, bolstering global digital safety.
Maintaining robust cybersecurity infrastructure and training programs are vital, but can be costly and time-consuming, especially for smaller businesses.
Commerce departments are cracking down on hacking tools coming from China and Russia, which is a smart move. But sometimes, we need to embrace the unexpected, like the experimental nature of games like Death Stranding, even if they don’t always pan out perfectly. This desire for pushing creative boundaries might just be the spark that ignites innovation in the digital world, much like these restrictions on hacking tools could lead to more secure and reliable commerce systems.
International Cooperation in Enforcement
International cooperation is essential for effective enforcement of the new rules. Sharing information and best practices among countries can help identify and track malicious actors more efficiently. Joint investigations and coordinated enforcement actions can significantly increase the likelihood of bringing violators to justice. Establishment of international agreements and protocols for data sharing and mutual legal assistance are crucial for facilitating this cooperation.
Examples of successful international cooperation in combating cybercrime can be leveraged for developing effective strategies.
Table of Enforcement Strategies and Effectiveness
| Enforcement Strategy | Description | Effectiveness (High/Medium/Low) | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enhanced Intelligence Gathering | Proactive monitoring of suspicious activity, leveraging advanced analytics and threat intelligence platforms. | High | Employing sophisticated algorithms to detect patterns in digital communications indicative of malicious intent. |
| Dedicated Investigative Teams | Specialized teams with expertise in cybersecurity and international law. | Medium | Forming task forces comprising investigators with expertise in network analysis and digital forensics. |
| Clear and Proportionate Penalties | Establishing a well-defined penalty structure for violations, tailored to the offense’s severity. | High | Imposing fines or criminal sanctions for unauthorized access and use of hacking tools. |
| Transparent Reporting Mechanisms | Creating transparent reporting channels to track the effectiveness of enforcement efforts and identify areas for improvement. | Medium | Publicly releasing statistics on successful investigations and enforcement actions. |
| International Agreements | Establishing international agreements for data sharing and mutual legal assistance. | High | Formalizing treaties and protocols that facilitate cross-border cooperation in cybercrime investigations. |
Future Implications and Projections

The new rules regarding hacking tools and their implications for global commerce represent a significant shift in international trade relations. These regulations, while aimed at mitigating cyber threats, inevitably introduce complexities and uncertainties into the global marketplace. Understanding the long-term impact, potential adjustments, and evolving trade scenarios is crucial for stakeholders to navigate this new landscape.
Long-Term Impact on Global Commerce
The new rules, by restricting the use and transfer of certain hacking tools, are expected to have a profound impact on global commerce. The restrictions will likely influence the development and deployment of new technologies, potentially impacting innovation and competitiveness in various sectors. Countries that heavily rely on technology transfer and collaboration may face challenges in adapting to the new norms.
Potential for Future Adjustments or Modifications to the Rule
Given the dynamic nature of technology and international relations, future adjustments or modifications to the rule are highly probable. The effectiveness of the current rules in addressing emerging threats will likely be assessed, prompting potential amendments to account for evolving cyber landscapes. The need for flexibility and adaptability in the face of technological advancements will become increasingly important.
This may involve revisions to the list of restricted tools, or changes to the enforcement mechanisms. For example, a growing sophistication of cyberattacks may necessitate more stringent rules and a faster response time for enforcement.
Potential Scenarios for the Evolution of International Trade Relations
Several scenarios regarding the evolution of international trade relations in light of these new rules can be envisioned. A cautious approach by nations may lead to increased scrutiny of technology transfers, potentially creating trade barriers and slowing down innovation. Conversely, a more collaborative approach focusing on international cooperation and information sharing could foster a more secure and predictable global trading environment.
Table of Possible Future Developments and Their Impact
| Future Development | Impact on Businesses | Impact on Governments | Impact on Consumers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Increased scrutiny of technology transfers | Higher compliance costs, slower innovation, potential trade disputes | Increased regulatory burden, need for international cooperation, diplomatic challenges | Potentially higher prices for goods and services, slower technological advancement |
| Increased international cooperation on cybersecurity | Enhanced security, potential for new markets, opportunities for collaboration | Improved global security, development of international standards, stronger diplomatic ties | Increased confidence in the security of online transactions, potential for enhanced online services |
| Development of new cybersecurity standards | Need for adaptation and investment in compliance | Need for developing and enforcing new standards, international harmonization | Potentially higher prices in the short term, increased trust in online transactions |
Conclusion
In conclusion, the commerce departments new rule hacking tools china russia represents a crucial step towards safeguarding international commerce. While it promises to enhance security, the rule also presents significant challenges for both China and Russia, potentially impacting their economic standing and international relations. The rule’s future success hinges on effective enforcement and a collaborative approach among nations, as well as the potential for this rule to drive innovation in cybersecurity and anti-hacking technologies.