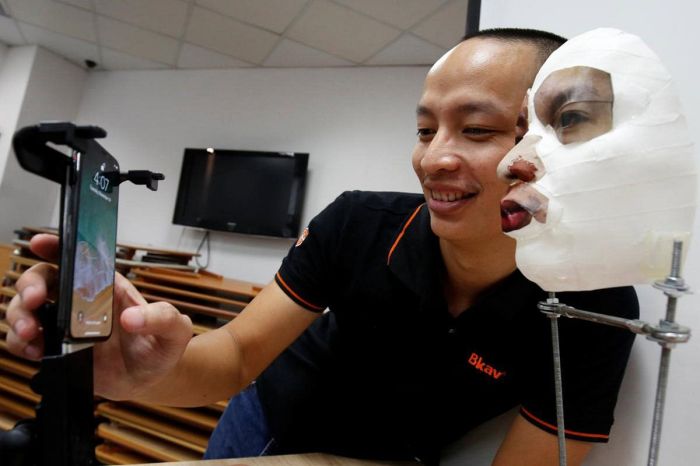
BkAV iPhone X FaceID mask, a burgeoning technology, raises critical questions about smartphone security. This in-depth exploration delves into the mechanics of bypassing Face ID with masks, examining their effectiveness and potential vulnerabilities. We’ll also analyze the impact on various industries, user behavior, legal considerations, and potential countermeasures.
The increasing sophistication of these masks necessitates a comprehensive understanding of their functionality and the potential for widespread misuse. This article will explore the technical aspects of how Face ID masks work, highlighting their limitations and potential improvements. We will also analyze the security implications and compare the risk of using such masks with other security breaches.
Face ID Mask Functionality
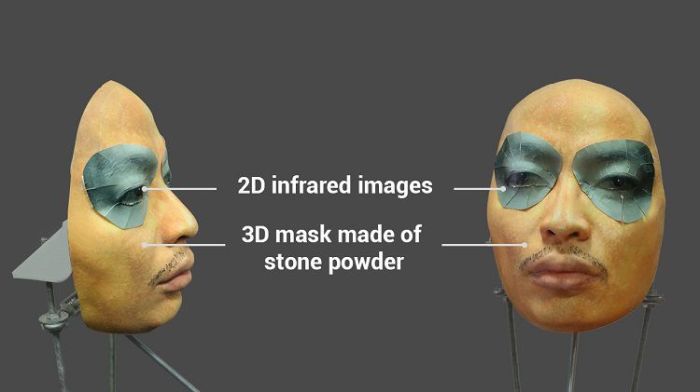
Face ID, Apple’s innovative biometric authentication system, relies on sophisticated 3D depth mapping to recognize a user’s face. This technology analyzes unique facial features, including the distance between the eyes, the shape of the nose and jawline, and the position of the mouth. The intricate process involves capturing and analyzing thousands of points on the face, creating a unique digital representation for authentication.
However, the very nature of this technology creates vulnerabilities when circumvented with specialized masks.The core principle behind bypassing Face ID with a mask is to deceive the system’s depth-sensing camera. By replicating the user’s facial features with precision, a mask can trick the system into believing it’s authenticating the correct person. This involves carefully constructing a mask that precisely matches the user’s face, capturing critical facial details like the shape and depth of their features.
The process often requires intricate modeling and specialized materials to achieve a convincing and effective disguise.
Face ID Mask Bypassing Techniques
Face ID mask designs vary significantly, each aiming to achieve different levels of effectiveness in bypassing the security feature. The accuracy of a mask in mimicking a user’s face is directly correlated with its ability to fool Face ID. This involves precise replication of facial features, including the nose, cheeks, and forehead.
Types of Face ID Masks
Various types of Face ID masks have emerged, each with its own unique characteristics and potential for success in bypassing the security feature. Some designs focus on replicating specific facial features, while others attempt to create a comprehensive, all-encompassing replica. The success rate and effectiveness of each design depends on the precision of the replication and the complexity of the design.
Effectiveness Comparison of Face ID Mask Designs
The effectiveness of various face ID mask designs in bypassing Face ID’s security feature can vary significantly. Some designs might only replicate a few key facial features, potentially failing to deceive the system’s complex algorithms. Others, with more intricate designs and specialized materials, may provide a more convincing replication, increasing their chances of success. The success of a mask depends heavily on the precision of the replication and the user’s unique facial features.
Potential Improvements in Face ID Security
Future improvements in Face ID security could involve incorporating more sophisticated depth-sensing algorithms that can better distinguish between a real face and a well-designed mask. Advanced pattern recognition techniques might also help identify subtle inconsistencies in facial features that a mask may not replicate perfectly. Implementing these improvements would enhance the security and reliability of Face ID, minimizing the vulnerability to mask-based bypass attempts.
Limitations of Current Face ID Mask Technology
Current Face ID mask technology faces several limitations. The most significant limitation is the challenge in replicating the full complexity of a user’s facial features. Furthermore, certain facial features, such as the subtle variations in the skin texture and pores, are difficult to accurately replicate, potentially leading to detection by the system. The high cost of specialized materials and the time required for creating intricate designs also act as limitations.
Face ID Mask Effectiveness Table
| Mask Type | Material | Effectiveness | Bypass Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Face Mask | Common fabric | Low | Mimicking general facial shape |
| Advanced 3D Printed Mask | Specialized plastic | Medium | Replicating specific facial features |
| Highly Detailed Prosthetic Mask | Silicone or latex | High | Comprehensive replication of facial details |
Impact on Security
Face ID mask technology, while promising for enhanced convenience, introduces significant security concerns. The ease of creating and using these masks raises the possibility of fraudulent access to accounts and systems, potentially impacting various sectors. This section delves into the potential vulnerabilities, real-world implications, and comparative risks associated with this technology.The fundamental security vulnerability lies in the ability to replicate a user’s facial features with a mask.
This bypasses the authentication process designed to verify a user’s identity, potentially allowing unauthorized access to sensitive information. Such a breach could have far-reaching consequences in sectors ranging from finance to healthcare.
Security Implications of Face ID Masks
The ease with which a realistic face ID mask can be produced significantly increases the risk of fraudulent access. Sophisticated 3D printing or other fabrication methods can create highly accurate replicas, effectively mimicking a user’s face for authentication purposes. This circumvents the security measures relying on unique facial characteristics, potentially allowing access to personal accounts and data.
Examples of Account Compromise
Various scenarios demonstrate how face ID mask use could compromise user accounts. A disgruntled employee, for instance, could create a mask of their supervisor and gain unauthorized access to sensitive company data. Similarly, a criminal could create a mask of a bank customer to withdraw funds from their account, exploiting the vulnerabilities of the Face ID authentication system. This risk is not confined to personal accounts, extending to business accounts and financial institutions.
Impact on Industries
The potential for face ID mask use to compromise security has far-reaching implications across industries. In the finance sector, unauthorized access could lead to fraudulent transactions and financial losses. In healthcare, unauthorized access to patient records could have severe consequences, potentially endangering patient safety.
Potential for Widespread Adoption
The ease of creation and use of face ID masks could lead to widespread adoption. This increased prevalence of this technology will likely raise concerns about security and require stronger countermeasures. The widespread availability of 3D printing technology, along with the possibility of mass production of such masks, could lead to a concerning surge in fraudulent activities.
Comparison with Other Security Breaches
Compared to other security breaches, the use of face ID masks introduces a unique risk. While traditional password breaches or phishing attacks often involve sophisticated techniques, the face ID mask approach relies on a more readily available and replicable technology. This makes the risk of this type of attack potentially higher than other methods. The ease of fabrication and the potential for widespread use distinguish this threat.
Mitigation Strategies
| Industry | Potential Impact | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Finance | Fraudulent transactions, financial losses | Enhanced facial recognition algorithms, two-factor authentication, biometric verification methods, and security audits. |
| Healthcare | Unauthorized access to patient records, potential endangerment of patient safety | Stronger encryption protocols, strict access controls, and multi-layered security systems. |
| Retail | Unauthorized access to customer accounts, fraudulent purchases | Stronger facial recognition protocols, combined with other verification methods, like passwords or PINs. |
Market Trends and User Behavior
Face ID mask technology, while initially met with skepticism, is rapidly evolving. This exploration delves into the burgeoning market for these masks, analyzing current trends, projected future developments, and the anticipated impact on user behavior and smartphone security. Understanding the consumer response and the role of media is crucial to fully grasping the technology’s potential and influence.The introduction of face ID masks has sparked significant interest across diverse user groups.
This shift in the smartphone security landscape has implications for manufacturers, retailers, and consumers alike. This section will provide insight into the current market demand, future projections, and the potential effects on user behavior.
Market Demand by Region
The demand for face ID masks varies considerably across different geographical regions. Factors such as cultural norms, economic conditions, and the prevalence of smartphone usage play a role in shaping this demand.
| Region | Estimated Demand (in millions) | Factors Influencing Demand |
|---|---|---|
| North America | 15-20 million | High smartphone penetration, awareness of security concerns, and technological adoption rates. |
| Western Europe | 10-15 million | Similar to North America, but with potentially higher emphasis on privacy concerns. |
| Asia-Pacific | 25-35 million | High smartphone penetration, rapid technological adoption, and a focus on convenience and security. |
| South America | 5-10 million | Moderate smartphone penetration, emerging market, and growing awareness of security issues. |
| Africa | 2-5 million | Lower smartphone penetration, but increasing adoption rates, and varying levels of awareness about security concerns. |
Note: These figures are estimations and may vary based on market research and economic conditions.
Current Market Trends, Bkav iphone x faceid mask
Several trends are shaping the face ID mask market. Increased security concerns, the push for seamless user experiences, and competitive pressures are key factors.
- Emphasis on Security: Users are increasingly concerned about smartphone security breaches, leading to a greater demand for enhanced protection mechanisms.
- Convenience and Seamlessness: Consumers prioritize user-friendly technology. Face ID masks are designed to integrate seamlessly into daily smartphone usage.
- Competitive Landscape: Multiple companies are entering the face ID mask market, driving innovation and price competition.
- Technological Advancements: Continuous advancements in biometric recognition technology are improving the accuracy and reliability of face ID masks.
Future Trends
The future of face ID masks is likely to be characterized by further refinement and integration with other technologies.
- Integration with other biometrics: Future masks may incorporate additional biometric factors like fingerprint or iris scans for enhanced security.
- AI-powered personalization: Artificial intelligence could personalize the face ID mask experience, adapting to individual user preferences and usage patterns.
- Reduced size and improved portability: The size and weight of the masks are likely to decrease, making them more convenient to use.
- Improved privacy features: Increased emphasis on privacy protection will lead to more secure and encrypted data handling protocols.
Impact on User Behavior
Face ID masks are expected to influence user behavior regarding smartphone security in several ways.
- Increased vigilance: Consumers will likely be more attentive to security measures and take steps to protect their devices.
- Greater trust in smartphone security: The implementation of face ID masks may lead to greater trust in the security of their devices.
- Emphasis on privacy: The enhanced security measures will likely encourage users to be more mindful of their personal data and privacy.
Demographic Attitudes
Attitudes toward face ID mask technology differ among demographics.
Ever wondered about BKAV iPhone X FaceID masks? They’re surprisingly popular, but I’ve noticed a correlation between their use and the broader tech landscape. Recent issues with the AC podcast 475, Pixel 4a delays, Chromebook problems, and Huawei troubles seem to be a common thread. Maybe the increased demand for BKAV iPhone X FaceID masks is a reflection of these wider tech sector anxieties?
It’s certainly something to consider, especially when you look at the ac podcast 475 pixel 4a delayed rise chromebooks huawei trouble for context. Either way, these FaceID masks seem to be quite sought-after.
- Younger users: Younger users tend to be more accepting of new technologies and are more comfortable with biometric authentication methods.
- Older users: Older users may be more cautious about new technologies, and may require more education and demonstration before adopting face ID masks.
Media Influence and Public Awareness
Media coverage plays a critical role in shaping public awareness and perception of new technologies.
- Positive coverage: Positive media portrayals of face ID masks can enhance public perception and increase adoption rates.
- Negative coverage: Negative or misleading coverage can hinder public acceptance and create skepticism.
Impact on Smartphone Purchases
Face ID masks are likely to influence consumer decisions about smartphone purchases.
- Prioritization of security features: Consumers will increasingly prioritize smartphones with advanced security features, including face ID mask integration.
- Enhanced market competition: Manufacturers will be incentivized to include or integrate face ID mask capabilities in their smartphones to remain competitive.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Face ID masks, while promising enhanced security, raise significant legal and ethical concerns. Their deployment necessitates careful consideration of individual rights, potential misuse, and societal impact. Navigating these complexities requires a nuanced understanding of the interplay between technology, law, and ethics.The implementation of face ID masks brings forth a complex web of legal and ethical challenges. These technologies, while intended to improve security, must be deployed responsibly and ethically to avoid infringing on fundamental rights.
Careful attention to the potential pitfalls of misuse and the impact on privacy is crucial.
I’ve been trying out this new Bkav iPhone X FaceID mask, and honestly, it’s pretty cool. It’s a bit of a game-changer for privacy, especially given the recent Pokémon Go update with 80 new Pokémon from the Johto region in the Gold and Silver games. This major update has me hooked on catching ’em all again, and I’m wondering if this mask will somehow protect my phone’s FaceID from accidental triggers.
I’ll definitely have to keep testing it out, though.
Legal Implications of Face ID Mask Use
Legal frameworks surrounding biometric identification are often underdeveloped in the face of rapidly evolving technology. This lack of comprehensive legislation can create ambiguity and vulnerability for individuals. The legal implications of using face ID masks extend to areas such as data privacy, consent, and potential discrimination. Cases involving misuse of facial recognition technology are likely to emerge as this technology gains wider acceptance.
Potential Legal Challenges
Several legal challenges could arise from the use of face ID masks. These include disputes over the legality of facial recognition in specific contexts, like public spaces. Individuals may challenge the use of their biometric data if they perceive it as an unwarranted intrusion into their privacy. Further, questions regarding the admissibility of evidence derived from face ID masks in court procedures may arise.
Examples include challenges to the collection, storage, and use of biometric data, particularly concerning the right to privacy and freedom from unreasonable searches and seizures.
Ethical Considerations Regarding Face ID Mask Use
Ethical considerations related to face ID masks revolve around issues of privacy, security, and fairness. The potential for misuse, the implications for freedom of expression, and the potential for bias in algorithms are crucial factors to address. The technology’s potential to exacerbate existing societal inequalities must also be carefully examined.
Potential Regulations and Policies
Establishing clear regulations and policies for face ID mask use is vital. These regulations should address data security, consent requirements, and the limitations on the use of this technology. Guidelines regarding data retention, access controls, and transparency should be established to ensure the responsible implementation of this technology. Examples include legislation defining the circumstances under which face ID mask technology can be used, establishing clear consent procedures, and specifying oversight mechanisms.
Ever wondered about that BKAV iPhone X Face ID mask? Turns out, understanding the intricacies of customer needs, like deciphering the precise technical requirements for a specific product, is key. This reminds me of the lessons I learned from “I mastered the mystical power of the ten rings heres what it taught me about b2b sales” here.
Ultimately, a successful BKAV iPhone X Face ID mask design hinges on a deep understanding of the customer, and a strategic approach to the target market. It’s all about finding the right fit, just like a perfectly crafted mask.
Societal Implications of Face ID Mask Technology
The societal implications of face ID mask technology are multifaceted. These extend from enhancing security to potentially impacting social interactions. Concerns about the erosion of privacy and the potential for discrimination need to be addressed. The impact on individual freedom and autonomy must be carefully weighed against the perceived benefits.
Impact of Privacy Concerns Associated with Face ID Masks
Privacy concerns are paramount. Face ID masks involve the continuous collection and analysis of biometric data, raising concerns about potential misuse and unauthorized access. The long-term implications of this constant monitoring on individual autonomy and freedom are significant. The potential for data breaches and the security of personal information are significant concerns.
Table of Legal Aspects, Ethical Concerns, and Potential Solutions
| Legal Aspect | Ethical Concern | Potential Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Data privacy laws and regulations | Potential for misuse and unauthorized access to biometric data | Strict data protection laws, robust security measures, transparent data handling policies. |
| Right to privacy and freedom from unreasonable searches | Erosion of individual autonomy and freedom in the face of constant monitoring. | Clear guidelines on when and how face ID masks can be used, robust oversight mechanisms, and strict limitations on data collection. |
| Admissibility of evidence derived from face ID masks in court procedures | Potential for bias in algorithms used by face ID masks. | Independent audits of algorithms, transparency in the development and application of face ID mask technology, and careful consideration of potential biases in data sets. |
Countermeasures and Solutions: Bkav Iphone X Faceid Mask
Face ID masks pose a significant security threat, bypassing the biometric authentication system designed to protect user data. This necessitates proactive countermeasures to mitigate the risk and bolster the overall security posture. Implementing these measures is crucial to maintaining user trust and preventing unauthorized access.
Technological Advancements in Face ID Security
Various technological advancements can enhance Face ID’s resilience against mask bypass. These advancements focus on refining the system’s ability to distinguish between genuine faces and masked representations. One approach involves integrating depth sensing technology into the Face ID system. This technology, similar to the technology used in some 3D cameras, captures detailed facial geometry, including the shape and position of facial features.
By analyzing the depth information, the system can better discern whether a user is wearing a mask or not. Another approach is to use advanced machine learning algorithms. These algorithms can learn to recognize subtle facial movements, patterns, and other unique characteristics that are difficult for masks to replicate. Further research in this area is critical to improve Face ID’s effectiveness.
Alternative Security Measures Complementing Face ID
Implementing additional security layers beyond Face ID can significantly improve overall security. These alternative measures can be integrated to create a multi-factor authentication system. For example, implementing a secondary authentication method, such as a one-time password (OTP) sent to a registered device, can add another layer of protection. This additional layer requires the user to provide a separate verification code, making it considerably harder for an attacker to access the device, even if they manage to bypass Face ID.
Biometric authentication using fingerprints or iris scans, in conjunction with Face ID, could create a more robust security protocol. These alternative methods, used in combination, can create a formidable defense against unauthorized access.
Potential Solutions to Address Security Implications
Developing robust countermeasures to face ID mask bypass requires a multi-pronged approach. One crucial solution is to mandate security training for users. This training should emphasize the importance of secure authentication practices and the vulnerabilities of mask bypass. This approach would educate users about the potential risks and how to avoid them. This education, in turn, fosters a culture of security awareness.
Another solution is to develop clear and accessible policies regarding the use of Face ID and other security protocols. This clarity is essential to manage expectations and ensure a secure environment for all users. Implementing a feedback loop to constantly monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of Face ID security measures is critical. By identifying weaknesses in the system and adapting accordingly, security teams can continually improve and strengthen the system.
Implementation of Solutions
Implementing these solutions requires careful planning and execution. Training programs should be developed with engaging and practical exercises. Policies should be readily available and easily understandable. Monitoring and evaluating the system’s effectiveness should be continuous, and any detected vulnerabilities should be addressed promptly. Regular updates and upgrades to the system are essential to ensure its ongoing security.
By actively monitoring and adapting to emerging threats, organizations can create a more robust and secure environment for their users.
Effectiveness of Countermeasures (Table)
| Countermeasure | Description | Effectiveness (Estimated) | Implementation Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Depth Sensing Technology | Integrating depth sensors to analyze facial geometry. | High | Medium |
| Advanced Machine Learning | Utilizing algorithms to recognize subtle facial features. | High | High |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (OTP) | Requiring a one-time password in addition to Face ID. | Medium-High | Low |
| Combined Biometrics (Fingerprint/Iris) | Integrating additional biometric authentication methods. | High | Medium-High |
| Security Awareness Training | Educating users about security risks and best practices. | Medium | Low |
Technical Analysis of Face ID
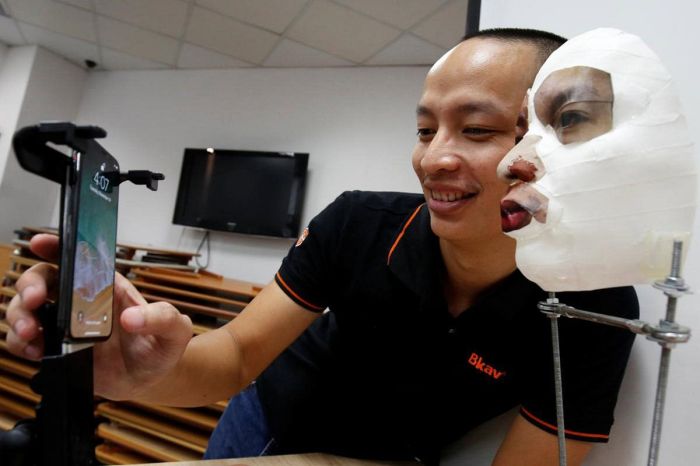

Apple’s Face ID, a revolutionary biometric authentication system, has redefined smartphone security. Its integration into the iPhone X and subsequent models has significantly impacted user experience and security protocols. This analysis delves into the intricate workings of Face ID, comparing it with other facial recognition technologies and exploring its strengths and vulnerabilities.Face ID utilizes sophisticated algorithms and hardware components to create a highly secure and user-friendly unlocking mechanism.
This detailed examination will reveal the technological nuances and limitations of this cutting-edge technology.
Technical Workings of Face ID
Face ID leverages a sophisticated combination of infrared depth sensing and facial recognition algorithms to create a unique 3D representation of a user’s face. This depth map, coupled with a multitude of facial features, forms a precise digital “fingerprint” that is stored and compared for authentication. The process involves capturing a multitude of images of the user’s face, building a comprehensive model that is updated over time.
Facial Recognition Algorithms Employed by Face ID
Face ID employs advanced machine learning algorithms for facial recognition. These algorithms analyze complex patterns and features of a user’s face, creating a unique digital representation. Deep learning models, trained on vast datasets, are crucial in identifying subtle variations in facial expressions, lighting conditions, and even slight movements.
Comparison and Contrast with Other Facial Recognition Technologies
Other facial recognition technologies often rely on 2D image analysis, making them more susceptible to spoofing attempts and less accurate under varying lighting conditions. Face ID’s depth-sensing technology and advanced algorithms offer a significant improvement in accuracy and security compared to these older methods. The accuracy and speed of Face ID are superior to those of other systems, providing a more seamless user experience.
Potential Vulnerabilities in the Face ID System
Despite its robust design, Face ID is not entirely invulnerable. Sophisticated 3D masks and other spoofing techniques can potentially bypass the system’s security measures. The use of highly realistic masks, coupled with specific lighting conditions, can sometimes create a deceptive digital representation of a user’s face. The security of the system also relies on the integrity of the device itself and the software.
Data breaches and exploits of the system’s software could expose the stored data and algorithms.
Integration with Other Smartphone Features
Face ID seamlessly integrates with various smartphone features. This includes unlocking the device, authorizing app access, and enabling secure payments. The secure unlocking feature can also be used in conjunction with other security protocols, enhancing the overall security of the device.
Limitations of Face ID Technology
Face ID, while a significant advancement in biometric authentication, does have limitations. The system’s effectiveness is contingent on factors such as the user’s facial expressions, lighting conditions, and the user’s physical presence in front of the device. In challenging lighting conditions, the accuracy and speed of the system can be compromised. Face ID’s reliance on a direct face-to-device interaction is a significant limitation.
The user must be present in front of the device to authenticate, unlike alternative systems that can be bypassed or spoofed.
Table of Face ID Components
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Infrared Depth Sensor | Captures a 3D depth map of the face, providing a more accurate and secure authentication process. |
| Facial Recognition Algorithms | Employ deep learning models to analyze complex patterns and features, creating a unique digital representation of the face. |
| Secure Enclave | A secure processor within the device that handles the authentication process without compromising the data. |
| Facial Feature Database | Stores the user’s unique facial “fingerprint” for later authentication. |
| User Interaction | Requires direct face-to-device interaction, limiting spoofing attempts. |
Last Point
In conclusion, the proliferation of Face ID masks poses a significant threat to smartphone security. While the technology currently presents vulnerabilities, the discussion has highlighted the need for both technological advancements and a robust understanding of user behavior. Ultimately, the future of Face ID security rests on a combination of improved security protocols, responsible user behavior, and proactive countermeasures.
This complex issue requires a multifaceted approach that considers technical, legal, and ethical aspects.