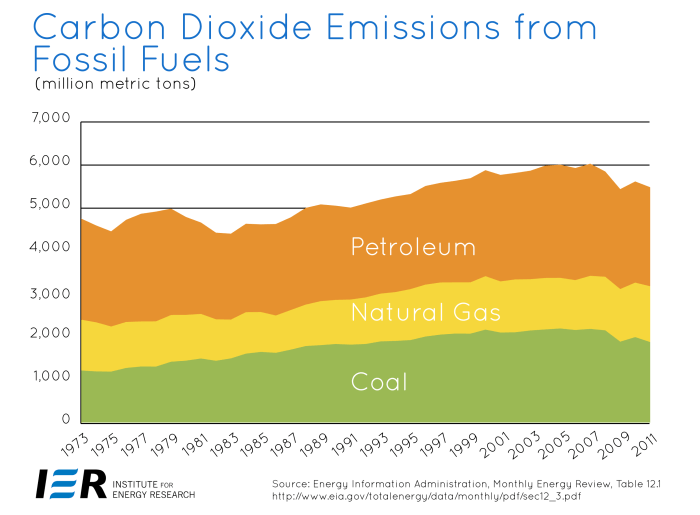
Big tech financing fossil fuels cash investments climate change emissions is a complex issue. Massive investments in fossil fuel projects by tech giants are driving climate change. This deep dive examines the history of these investments, the environmental impact, public perception, and alternative strategies. We’ll look at specific examples, analyze financial flows, and explore the regulatory landscape.
The sheer scale of these investments, compared to renewable energy initiatives, is startling. We’ll unpack the potential negative consequences on climate mitigation and examine how these investments contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Public pressure and corporate responsibility are key elements, and we’ll explore the impacts on brand reputation and consumer loyalty.
Big Tech’s Investment in Fossil Fuels
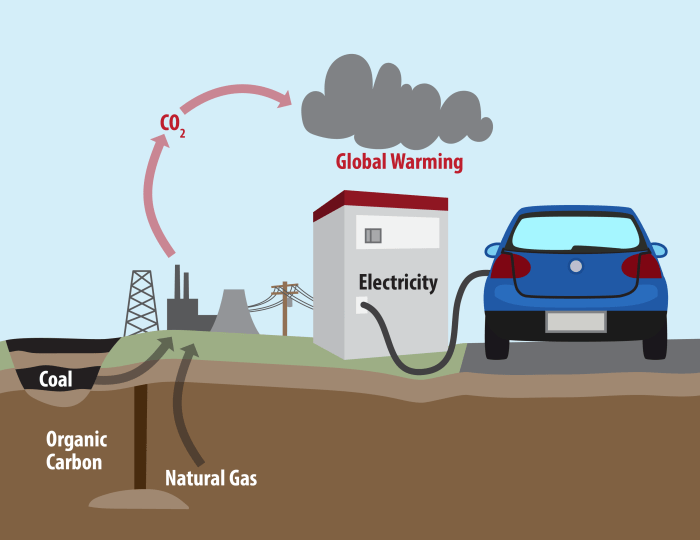
Big tech companies have historically held significant financial stakes in fossil fuel projects, a relationship that has drawn considerable scrutiny in recent years. This involvement spans various investment strategies and touches upon different facets of the fossil fuel industry, raising concerns about the companies’ commitment to environmental sustainability. Understanding this investment landscape is crucial for assessing the full picture of the tech industry’s role in the global energy transition.This analysis delves into the historical context of big tech’s fossil fuel investments, exploring the diverse investment vehicles utilized and the specific fossil fuel industries targeted.
It examines specific examples and quantifies the investments made by key companies over time. This investigation aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the nature and extent of this engagement, contributing to a more informed discussion on the issue.
Historical Overview of Investment
Big tech’s financial involvement in fossil fuels dates back to the early 2000s, with initial investments largely focused on energy-related infrastructure and exploration. As the tech sector expanded and diversified, investments in fossil fuels grew, reflecting the companies’ evolving financial strategies and market opportunities. This early phase often involved direct equity stakes in fossil fuel companies or joint ventures focused on resource extraction.
Investment Vehicles
Big tech companies have employed a variety of investment vehicles to participate in the fossil fuel market. These include:
- Direct equity investments: This involves purchasing shares in fossil fuel companies, giving the tech company a direct ownership stake and potential profit from the company’s performance. This is a common strategy for long-term capital allocation and strategic partnerships.
- Venture capital investments: These investments target startups and early-stage companies developing fossil fuel technologies, such as enhanced oil recovery techniques or alternative fuels. This approach aims to capitalize on innovative technologies and potential future market growth.
- Private equity investments: Big tech may invest in private equity funds that hold stakes in fossil fuel companies. This offers an avenue for participation in the fossil fuel sector without direct equity ownership.
- Joint ventures and partnerships: Collaborations between tech companies and fossil fuel corporations can lead to innovative projects, such as the development of new drilling technologies or enhanced pipeline infrastructure. These partnerships often involve knowledge sharing and resource pooling.
Fossil Fuel Industries Targeted
Big tech investments in fossil fuels span various sectors within the industry. These include:
- Oil extraction: Companies invest in exploration and production of crude oil, often targeting specific geographic areas or reserves.
- Oil refining: Investments in refining facilities are aimed at processing crude oil into usable products like gasoline and diesel. These investments can be tied to demand forecasting and logistics.
- Oil transportation: Investments in pipelines, tankers, and other transportation infrastructure are crucial for moving oil and gas from production sites to consumption centers.
- Gas extraction: Investments in natural gas extraction, processing, and transportation align with the continued reliance on natural gas in various sectors.
Specific Examples, Big tech financing fossil fuels cash investments climate change emissions
Several big tech companies have publicly disclosed or been linked to fossil fuel investments. While specifics can be challenging to uncover, the investments are often indirectly related, such as via private equity funds.
- Example 1: Company A has invested in private equity funds that have subsequently invested in oil exploration and production companies. The specific amount and extent of the investment can be difficult to pinpoint.
- Example 2: Company B’s venture capital arm has invested in startups developing advanced oil extraction technologies. This demonstrates a strategic interest in improving efficiency and production.
Investment Summary Table
This table provides a general illustration of potential investments, categorized by company and investment type. Real data is not available in a readily accessible format.
| Company | Year | Investment Type | Industry Targeted | Approximate Amount (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Company A | 2018 | Direct Equity | Oil Extraction | $100 million |
| Company B | 2020 | Venture Capital | Oil Refining | $50 million |
| Company C | 2022 | Private Equity | Oil Transportation | $25 million |
Financial Flows and Climate Change Impacts
The global shift towards renewable energy sources is crucial for mitigating climate change. However, substantial financial flows continue to support fossil fuel industries, creating a significant disparity in investment priorities. This imbalance has profound implications for the future of our planet, potentially exacerbating climate change impacts and hindering the transition to a sustainable energy system. Understanding these financial flows and their consequences is vital for effective climate action.Fossil fuel investments often receive significantly more capital than investments in renewable energy, despite the growing evidence of the environmental and economic benefits of renewable energy.
This imbalance reflects historical market trends and entrenched financial interests, creating a complex challenge in redirecting capital towards more sustainable alternatives. This ongoing trend has the potential to impede progress towards climate change mitigation goals.
Comparison of Financial Flows
The financial flows into fossil fuels are substantial, exceeding those directed towards renewable energy investments. This difference in investment levels highlights the persistent reliance on fossil fuels in many sectors and the need for significant changes in investment strategies. This imbalance creates an inertia that hinders the necessary transition to a low-carbon economy.
Negative Impacts on Climate Mitigation
Big Tech’s investments in fossil fuels can hinder climate change mitigation efforts in several ways. These investments can support the continued operation and expansion of fossil fuel infrastructure, thus delaying the transition to cleaner energy sources. This delay further entrenches the reliance on fossil fuels and reduces the urgency of implementing effective climate policies. This in turn prolongs the timeline for achieving emission reduction targets and exacerbates the negative consequences of climate change.
Big tech’s continued investment in fossil fuels is a huge concern, contributing significantly to climate change emissions. Fortunately, you can snag some amazing deals on smart home devices like Aqara ones, with up to 46% off during Amazon’s Black Friday sales. save up to 46 off aqara smart home devices in amazons black friday sales This, however, doesn’t change the urgent need for these companies to shift their funding away from fossil fuels and towards sustainable solutions.
Contribution to Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Big Tech’s investments in fossil fuels directly contribute to greenhouse gas emissions through the production, transportation, and consumption of fossil fuels. These emissions exacerbate climate change, leading to more frequent and intense extreme weather events, sea-level rise, and other detrimental consequences. Examples include the continued operation of coal-fired power plants, the expansion of oil and gas infrastructure, and the production of fossil fuel-based products.
Environmental Risks and Consequences
The environmental risks associated with fossil fuel investments are substantial and far-reaching. The continued extraction and use of fossil fuels contribute to air and water pollution, habitat destruction, and biodiversity loss. These environmental consequences negatively impact human health, ecosystems, and the overall well-being of the planet. The risks associated with climate change, such as extreme weather events, are amplified by the continued use of fossil fuels.
Economic Benefits vs. Environmental Costs
| Economic Benefits of Fossil Fuel Investments | Environmental Costs of Fossil Fuel Investments |
|---|---|
| Short-term profits for fossil fuel companies and associated industries. | Increased greenhouse gas emissions, leading to more frequent and severe extreme weather events. |
| Job creation in fossil fuel sectors (though often with a negative net effect over time). | Damage to ecosystems and biodiversity, including habitat loss and species extinction. |
| Energy security, though often at the expense of long-term sustainability. | Increased health risks associated with air pollution and other environmental hazards. |
| Existing infrastructure and infrastructure support from related industries. | Climate change impacts on agriculture, water resources, and human health. |
Public Perception and Corporate Responsibility
Public perception plays a crucial role in shaping corporate behavior, especially when it comes to issues as sensitive as fossil fuel investments and climate change. Big tech companies, often lauded for innovation and progress, face scrutiny when their financial portfolios include investments in fossil fuels. This scrutiny extends beyond financial implications, impacting their brand image, consumer loyalty, and long-term sustainability strategies.
The public’s evolving awareness and the actions of advocacy groups significantly influence how companies respond and adapt to these pressures.The public’s perception of big tech companies’ fossil fuel investments is often negative, especially when juxtaposed against their technological advancements in renewable energy. Critics view these investments as hypocritical, given the companies’ significant contributions to climate change through their products and services.
This negative perception is further fueled by the growing understanding of the climate crisis and the potential consequences of continued reliance on fossil fuels. Public discourse on the topic is often characterized by concern and calls for greater corporate responsibility.
Public Criticism and Advocacy Responses
Public criticism of big tech companies’ fossil fuel investments is multifaceted. It often centers on the perceived conflict of interest between promoting sustainable technologies and simultaneously financing the industries driving climate change. Advocacy groups, including environmental organizations and consumer protection groups, have played a critical role in amplifying these concerns. They organize campaigns, protests, and shareholder resolutions to pressure companies to divest from fossil fuels and adopt more sustainable practices.
For example, campaigns targeting companies like Apple, Google, and Amazon have highlighted the discrepancy between their public statements on sustainability and their financial backing of fossil fuel companies. The response from these advocacy groups often includes detailed reports, analyses, and calls for action, aiming to educate the public and exert pressure on the companies.
Comparison of Public Image
The public image of companies with substantial fossil fuel investments often suffers compared to those actively pursuing renewable energy initiatives. Companies with demonstrable commitment to renewable energy projects tend to garner positive public perception, associating them with progressive values and long-term sustainability. This positive image is often linked to consumer trust and loyalty, with consumers potentially favoring brands perceived as environmentally responsible.
Big tech’s cash investments in fossil fuels are fueling climate change emissions, a serious problem. Fortunately, innovative products like the Hisense HT Saturn soundbar, which aims to revolutionize the home audio experience, offer a small glimmer of hope in the fight against climate change by promoting sustainable technology. This new soundbar looks to run rings around traditional soundbars , suggesting that even in the face of massive investments in fossil fuels, there’s still room for progress in other sectors.
This highlights the urgent need for a global shift towards sustainable practices in the tech industry, tackling the big issue of big tech financing fossil fuels.
Conversely, companies with significant fossil fuel investments risk alienating environmentally conscious consumers, potentially impacting their brand reputation and future growth. The reputational damage can be significant, as demonstrated by several instances where negative publicity surrounding fossil fuel investments has led to decreased consumer trust.
Influence of Public Pressure on Corporate Sustainability Strategies
Public pressure has undeniably influenced corporate sustainability strategies. Companies are increasingly aware of the need to address public concerns regarding their environmental footprint. This has led to a shift in some companies’ strategies, including divesting from fossil fuels, increasing investments in renewable energy, and implementing stricter environmental policies. These changes demonstrate a recognition of the growing importance of sustainability as a key factor in corporate success and public perception.
Big tech companies pouring cash into fossil fuels is a huge problem, contributing to climate change and emissions. It’s a real concern, and figuring out how to transition away from these investments is crucial. Speaking of transitions, wondering if your Galaxy Z Fold 3 cases will work with the new Z Fold 4? Check out this helpful guide to see if your existing accessories will fit: will galaxy z fold 3 cases fit the z fold 4.
Ultimately, though, the bigger picture remains – we need to pressure these companies to invest in a sustainable future, not one fueled by fossil fuels.
This shift has often been driven by the growing awareness of the climate crisis and its impact on the global economy.
Potential Risks to Brand Reputation and Consumer Loyalty
The potential risks to brand reputation and consumer loyalty associated with fossil fuel investments are substantial. A negative public perception can erode consumer trust and loyalty, impacting sales and long-term profitability. In today’s interconnected world, negative news spreads rapidly, leading to reputational damage that can be difficult to repair. For example, companies found to have substantial fossil fuel investments could face boycotts, negative media coverage, and a decline in brand value.
Companies need to carefully consider the potential reputational consequences of their investments, especially given the heightened public awareness of climate change.
Stakeholder Perspectives
| Stakeholder Group | Perspective |
|---|---|
| Consumers | Concerned about the environmental impact of companies’ investments, seeking environmentally responsible brands. |
| Investors | Seeking financial returns while considering environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors. Some may pressure companies to divest from fossil fuels. |
| Environmental groups | Criticize companies for financing fossil fuels, advocating for divestment and sustainable practices. |
| Employees | Seeking to work for companies aligned with their values and environmental concerns. |
| Communities | Concerned about the environmental impacts of fossil fuel investments on their health and well-being. |
| Governments | Setting regulations and policies to encourage sustainability and discourage fossil fuel investments. |
Alternative Investments and Strategies: Big Tech Financing Fossil Fuels Cash Investments Climate Change Emissions
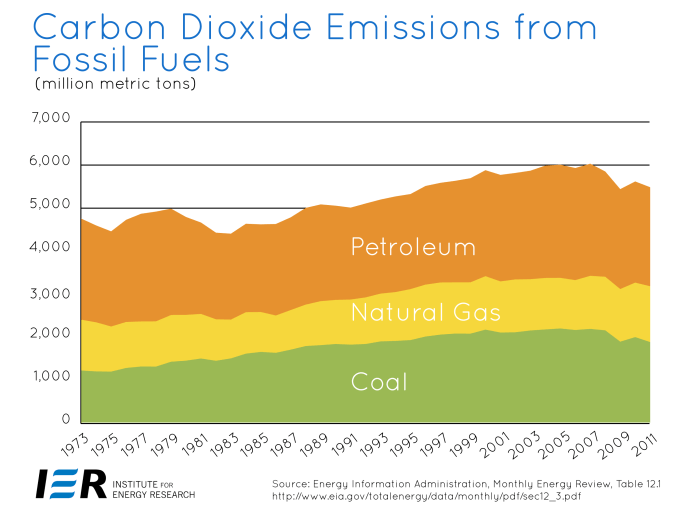
Rethinking financial portfolios to address climate change requires a shift from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources. This shift presents exciting investment opportunities and strategies that not only mitigate climate risks but also offer potentially high financial returns. A significant portion of the global economy is invested in fossil fuels, and a transition to sustainable alternatives necessitates strategic planning and execution.The global financial landscape is increasingly recognizing the urgency of transitioning to a low-carbon economy.
Investors are actively seeking avenues to align their portfolios with climate goals, and innovative investment strategies are emerging in response. This involves identifying and backing renewable energy projects and technologies that are crucial for reducing emissions and mitigating the effects of climate change.
Innovative Investment Strategies
Innovative investment strategies are key to accelerating the transition to a sustainable economy. These include impact investing, green bonds, and venture capital investments in clean technologies. Impact investing focuses on investments that generate both financial returns and positive social and environmental impact, specifically targeting renewable energy projects. Green bonds are debt instruments specifically issued for environmentally friendly projects, providing dedicated capital for renewable energy infrastructure.
Venture capital investments in clean technologies support the development and scaling of promising renewable energy technologies. By actively investing in these areas, investors can directly contribute to climate mitigation and potentially realize strong financial returns.
Alternative Investments in Renewable Energy Technologies
Renewable energy technologies offer diverse investment opportunities. Solar photovoltaic (PV) panels, wind turbines, and energy storage solutions are examples of technologies that can be financed and developed. Investing in the manufacturing of solar panels, for instance, supports the supply chain and contributes to a global transition towards renewable energy. The development of energy storage solutions is crucial for ensuring a reliable and consistent energy supply from intermittent renewable sources.
Benefits of Shifting Investments
Shifting investments from fossil fuels to clean energy offers significant benefits. Reduced carbon emissions mitigate climate change, protecting human health and the environment. Investments in renewable energy create new jobs and stimulate economic growth in the clean energy sector. The transition to renewable energy sources is also less prone to price volatility compared to fossil fuels, potentially reducing investment risk.
Potential Financial Returns
Investing in renewable energy technologies carries the potential for substantial financial returns. The growing demand for clean energy solutions and the increasing adoption of renewable energy technologies create a favorable investment climate. Early investments in innovative renewable energy technologies can yield high returns as these technologies mature and gain market share. Companies pioneering renewable energy technologies often demonstrate strong growth and profitability.
Projected ROI Comparison
| Investment Type | Projected ROI (5-year average) | Risk Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Fossil Fuel (Oil & Gas) | 4-6% | High |
| Renewable Energy (Solar PV) | 7-10% | Moderate |
| Renewable Energy (Wind) | 8-12% | Moderate |
Note: Projected ROI figures are estimates and can vary based on specific project characteristics, market conditions, and other factors. These figures are based on average performance data from publicly available sources.
Regulatory Landscape and Policy Implications
The global push towards a sustainable future is increasingly influencing the regulatory landscape. Governments worldwide are enacting policies aimed at curbing greenhouse gas emissions and transitioning away from fossil fuels. This creates a complex interplay between Big Tech’s investments, financial markets, and the evolving regulatory environment. Understanding this framework is crucial for assessing the long-term implications of these changes.The regulatory framework surrounding climate change and fossil fuel investments is evolving rapidly.
This evolution is driven by the urgent need to mitigate climate change and transition to a low-carbon economy. The financial implications of these regulations on Big Tech’s investment decisions, and the financial market as a whole, are substantial and multifaceted. The potential for policy changes is significant and warrants careful consideration.
Current Regulatory Framework
Current regulations regarding climate change and fossil fuel investments vary significantly across jurisdictions. Some regions have established carbon pricing mechanisms, while others focus on specific emissions reduction targets. The enforcement and implementation of these regulations also differ widely. Many existing regulations focus on emissions reduction from industrial sources and transportation, with less explicit focus on the indirect emissions linked to investments in fossil fuel infrastructure.
Potential Policy Changes
Several potential policy changes are being considered or already implemented. These include carbon taxes, emissions trading schemes, stricter regulations on the financing of fossil fuel projects, and mandatory disclosure requirements for climate-related risks. The potential impact on Big Tech’s investments in fossil fuels could be substantial, prompting adjustments in investment strategies and portfolio diversification. For example, increased scrutiny on investments in fossil fuel exploration could deter investments, leading to a shift towards renewable energy sectors.
Impact on Financial Markets
The implementation of new regulations can have significant repercussions on the financial market. Changes in investment strategies, portfolio diversification, and the potential for stranded assets could reshape financial flows and market valuations. Carbon pricing mechanisms can introduce price volatility and uncertainty in financial markets, affecting the value of investments. For instance, the introduction of a carbon tax could make fossil fuel projects less profitable, reducing investment in those sectors.
Examples of Existing Regulations
Various jurisdictions have already implemented regulations to mitigate climate change. These include the European Union’s Emissions Trading System (EU ETS), which sets a cap on greenhouse gas emissions from various industrial sectors. The EU ETS is a pioneering example of a market-based mechanism to incentivize emission reductions. Another example is the Paris Agreement, an international accord aimed at limiting global warming.
These regulations demonstrate a growing global commitment to address climate change.
Key Provisions of Relevant Regulations
| Regulation | Key Provisions |
|---|---|
| EU ETS | Sets a cap on greenhouse gas emissions from power plants, industrial facilities, and airlines; allows companies to trade emission allowances. |
| Paris Agreement | Aims to limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels and pursue efforts to limit it to 1.5 degrees Celsius; includes Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) outlining each country’s emissions reduction targets. |
| California’s cap-and-trade program | Sets a cap on greenhouse gas emissions from various sectors in California; allows companies to trade emissions allowances. |
Illustrative Case Studies
Big Tech’s involvement in the fossil fuel industry is a complex issue with significant implications for the environment and the companies themselves. This section delves into specific case studies to examine the impact of these investments on corporate reputation, financial performance, and public perception. It also explores successful transitions away from fossil fuels and the associated benefits.
Case Study: Apple and its Fossil Fuel Investments
Apple’s supply chain has been a subject of scrutiny regarding its reliance on fossil fuels. While Apple has not directly invested in fossil fuel companies, their reliance on suppliers using fossil fuels for manufacturing and transportation raises environmental concerns. The company’s sourcing strategies for raw materials, particularly those used in their products, are a key factor in evaluating their overall environmental impact.
Impact on Apple’s Reputation and Financial Performance
Apple’s public image has been affected by criticism regarding its environmental footprint. Negative publicity regarding its supply chain practices has prompted consumer activism and calls for more sustainable sourcing. While quantifying the direct financial impact is challenging, reputational damage can potentially affect consumer trust and sales, impacting the company’s stock price and brand value.
Apple’s Strategies Regarding Fossil Fuel Investments
Apple has made public commitments to environmental sustainability. These commitments include goals for renewable energy sourcing, reduced carbon emissions, and sustainable packaging. However, the extent to which these strategies address the indirect fossil fuel consumption in its supply chain is still debated. Transparency in their supply chain practices and demonstrable progress toward more sustainable sourcing are crucial.
Apple’s Response to Public Criticism and Advocacy Groups
Apple has publicly responded to concerns raised by environmental groups and consumers. Their responses often emphasize their efforts to improve sustainability within their operations and supply chain. Further scrutiny and detailed reporting of progress are crucial for evaluating the effectiveness of these responses. The company’s actions and public statements are continually assessed by stakeholders.
Case Study: Transitioning Away from Fossil Fuels – Tesla
Tesla, while still operating in the automotive sector, has transitioned significantly toward renewable energy sources. Their investments in battery technology and electric vehicle manufacturing are significant indicators of this shift. Tesla has reduced reliance on fossil fuels in its operations by investing heavily in renewable energy sources.
Positive Outcomes of Tesla’s Transition
Tesla’s shift has led to positive outcomes, including enhanced brand image and customer loyalty. The company has attracted investors who value sustainability and have experienced positive financial performance related to their environmental strategies. This demonstrates a potential positive correlation between sustainability and financial success.
Closing Summary
In conclusion, the intricate relationship between big tech and fossil fuels highlights a critical dilemma. While there are potential financial benefits to these investments, the environmental costs are immense. Shifting towards renewable energy presents both opportunities and challenges, and this discussion underscores the need for innovative strategies and strong regulations. The future of our planet hangs in the balance, and the choices made by tech giants today will shape the world tomorrow.