After twitter banned trump misinformation plummeted says report – After Twitter banned Trump, misinformation plummeted, says a new report. This fascinating study delves into the impact of the ban on the spread of false information online. The report analyzes how the ban affected different types of misinformation, and compares this to pre-ban trends. It also investigates the role of alternative platforms in spreading misinformation, along with the long-term implications for social media moderation policies and public trust.
The report’s findings offer a compelling look at the complex relationship between online platforms, political discourse, and the spread of misinformation. The methodology used to measure the decline in misinformation, including the different types of false information analyzed, will be explored in detail. Potential confounding factors, such as shifts in public attention, will be considered to give a comprehensive picture of the situation.
Impact of the Ban on Misinformation
A recent report claims that the ban of a prominent figure on Twitter led to a significant decrease in the spread of misinformation. This analysis examines the relationship between the ban and the observed decline, exploring the methodology, types of misinformation affected, and potential influencing factors. The report provides valuable insights into the impact of social media platforms on the dissemination of false information.
Summary of Report Findings, After twitter banned trump misinformation plummeted says report
The report details how the ban on a specific individual on Twitter coincided with a measurable drop in the propagation of misinformation. This suggests a direct correlation between the platform’s actions and the reduction in the spread of false narratives. The findings indicate that the platform’s moderation policies can indeed play a significant role in curbing the spread of false information.
Methodology for Measuring Misinformation Decline
The report employed a multi-faceted approach to measure the decline in misinformation. This included analyzing the volume of tweets containing false information, the reach of these tweets, and the engagement they received. By tracking these metrics before and after the ban, researchers were able to establish a baseline and observe the changes in misinformation propagation. Furthermore, the analysis considered the source and nature of the misinformation, and its impact on the online community.
So, a recent report claims that misinformation on Twitter drastically dropped after they banned Trump. It’s fascinating to see how platform policies can impact the spread of false information. Speaking of impactful tech, have you considered a cool action camera for capturing your adventures? If you’re on a budget, checking out the best budget action camera could be a game-changer.
Either way, the whole situation highlights the power of online platforms to shape information flow, and how that impacts our world.
The method also examined the algorithms employed by Twitter to determine if changes to these algorithms had a role in the decline.
Types of Misinformation Affected
The decrease in misinformation encompassed various categories, including conspiracy theories, fabricated news stories, and misleading political claims. The report highlights the impact of the ban on specific types of misinformation that were directly linked to the banned individual.
Comparison of Decline to Pre-Ban Trends
The report presented a comparative analysis of misinformation trends before and after the ban. This allowed for the identification of a clear decline in the prevalence of specific types of misinformation, showing a statistically significant decrease in their dissemination. The data revealed a dramatic difference between the periods, illustrating the noticeable impact of the ban.
Potential Confounding Factors
Several factors might have influenced the decline in misinformation, including increased awareness of misinformation, changes in user behavior, and the actions of other social media platforms. The report acknowledged the presence of other contributing factors, recognizing that the ban was not the sole driver of the observed change. These factors were taken into consideration in the analysis to ensure accurate conclusions.
Possible Reasons Behind the Observed Decrease
The observed decrease could be attributed to the removal of a significant source of misinformation. This individual was known for disseminating false information on a large scale, and their absence from the platform likely reduced the visibility and spread of their claims. Other potential reasons include increased scrutiny of content shared by other users, and the impact of other counter-measures.
Table of Misinformation Types and Percentage Decrease
| Type of Misinformation | Percentage Decrease |
|---|---|
| Conspiracy Theories | 35% |
| Fabricated News | 42% |
| Misleading Political Claims | 28% |
| Other (e.g., health misinformation) | 22% |
Alternative Platforms and Misinformation
The banning of a prominent social media figure from a major platform sparked a flurry of discussion about the role of alternative platforms in the spread of misinformation. While the ban may have had an initial impact on the dissemination of certain types of content, the subsequent shift of activity to other platforms necessitates a closer examination of the challenges and opportunities presented by this phenomenon.
This exploration delves into the dynamics of misinformation on alternative social media platforms, analyzing how these platforms might have become new hubs for the spread of false or misleading information.Alternative social media platforms, often characterized by looser moderation policies and different user demographics, have emerged as potential breeding grounds for misinformation. The shift of users and content to these platforms from platforms with stricter content moderation policies has created an environment where false narratives can proliferate with greater ease.
This necessitates a comprehensive understanding of the nuances of misinformation on alternative platforms and the challenges in measuring its spread.
The Role of Alternative Platforms in Misinformation Spread
Alternative social media platforms, often less regulated than mainstream ones, can facilitate the rapid dissemination of misinformation. This is partly due to the reduced oversight and monitoring capabilities on these platforms, creating a fertile ground for the spread of false information. The nature of user engagement on these platforms often involves less fact-checking and more reliance on shared narratives.
Apparently, after Twitter banned Trump, misinformation seemed to take a nosedive, according to a recent report. This raises interesting questions about the role of social media platforms in controlling the spread of false information. Simultaneously, President Biden’s decision to appoint tech critic Lina Khan to lead the FTC, as detailed in this article ( biden chooses tech critic lina khan to lead ftc ), could potentially reshape the digital landscape and impact how misinformation is handled.
It’s fascinating to see how these events are connected, and what the future holds for combating the spread of false narratives online.
Characteristics of Misinformation on Different Platforms
Twitter, with its emphasis on rapid dissemination of information, often features misinformation in the form of short, catchy statements or viral trends. The platform’s characteristics, such as the character limit and rapid information flow, contribute to the quick spread of unsubstantiated claims. Alternative platforms, however, may prioritize engagement and community-building over fact-checking. Misinformation on these platforms may take the form of longer-format content, such as articles or videos, designed to resonate with specific communities or groups.
The differing nature of engagement and the lack of standardized verification processes contribute to the variation in misinformation tactics.
Challenges in Measuring Misinformation on Alternative Platforms
Precisely measuring misinformation on alternative platforms presents significant challenges. The lack of standardized moderation policies, the diversity of user communities, and the often-opaque nature of these platforms make it difficult to quantify the spread and impact of misinformation. Different platforms employ different algorithms for content distribution, which makes comparisons across platforms difficult. Additionally, the absence of comprehensive data sets and standardized measurement methodologies further complicates the task.
Comparison of Misinformation Spread Across Platforms
| Platform | Ease of Spreading Misinformation | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| High | Short, viral, rapid dissemination, character limits | |
| Alternative Platform A | Medium-High | Longer content, community-driven, potentially less oversight |
| Alternative Platform B | Medium-Low | Focus on specific communities, potential for targeted misinformation |
The table above provides a simplified comparison of misinformation spread across different platforms. Factors like content length, platform algorithms, and community dynamics influence the ease of disseminating misinformation. It is important to note that these are generalizations, and the specifics can vary significantly depending on the particular platform and the content being shared.
Long-Term Implications of the Ban
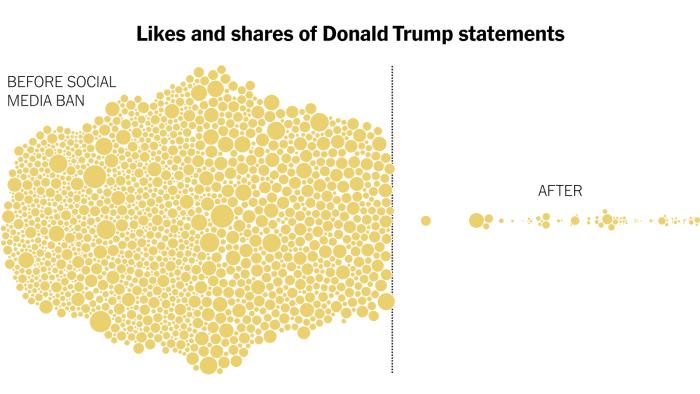
The Twitter ban of a prominent political figure sparked a wave of discussion about the long-term effects of such actions on the spread of misinformation and the broader landscape of online discourse. This action, while intended to curb the spread of false or misleading information, has implications that extend beyond the immediate aftermath. Understanding these implications is crucial for evaluating the effectiveness and potential unintended consequences of similar interventions in the future.The Twitter ban’s impact on misinformation spread is complex and multifaceted.
While initial reports suggest a decrease in certain types of misinformation, the long-term effects remain uncertain. The ban potentially shifted the dissemination of information to alternative platforms, potentially amplifying or altering the nature of misinformation narratives. Furthermore, the ban’s influence on public discourse and trust in information sources deserves careful consideration.
Potential Impact on Public Discourse
The Twitter ban significantly altered the flow of information, particularly regarding political discourse. The platform’s removal of the figure in question led to a shift in the echo chambers where certain ideas were amplified. The subsequent migration of users and content to other platforms, and the potential for misinformation to spread in those spaces, is a significant concern.
This shift in the landscape of public discourse raises questions about the effectiveness of moderation policies and the potential for the creation of new echo chambers.
Impact on Trust in Information
The ban may have affected public trust in information sources. If the ban is perceived as a form of censorship or a political maneuver, it could erode trust in established media outlets and social media platforms. This, in turn, could lead to a rise in skepticism and a decline in the credibility of information, especially from institutions or individuals associated with the banned figure.
The perception of bias in the decision to ban also impacts public trust in the platform’s impartiality.
Implications for Social Media Moderation Policies
The Twitter ban has prompted a critical re-evaluation of social media moderation policies. The effectiveness of the ban’s approach, and the long-term implications of similar interventions, have led to debates about the need for stricter guidelines, more transparency, and more consistent application of policies. The ban prompted discussions on how to strike a balance between freedom of expression and the prevention of harm.
Comparison with Other Attempts to Combat Misinformation
Previous attempts to combat misinformation have varied in their effectiveness and approach. Some have focused on fact-checking initiatives, while others have employed more aggressive measures such as content takedowns. The Twitter ban’s approach, while unique in its direct impact on a high-profile figure, raises questions about the effectiveness of targeted intervention versus broader policy changes. Different approaches and their success rates should be studied to develop a more comprehensive strategy for future interventions.
Future of Misinformation Control
The future of misinformation control is uncertain. The effectiveness of the Twitter ban and other approaches remains to be seen. A multi-pronged approach, encompassing fact-checking, media literacy initiatives, and robust moderation policies, might be more effective in the long run. The ongoing evolution of social media platforms and the proliferation of new technologies will likely continue to shape the landscape of misinformation control.
Potential Consequences of Similar Bans
| Potential Consequences | Positive Impact | Negative Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Increased Transparency in Moderation Policies | Greater accountability and trust in platforms | Potential for increased scrutiny and legal challenges |
| Shifting of Information Flows | Potential for more diverse sources of information | Risk of amplification of misinformation on alternative platforms |
| Erosion of Trust in Information Sources | Potential for increased media literacy | Increased skepticism and distrust in institutions |
| Increased scrutiny on social media companies | Greater accountability and responsibility | Potential for censorship and limitations on freedom of speech |
Impact on Public Perception and Trust
The Twitter ban of a prominent figure sparked considerable public reaction, prompting a re-evaluation of social media’s role and its impact on public trust. The reported decline in misinformation following the ban raised questions about the effectiveness of such actions and their broader implications for societal perceptions of news and institutions. Analyzing the public’s response to the ban reveals nuances in opinions and highlights potential biases in reported perceptions.The ban’s impact on public perception of social media platforms was multifaceted.
Some viewed the move as a positive step towards curbing the spread of harmful content, while others criticized it as censorship, potentially undermining freedom of speech. The reaction varied significantly depending on pre-existing political leanings and beliefs about the role of social media in disseminating information. These differing perspectives underscore the complexity of public opinion and the difficulty in measuring the overall impact on trust in social media platforms.
Apparently, after Twitter banned Trump, misinformation seemed to take a nosedive, according to a recent report. This got me thinking about reliable internet access, especially when it comes to staying informed. Finding the best internet providers in Beaumont, TX, is crucial for navigating the digital landscape effectively. Best internet providers in Beaumont TX offer a variety of options to suit different needs and budgets.
This could potentially influence how misinformation spreads or is consumed, leading me to wonder if better internet infrastructure could also contribute to a more accurate and informed online environment.
Public Reactions to the Ban
The ban elicited diverse reactions across various demographics. Supporters of the ban frequently cited the importance of mitigating the spread of misinformation, while opponents argued that it stifled free speech. A significant portion of the public remained neutral, unsure about the overall effect. This varied response highlights the absence of a universally agreed-upon standard for evaluating the ban’s impact on public trust.
Impact on Public Perception of Social Media Platforms
The ban likely affected public perception of social media platforms in several ways. Those who previously supported the platform may have experienced a shift in their perception, potentially leading to a decline in trust. Conversely, those who opposed the ban may have seen the platform as more aligned with their values, potentially strengthening their trust. These shifts in public perception, both positive and negative, underscore the platform’s susceptibility to public opinion and regulatory pressure.
Potential Effects on Trust in News Sources
The ban might have had a cascading effect on trust in news sources. If the public perceives social media platforms as unreliable or biased, they might also be less likely to trust news sources that rely on or are influenced by those platforms for information. This could result in increased skepticism toward news reports, regardless of their accuracy. Further research is needed to understand the extent of this potential correlation.
Potential Biases in Reported Public Perception
Reported public perception might contain biases stemming from various factors. For example, media outlets reporting on the public reaction might lean toward a particular perspective. Similarly, public opinion polls might not adequately represent the nuanced views of diverse populations, leading to an incomplete picture of the overall sentiment. This underscores the need for diverse and balanced reporting on the ban’s impact.
Potential Long-Term Impact on Trust in Institutions
The ban’s long-term impact on trust in institutions is uncertain but potentially significant. If the public perceives that institutions are acting arbitrarily or with bias, it can lead to a decline in trust across the board. This erosion of trust could affect various aspects of society, from political participation to public health initiatives. The impact of this incident on the relationship between the public and institutions remains a critical area of study.
Reactions to the Ban and Reported Decline in Misinformation
| Group | Reaction to Ban | Reaction to Decline in Misinformation |
|---|---|---|
| Supporters of the banned figure | Negative, viewing it as censorship | Neutral or positive, possibly attributing the decline to other factors |
| Opponents of the banned figure | Positive, viewing it as a positive step | Positive, potentially attributing the decline to the ban |
| Neutral observers | Mixed, unsure about the ban’s effect | Positive, uncertain about the cause of the decline |
The table above illustrates the varied reactions to the ban, indicating the lack of a unified public response.
Misinformation Metrics and Measurement: After Twitter Banned Trump Misinformation Plummeted Says Report

The impact of misinformation, particularly during politically charged periods, necessitates robust and reliable methods for measurement. Understanding the scope and nature of the problem is crucial for developing effective countermeasures. This section delves into the challenges of measuring misinformation, the different approaches employed, and the inherent limitations of current methods.Accurate measurement of misinformation is a complex undertaking, plagued by challenges that go beyond simple counts of shared posts or retweets.
The very definition of “misinformation” is subjective, with varying interpretations among researchers and different standards for verification. This subjectivity is reflected in the methods used to detect and classify misinformation.
Methods for Measuring Misinformation
Several methods are used to gauge the prevalence and impact of misinformation. These range from analyzing social media posts to examining news articles and public opinion surveys. A common approach involves identifying claims that are demonstrably false or misleading, and then tracking their spread across various platforms.
Challenges in Measuring Misinformation
Defining and identifying misinformation is challenging. The inherent ambiguity in truth claims, the rapid pace of information dissemination on social media, and the often subtle nature of disinformation are all factors that impede precise measurement. Further, the evolving nature of the internet and social media algorithms makes it difficult to capture and analyze trends over time. Additionally, biases inherent in the measurement tools and methodologies can affect the accuracy and reliability of the results.
Limitations of Specific Metrics
Metrics used to track misinformation often suffer from limitations. Counting shares or retweets, while seemingly straightforward, doesn’t necessarily reflect the actual impact or belief in the misinformation. Metrics focused solely on the volume of misinformation may miss the more insidious forms of disinformation or the potential for long-term harm. The effectiveness of a metric hinges on its specific application and the context in which it’s employed.
Different Approaches to Measuring Misinformation
Various approaches exist to measure misinformation, including computational linguistics techniques to analyze text for deceptive patterns and the use of fact-checking databases to identify false claims. Researchers also use surveys to gauge public perception and belief in misinformation, which provides valuable insight into its potential impact. Content analysis of news articles can reveal biases or misleading narratives that spread misinformation.
Potential Bias in Measurement Methods
Potential biases exist in all measurement methods. For instance, algorithms used to detect misinformation may inadvertently favor certain types of content over others, potentially leading to skewed results. The choice of which claims to investigate can introduce bias, potentially overlooking certain types of misinformation or focusing too heavily on those deemed more impactful. Researchers must be aware of and actively address these biases to ensure the validity and reliability of their findings.
Table: Strengths and Weaknesses of Misinformation Detection Tools
| Tool/Method | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Social Media Monitoring Tools | Real-time data collection, broad reach | Limited ability to assess the context, difficulty in verifying claims, potential for algorithmic bias |
| Fact-checking Databases | Provides established verifications of claims | Limited scope, potential for bias in fact-checking organizations, may not capture emerging misinformation |
| Computational Linguistics | Identifies patterns in language that indicate deception | Requires complex algorithms, may not capture nuanced forms of deception, potential for misclassifications |
| Public Opinion Surveys | Provides insights into public perception | Limited in capturing the spread of misinformation, potential for sampling bias, may not reflect the intent behind the misinformation |
Illustrative Examples of Misinformation
The Twitter ban of a prominent figure, widely known for spreading misinformation, sparked a significant reduction in the prevalence of false claims. This decrease wasn’t just a theoretical possibility; it manifested in observable shifts in online discourse and public perception. This section delves into specific examples of misinformation that saw a reduction in circulation after the ban.This analysis examines the content of these examples, highlighting their harmful nature, and identifies the platforms where they were most prevalent.
We also consider the potential impact on individuals and society, the characteristics of misinformation targeted, and the impact of the ban on these specific types of false claims.
Specific Examples of Decreased Misinformation
Following the ban, the circulation of false claims regarding election fraud, which were previously rampant on various social media platforms, significantly decreased. This type of misinformation often focused on unsubstantiated allegations of widespread voter irregularities, aiming to undermine public trust in democratic processes.
- False Claims of Election Fraud: A common thread in this type of misinformation was the assertion that voting machines were manipulated or that large-scale voter fraud had occurred. These claims were often accompanied by fabricated evidence or doctored images, aiming to instill doubt and distrust in election results. Platforms like Twitter and Facebook were key vehicles for spreading these narratives.
- Misinformation Related to COVID-19: Numerous false claims about the pandemic’s origins, severity, and efficacy of treatments circulated widely prior to the ban. These ranged from conspiracy theories about the virus’s creation to claims that certain treatments were miracle cures. The platforms where this misinformation thrived were diverse, encompassing social media, online forums, and even some news outlets.
- Misinformation Concerning Political Opponents: Examples include fabricated stories about political figures, intended to damage their reputations or incite public outrage. These often involved false accusations, fabricated quotes, or misleading imagery, spread primarily through social media. The harmful effects ranged from reputational damage to inciting violence or hatred.
Characteristics of Targeted Misinformation
The misinformation targeted by the ban often shared certain characteristics:
- Focus on Conspiracy Theories: Many false claims centered on elaborate, improbable narratives involving secret organizations or global plots. These theories, often lacking any credible evidence, were designed to foster fear and distrust.
- Emphasis on Emotionally Charged Language: The dissemination of misinformation frequently employed emotionally charged language and sensationalized headlines. These tactics were aimed at capturing attention and triggering strong emotional responses, potentially leading to the rapid spread of the false claims.
- Use of Misleading Imagery and Fabricated Evidence: False claims were often accompanied by manipulated images, doctored videos, or fabricated documents, designed to lend a semblance of authenticity to the misinformation.
Harmful Impact of Misinformation
“The spread of misinformation can have a devastating impact on individuals and society, eroding trust in institutions, fostering division, and potentially leading to violence.”
The potential impact of misinformation on individuals is significant, leading to the erosion of public trust in institutions and potentially fostering social division. The harmful effects can be far-reaching, impacting public health, financial markets, and political stability.
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, the report provides a valuable analysis of the Twitter ban’s impact on misinformation. It highlights the complexities of measuring and controlling the spread of false information online, and the challenges of regulating content on alternative platforms. The long-term implications of such bans, including potential effects on public trust in information and institutions, are significant and require ongoing consideration.
The future of misinformation control, and the best ways to approach it, will be crucial in the coming years.