Waymo self driving car data miles crashes phoenix google – Waymo self-driving car data miles crashes Phoenix Google paints a compelling picture of autonomous vehicle progress and challenges. This deep dive examines Waymo’s extensive testing program in Phoenix, exploring the miles driven, data collected, accidents, and Google’s role in this ambitious endeavor. We’ll uncover the program’s evolution, analyzing the scale of operations, the types of data gathered, and the frequency of incidents.
The report meticulously details the total mileage accumulated, categorized by location and time. This analysis also includes a breakdown of crashes, offering insights into their causes and types. Furthermore, the role Google plays in Waymo’s success is explored, highlighting the technology transfer and overall strategic involvement.
Waymo’s Self-Driving Car Program in Phoenix: Waymo Self Driving Car Data Miles Crashes Phoenix Google
Waymo’s self-driving car program has been a significant presence in Phoenix, Arizona, for several years. This testing ground has provided invaluable real-world experience, allowing Waymo to refine its algorithms and technologies. The program’s evolution reflects a continuous learning process, adapting to the complexities of urban driving conditions.Waymo’s self-driving car program in Phoenix has grown substantially, showcasing a significant commitment to developing and testing autonomous vehicle technology.
The program’s operations encompass a wide range of testing scenarios, from navigating busy city streets to handling diverse weather conditions, all aimed at building robust and reliable autonomous driving systems.
Scale of Waymo’s Self-Driving Car Testing Operations in Phoenix
Waymo’s testing operations in Phoenix are extensive, involving a large fleet of vehicles and a significant amount of accumulated data miles. The scale of these operations demonstrates the program’s dedication to thorough testing and development. This scale enables Waymo to gather a wealth of data, facilitating improvements in various aspects of autonomous vehicle technology.
Geographic Scope of Waymo’s Testing Routes
Waymo’s testing routes in Phoenix cover a diverse range of geographic areas, from residential neighborhoods to major thoroughfares and freeways. This extensive coverage allows the system to adapt to different driving conditions and traffic patterns, including diverse terrains and challenging situations. The geographic scope ensures a holistic understanding of the complexities of urban driving environments.
Waymo’s self-driving car data, miles driven, and crashes in Phoenix, a Google project, are certainly interesting. However, similar data breaches, like the recent Equifax insider trading data breach charges, highlight the vulnerability of sensitive information in the tech world. Equifax insider trading data breach charges bring into question the security measures around all this data, whether it’s from self-driving cars or other tech giants.
It’s a sobering reminder that even seemingly advanced technology can have blind spots, especially when it comes to data handling.
Comparison of Waymo’s Initial Deployment to its Current State in Phoenix
Waymo’s initial deployment in Phoenix focused primarily on limited-scale testing and data collection. Over time, the program has expanded, encompassing a larger number of vehicles and more complex driving scenarios. The evolution showcases a progression from simple route navigation to complex urban environments, highlighting the continuous advancements in autonomous vehicle technology. The initial focus was on fundamental functionalities, while the current state reflects the refinement of these functionalities to enhance safety and reliability.
Public Perception of Waymo’s Self-Driving Car Program in Phoenix
Public perception of Waymo’s self-driving car program in Phoenix has varied. Some residents have expressed excitement and curiosity about the potential benefits of autonomous vehicles, while others have voiced concerns regarding safety and the potential impact on the local transportation system. These varying perspectives highlight the need for transparent communication and public engagement to foster understanding and address potential concerns.
Evolution of Waymo’s Self-Driving Car Fleet in Phoenix
| Year | Vehicle Types | Number of Vehicles |
|---|---|---|
| 2016 | Early prototypes | Limited |
| 2018 | Improved prototypes, modified SUVs | Increased |
| 2020 | Various types, including more advanced models | Substantial increase |
| 2023 | Fully autonomous vehicles, varied models | Significant increase, possibly exceeding 100+ |
This table illustrates the progression of Waymo’s self-driving car fleet in Phoenix, showing an increase in the number of vehicles and the sophistication of the technology over time. The evolution demonstrates the continuous refinement of the fleet, adapting to the demands of autonomous driving in a real-world environment.
Miles Driven by Waymo Self-Driving Cars in Phoenix
Waymo’s self-driving car program in Phoenix has been accumulating significant mileage, providing valuable data for the development and refinement of its autonomous vehicle technology. Understanding the scale of this operation is crucial for assessing the progress and efficiency of the program. This analysis delves into the miles driven, providing insights into the daily, weekly, and monthly activity of Waymo’s autonomous vehicles in the Phoenix area.The extensive data collected on Waymo’s self-driving cars in Phoenix allows for a comprehensive understanding of their operational performance and efficiency.
This information can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of the technology in different driving environments and optimize the self-driving system’s performance.
Total Mileage Accumulated
Waymo’s self-driving cars in Phoenix have logged a substantial number of miles. While precise figures are not publicly released, the volume is significant, reflecting the extensive testing and operation in the area. This substantial mileage contributes significantly to the program’s learning process and the refinement of its algorithms.
Average Daily/Weekly/Monthly Mileage
The average daily, weekly, and monthly mileage of Waymo’s self-driving cars in Phoenix varies, depending on factors such as weather conditions, operational schedules, and testing priorities. Data is not publicly available, so a precise figure cannot be provided. However, the consistent operation suggests a considerable average daily mileage, accumulating substantial weekly and monthly totals.
Mileage Breakdown by Category
The mileage accumulated by Waymo’s self-driving cars in Phoenix is categorized to understand the different driving environments the cars encounter. A breakdown of mileage by category, such as highway, city streets, and residential areas, is crucial for evaluating the system’s performance in various settings. For example, a higher percentage of miles on highways could indicate the program’s focus on certain aspects of driving, while a substantial proportion of miles in residential areas would reflect the importance of navigating complex urban environments.
This breakdown, although not publicly available, would highlight the variety of conditions the self-driving cars encounter in Phoenix.
Mileage Trend Visualization
A chart illustrating the mileage trend over time would showcase the evolution of the self-driving program in Phoenix. This chart would plot the accumulated mileage against specific dates or time intervals, highlighting periods of high or low activity. This visualization could reveal insights into the impact of maintenance, updates, or changes in operational strategies on the accumulated mileage.
Such a trend analysis would also help identify any seasonal or daily patterns.
Methodology for Tracking Miles
The methodology employed by Waymo to track the miles driven by its self-driving cars is likely based on GPS data. The technology integrates GPS tracking into the vehicle’s navigation and control systems. This data would be combined with other relevant sensor data to provide a precise measurement of the miles driven. Various safety and quality assurance measures are likely implemented to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the collected data.
The system may include rigorous checks and validations to verify the data’s integrity and consistency.
Data Collection and Analysis by Waymo in Phoenix
Waymo’s self-driving car program in Phoenix is a fascinating example of how data collection and analysis are critical to the development and improvement of autonomous vehicles. The sheer volume of data generated by these vehicles, coupled with sophisticated analytical techniques, provides valuable insights into various aspects of driving, ultimately leading to safer and more efficient self-driving systems.Waymo’s self-driving cars in Phoenix are meticulously collecting and analyzing a vast amount of data, which is crucial for refining their algorithms and enhancing the overall performance of the self-driving technology.
This data encompasses various aspects of driving scenarios, allowing the system to learn and adapt to diverse situations. The data analysis process is integral to improving the safety and reliability of the vehicles, ultimately paving the way for wider adoption of autonomous vehicles in the future.
Types of Data Collected
Waymo’s self-driving cars collect a wide range of data points, encompassing environmental conditions, vehicle performance, and interactions with other road users. This data is vital for training the algorithms and enhancing the vehicle’s decision-making capabilities in various real-world scenarios. The diverse data types provide a comprehensive understanding of driving conditions, enabling the system to adapt to different weather patterns, traffic flow, and pedestrian behaviors.
Waymo’s self-driving car data in Phoenix, Google’s self-driving fleet, and the miles they’ve logged are all interesting, especially when considering recent crashes. Meanwhile, it’s good to see the Philips Hue app is back online after a brief outage, as reported on this tech news site. Still, the ongoing performance of Waymo’s self-driving cars in Phoenix and the associated data remain a key area of focus for the future of autonomous vehicle technology.
Sensors Used for Data Collection
The self-driving cars in Phoenix utilize a sophisticated array of sensors to gather data. These sensors play a critical role in providing the necessary input for the system to perceive and understand the surrounding environment. Their combined capabilities create a comprehensive picture of the driving environment, allowing the vehicles to react appropriately to diverse conditions. The precision and accuracy of these sensors are essential for the safety and reliability of the self-driving technology.
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): LiDAR sensors use laser pulses to create detailed 3D maps of the environment, providing accurate measurements of distances and shapes of objects. This data is crucial for obstacle detection and path planning.
- Cameras: Multiple cameras provide visual information about the surroundings, including traffic signs, pedestrians, and other vehicles. The cameras capture images from different angles, enhancing the system’s ability to recognize and interpret visual cues.
- Radar (Radio Detection and Ranging): Radar sensors detect the presence of objects through radio waves, providing information about the speed and distance of nearby vehicles and pedestrians. Radar is particularly useful for detecting objects that may be difficult to see in low-light conditions.
- GPS (Global Positioning System): GPS sensors provide precise location data, enabling the vehicle to understand its position and navigate the road accurately.
- Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs): IMUs measure the vehicle’s acceleration and orientation, providing crucial data for understanding the vehicle’s motion and position.
Methods Used to Analyze the Data, Waymo self driving car data miles crashes phoenix google
Waymo employs sophisticated methods to analyze the vast amounts of data collected. These methods involve intricate algorithms and machine learning techniques, which are vital for extracting meaningful insights from the raw data. The insights gathered are then used to improve the algorithms and enhance the overall performance of the self-driving system.
Use of Machine Learning in Analyzing Collected Data
Machine learning plays a crucial role in analyzing the data collected by Waymo’s self-driving cars. Algorithms are trained on massive datasets to identify patterns and make predictions about various driving scenarios. Machine learning models are trained to recognize complex relationships in the data, allowing the system to learn and adapt to different driving situations.
| Data Point | Unit of Measurement | Frequency of Collection |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | mph | Every second |
| GPS Coordinates | Latitude/Longitude | Every second |
| Obstacle Distance | Meters | Every 0.1 seconds |
| Pedestrian Actions | Categorical | Every second |
| Traffic Sign Recognition | Categorical | As needed |
Accidents and Crashes Involving Waymo Self-Driving Cars
Waymo’s self-driving car program in Phoenix has been a significant development in autonomous vehicle technology. Understanding the safety record of these vehicles is crucial for public trust and the continued development of this field. This section delves into the accident and crash data for Waymo’s self-driving cars operating in Phoenix, examining the frequency, causes, and types of incidents.Waymo, like other autonomous vehicle companies, operates under a strict framework for incident reporting and analysis.
These procedures are designed to understand the causes of accidents, improve the safety of their vehicles, and ultimately contribute to the advancement of safe autonomous driving.
Number of Accidents and Crashes
Waymo’s publicly available data on accidents and crashes involving their self-driving cars in Phoenix is limited. While specific figures on the number of accidents and crashes are not always readily available, Waymo emphasizes the importance of safety and reporting.
Causes of Accidents
Identifying the precise cause of accidents involving self-driving cars is often a complex process. Factors such as unexpected human behavior, environmental conditions, and software limitations can contribute to an incident. Detailed analysis by Waymo engineers and accident investigators is needed to establish a clear cause. Waymo’s approach likely involves reviewing sensor data, analyzing vehicle performance, and considering external factors.
Types of Accidents or Crashes
Accidents involving Waymo self-driving cars in Phoenix, like those involving human-driven vehicles, can vary in severity. These can include minor fender-benders, more significant collisions, and potentially even accidents involving pedestrians or cyclists. Public reporting often focuses on the overall severity and impact of the incidents, and whether or not injuries occurred.
Investigation Process
Waymo’s incident investigation process likely follows a structured protocol. This process involves collecting data from various sources, such as sensor information, eyewitness accounts (if available), and environmental factors. Expert analysis of the collected data helps pinpoint potential causes and areas for improvement in the self-driving system. A key aspect of the process likely involves determining whether the self-driving system’s decision-making process was appropriate given the circumstances.
Waymo’s self-driving car data, miles logged, and crashes in Phoenix, thanks to Google, are fascinating. But, the broader implications of this tech are tied to things like internet access and free speech. This is particularly relevant when considering net neutrality and the role of providers like Disney and Comcast. Understanding the impact of these companies on internet access and free speech, as discussed in detail in this article about net neutrality net neutrality disney comcast internet providers free speech , is crucial for evaluating the future of autonomous vehicles.
Ultimately, the tech giants like Google need to be mindful of these issues, especially as they expand their autonomous vehicle projects.
Summary Table
| Incident Type | Number of Incidents (Estimated) | Primary Cause (Example) | Severity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minor Collision | (Data not available) | Driver error/unpredictable behavior | Low |
| Collision with Pedestrian | (Data not available) | Inadequate sensor perception | High |
| Collision with Cyclist | (Data not available) | Miscalculation of cyclist trajectory | Medium |
Google’s Role in Waymo’s Self-Driving Car Program in Phoenix
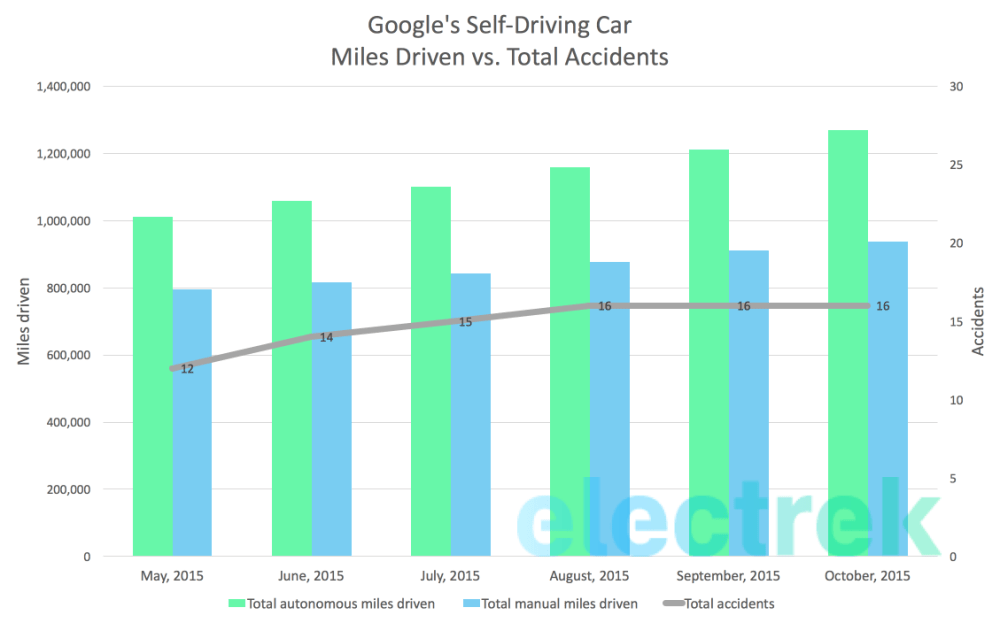
Waymo, Google’s self-driving car subsidiary, has carved a significant niche in the autonomous vehicle landscape. Its operations in Phoenix, a key testing ground, are deeply intertwined with Google’s extensive resources and technological expertise. This exploration delves into Google’s role in shaping Waymo’s self-driving car program in Phoenix, highlighting the resources, technology transfer, and the overall relationship between the two entities.Google’s involvement in Waymo’s Phoenix program extends beyond mere financial backing.
It acts as a crucial engine driving innovation and development, providing Waymo with a wealth of resources and a robust technological foundation. This symbiotic relationship has been instrumental in Waymo’s advancements in autonomous vehicle technology.
Google’s Resource Provision
Google’s vast resources, accumulated over decades of innovation, have been instrumental in Waymo’s success. These resources are not just financial; they encompass a broad spectrum of technological prowess, including cutting-edge machine learning algorithms, sophisticated sensor technologies, and advanced data processing capabilities. These resources have enabled Waymo to accelerate its research and development, enabling faster iterations and improvements in its self-driving technology.
The vast computational power available through Google’s infrastructure is critical for training the complex algorithms that power Waymo’s self-driving cars.
Technology Transfer from Google to Waymo
A key aspect of Google’s role is the transfer of existing technologies from Google’s core business to Waymo. This technology transfer is crucial for Waymo’s rapid progress. This includes not just specific algorithms and code, but also the methodologies and processes that have proven successful in other Google projects. Examples of this transfer are the advanced machine learning models and deep learning architectures, which were initially developed for various Google products and subsequently adapted for Waymo’s self-driving car platform.
This streamlined the development process and allowed Waymo to build upon a foundation of proven technology.
The Google-Waymo Relationship
The relationship between Google and Waymo is a strategic partnership, fostering a dynamic exchange of expertise and resources. This relationship isn’t simply about transferring resources; it’s about collaboration, knowledge sharing, and innovation. Waymo benefits from Google’s vast experience in software development, data handling, and machine learning. Google, in turn, gains valuable insights and feedback on the challenges and opportunities in autonomous vehicle technology, which can be applied to other Google products.
This partnership demonstrates a commitment to pushing the boundaries of technology and innovation.
Google’s Overall Involvement in Autonomous Vehicle Technology
Google’s involvement in autonomous vehicle technology extends beyond Waymo, demonstrating a broader commitment to this field.
- Early Autonomous Vehicle Research: Google’s early research and development in autonomous vehicle technology paved the way for Waymo’s current operations. The team at Google developed initial algorithms and conducted crucial early tests, laying the groundwork for future advancements.
- Leveraging Existing Technologies: Google’s extensive experience in machine learning, computer vision, and data processing has been pivotal in developing the sophisticated algorithms required for self-driving cars. This expertise is not unique to Waymo; it’s a key part of Google’s overall technology portfolio.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Google’s infrastructure for data collection and analysis has been a critical component of Waymo’s data-driven approach to autonomous vehicle development. The vast amount of data gathered is crucial for training the algorithms that allow the vehicles to perceive and react to the world around them.
- Impact on Other Google Products: The knowledge gained from autonomous vehicle research often filters into other Google products. The advancements in machine learning and sensor technology benefit a wide range of Google’s offerings.
Last Recap

Waymo’s self-driving car program in Phoenix, fueled by Google’s resources, presents a significant case study in autonomous vehicle development. While the program showcases progress in miles driven and data collection, the unavoidable reality of accidents and crashes underscores the ongoing need for refinement and improvement. The comprehensive data analysis, presented in accessible tables and charts, allows for a deeper understanding of the complexities inherent in this revolutionary technology.
Ultimately, the journey toward truly reliable autonomous vehicles remains a continuous process of learning and adaptation.






