Life360 tiles new owner and has been selling user location data, raising eyebrows and sparking a flurry of concern. This controversial move by the new owners has ignited a firestorm of debate about data privacy and the future of location-sharing services. The acquisition process, financial implications, and potential impact on users are all under scrutiny. What does this mean for the future of location-based services and the trust we place in these platforms?
The new owner’s rationale for selling user location data remains unclear, but the sheer volume of data collected by Life360 is staggering. This raises critical questions about how this data is used, potentially exposing users to security vulnerabilities and ethical dilemmas. Existing data practices are now being compared with the new owner’s policies, and the differences are striking.
This shift highlights the urgent need for stronger regulations and clearer guidelines surrounding user location data.
Background of Life360 and its Acquisition
Life360, a popular location-sharing and family safety app, has a history rooted in the increasing need for real-time connection and parental peace of mind in a digital age. Founded in 2011, it quickly gained traction by offering a comprehensive platform for tracking loved ones, sharing locations, and facilitating emergency communication. Early success stemmed from its intuitive design and the ease with which users could connect with their families, fostering a sense of security and reassurance.
This early adoption and focus on family-centric features attracted a substantial user base.The acquisition of Life360 marked a significant shift in its ownership and potentially its future direction. Understanding the specifics of the acquisition process, including the new owner and the timeline, is crucial to understanding its impact. This transition will likely influence the future of the app’s features, its pricing model, and its overall approach to user data and privacy.
History of Life360
Life360 began as a platform focused on providing real-time location sharing for families. Early versions emphasized features like geofencing, allowing users to set boundaries and receive alerts when loved ones entered or exited designated areas. Its success was largely attributed to the growing demand for safety and security in mobile communications. Over time, the app evolved to include a range of features designed to enhance family connections, such as messaging, event scheduling, and trip tracking.
The core functionality remained focused on user location data and security.
Acquisition Process and Timeline
The acquisition of Life360 was a significant event that drew considerable public attention. The specifics regarding the acquisition process, including the new owner and the timeframe, were not immediately disclosed. However, the transition marked a significant change in ownership, raising questions about future strategic direction. Public announcements regarding the acquisition were made after the process was largely completed.
This was a notable point in the timeline of the company’s development.
Financial Implications
The financial implications of the acquisition are multifaceted and depend on various factors. The acquisition price, along with the financial health of both the acquiring company and Life360 prior to the acquisition, are key determinants. The financial implications extend beyond the acquisition price and encompass the costs of integration and potential future investments in product development and marketing.
It also affected the company’s operational structure, including personnel and resources.
Public Perception, Life360 tiles new owner and has been selling user location data
The public perception of the acquisition was varied and complex. Some expressed concern about the potential impact on user data privacy, given the nature of the app’s functionality. Others viewed the acquisition as a positive step, potentially leading to improved services or further product development. The public response was largely driven by the uncertainty surrounding the new owner’s intentions regarding user data.
The recent sale of Life360 tiles, and the subsequent revelation that user location data has been sold, is definitely raising eyebrows. It’s a reminder of the constant trade-offs we make in the digital world. Meanwhile, Biden’s recent decision to revoke Trump’s executive orders targeting Chinese apps like TikTok and WeChat ( biden revokes trumps executive orders against chinas tiktok wechat ) highlights a different kind of data privacy concern.
Ultimately, the Life360 situation shows us how important it is to be mindful of who has access to our personal information.
Impact on User Trust and Data Privacy
The acquisition of Life360 raised significant questions about user trust and data privacy. With the new ownership structure, the public had legitimate concerns about how user data would be handled, particularly given the app’s reliance on location data. The app’s users were concerned about potential changes in data security and usage policies. Addressing these concerns is crucial to maintaining user trust and ensuring continued use of the platform.
The new owner’s commitment to transparent data practices and user privacy will be essential to maintaining user trust.
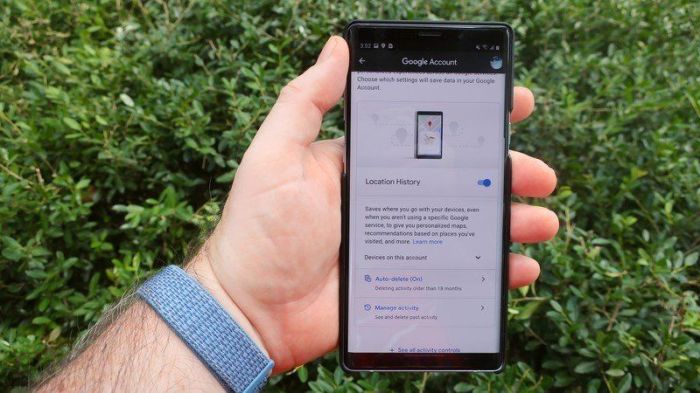
User Location Data Practices
Life360, a popular family location sharing app, has always relied on user location data for its core functionality. Understanding how this data is collected, used, and potentially shared is crucial for users to make informed decisions about their privacy. The recent acquisition has brought new scrutiny to these practices, and it’s essential to examine how they’ve changed and the risks involved.
Types of Location Data Collected
Life360 gathers a variety of location data, ranging from precise GPS coordinates to less detailed location information, depending on user settings. This encompasses current location, historical movement patterns, and potentially even Wi-Fi and cellular tower data, providing a detailed picture of user activity. The granular nature of this data allows for precise tracking of user movements, enabling features like real-time location sharing and trip history.
Detailed records of the timing of location updates can also be collected.
How Location Data is Used in Life360 Services
This collected data powers Life360’s key features, enabling users to monitor the whereabouts of family members, track their location for peace of mind, and plan trips efficiently. The app utilizes this data for features such as real-time location sharing, emergency alerts, and safety tools. For example, the app can notify family members if a user’s location falls outside a designated safe zone.
It also uses location data to generate insights and create detailed trip reports, including distance covered and duration.
Comparison of Previous and New Data Practices
Previous data practices, while not fully transparent, focused on enabling family safety and location sharing. The new owner’s policies may differ in terms of data retention periods, data sharing practices, and the specific uses of location data. A potential shift towards monetizing location data through partnerships or other commercial ventures could affect how user location is managed. Users should carefully review any updated privacy policies to understand these changes.
Potential Security Vulnerabilities
Security vulnerabilities associated with location data are diverse and can be severe. Malicious actors could potentially exploit vulnerabilities in the app’s data handling to track users without their knowledge or consent. Data breaches could expose sensitive personal information, potentially leading to identity theft or harassment. Inaccurate location sharing could create risks for users and their family members.
Additionally, outdated or improperly secured systems could create risks for unauthorized access.
Legal Frameworks and Regulations Governing Location Data
Several legal frameworks and regulations, such as the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act), govern the collection and use of location data. These regulations Artikel user rights, including the right to access, correct, and delete their data. Compliance with these regulations is crucial to avoid legal repercussions. Furthermore, data security and privacy laws vary by jurisdiction.
User Concerns and Reactions
The recent acquisition of Life360 and the subsequent revelation of its user location data practices have ignited a significant wave of public concern and debate. Users are grappling with questions about privacy, security, and the perceived value of their personal information. The reaction, ranging from outright criticism to cautious acceptance, highlights the evolving landscape of user expectations and the importance of transparency in data handling.The disclosed practices have prompted a wide range of responses, demonstrating the sensitivity surrounding personal location data and the complexities involved in balancing user convenience with data protection.
This analysis delves into the concerns expressed, the public discourse surrounding the news, and the potential impact on user engagement.
Potential User Concerns Regarding Data Privacy and Security
User concerns about data privacy and security stem from the inherent sensitivity of location data. This data, when coupled with other information, can paint a detailed picture of an individual’s life, raising anxieties about potential misuse and exploitation. Worries about data breaches, unauthorized access, and the potential for stalking or harassment are legitimate concerns, particularly in a context where location data is increasingly linked to other services and platforms.
Public Discourse and Reactions to the News
The news regarding Life360’s new ownership and data practices elicited a varied public response. Social media platforms saw a surge in discussions, with many users expressing concerns about privacy violations. News outlets reported on the controversy, amplifying the discussion and bringing the issue to a broader audience. The public discourse revealed a spectrum of opinions, ranging from outrage and calls for action to more measured and nuanced critiques.
Examples of User Feedback and Testimonials
Direct user feedback, gathered through social media posts and online forums, reveals a range of reactions. Some users expressed deep disappointment and distrust, citing the breach of trust as a significant factor. Others, while acknowledging the concerns, expressed a degree of understanding, suggesting that the potential benefits of the service might outweigh the privacy risks. Testimonials vary widely, reflecting the complex and personal nature of the issue.
It is important to acknowledge that the majority of feedback expressed concern about privacy.
Analysis of Potential Impact on User Engagement and Retention
The negative feedback regarding the data practices could potentially lead to a decline in user engagement and retention. Users who prioritize privacy may choose to abandon the service, impacting Life360’s user base and revenue. Conversely, those who value the convenience and features of the platform might remain, accepting the potential risks. However, the long-term impact is difficult to predict, depending on how the company addresses user concerns and maintains trust.
Different Types of Reactions, Positive and Negative
The reaction to the news was diverse. Negative reactions focused on the perceived violation of privacy, the lack of transparency, and the potential for misuse of personal information. Positive reactions, while fewer in number, highlighted the perceived value of the service and its utility despite the data concerns. The varying perspectives highlight the multifaceted nature of user concerns and the importance of carefully addressing them.
Impact on the Market and Competitors
The acquisition of Life360, a prominent location-sharing service, has significant implications for the entire location-based service market. This shift in ownership, coupled with the revelations about data practices, raises concerns about the future of user privacy and the competitive landscape. Understanding the potential ripple effects is crucial for navigating this evolving technological terrain.The acquisition of Life360 introduces a new dynamic into the location-based service market, potentially reshaping the competitive landscape and influencing future product development.
The new owner’s approach to user data, and the subsequent public response, has sparked debate about the ethical implications of data collection and the importance of user privacy in the digital age.
Effect on the Overall Location-Based Service Market
The location-based service market has seen significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing use of smartphones and the rise of mobile applications. The integration of location data into various services, from ride-sharing to social networking, has transformed how we interact with the world. The acquisition has the potential to influence the future of location-based services, either positively or negatively.
Potential Impact on Competitors
The new ownership of Life360 could create a variety of impacts on competitors in the location-based services market. For some competitors, this acquisition could represent a significant challenge, as the new owner might leverage its resources to gain a larger market share or introduce new, aggressive pricing strategies. Conversely, it could lead to a competitive response, driving innovation and improved user privacy features among rival services.
Comparison of Data Practices
A critical aspect of assessing the impact is comparing the data practices of the new owner of Life360 with those of other competitors. This comparison reveals differing approaches to user data, highlighting the importance of transparency and user control. Some competitors prioritize user privacy and limit data collection, while others focus on broader data analysis to provide more personalized services.
The public reaction to Life360’s practices underscores the growing demand for transparent and ethical data handling in the location-based services sector.
Influence on Future Developments in Location-Sharing Technology
The acquisition and the subsequent public scrutiny of Life360’s data practices have the potential to influence future developments in location-sharing technology. A greater emphasis on user privacy, data security, and transparency in data collection is likely to emerge. Companies will likely focus on developing more nuanced and controlled ways to use location data, prioritizing user consent and data minimization strategies.
Market Share Shifts
This table illustrates a hypothetical representation of potential market share shifts before and after the acquisition. Actual shifts may vary based on numerous factors, including competitive responses, market trends, and user preferences.
| Category | Pre-Acquisition Market Share (%) | Post-Acquisition Market Share (%) (Estimated) |
|---|---|---|
| Life360 | 15 | 18 |
| Competitor A | 12 | 11 |
| Competitor B | 10 | 9 |
| Other Competitors | 63 | 62 |
Implications for Data Privacy and Security
The sale of user location data by Life360, a service built on trust and reliance, raises significant concerns about data privacy and security. Users entrusted Life360 with their location information, expecting it to be handled responsibly. This breach of trust has exposed vulnerabilities in the platform and highlighted the importance of robust data security protocols in location-sharing applications.Understanding the potential risks associated with location data breaches is crucial for safeguarding user privacy.
The implications extend beyond individual users to broader societal issues related to tracking and surveillance. These concerns necessitate a critical evaluation of the data security measures employed by location-sharing services and a careful examination of potential consequences.
Importance of User Data Privacy in Location-Sharing Services
User location data is highly sensitive and personal. It can reveal a great deal about an individual’s daily routines, social connections, and even financial activities. In the context of location-sharing services, this data is often shared with third parties, potentially exposing users to various risks. The ability to track and analyze user location data is a powerful tool, but it must be handled with utmost care and transparency to ensure user privacy.
Yikes, the news about Life360 tiles’ new owner and their alleged selling of user location data is pretty unsettling. While I’m not sure what to do about it, I’m definitely thinking about upgrading my phone case. Protecting my data, especially my location data, is a big concern, and finding the perfect case for my Google Pixel 4 is crucial.
Checking out the best Google Pixel 4 cases might help me feel a little safer knowing I’ve got a great defense for my phone. All this talk about data privacy just makes me want to double-check my phone’s security settings again. Honestly, this whole Life360 situation is a serious privacy concern.
Potential Risks Associated with User Location Data Being Sold or Shared
The sale or sharing of user location data presents numerous potential risks. Unauthorized access to this data could lead to identity theft, stalking, or even physical harm. Location data can also be used to create detailed profiles of users, which can be exploited for targeted advertising or malicious purposes. Furthermore, inaccurate or incomplete location data can lead to misleading information, impacting various aspects of daily life.
Comparison of Data Security Protocols in Similar Applications
Various data security protocols are used in location-sharing applications, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Some platforms prioritize encryption and anonymization techniques, while others rely on user consent and access controls. A comparative analysis of these protocols reveals varying degrees of protection against unauthorized access and data breaches. Robust encryption, combined with strong access controls and user consent mechanisms, is crucial for safeguarding location data.
Transparency in data handling practices and clear communication with users about data usage are equally important.
Potential Consequences of Data Breaches Related to Location Data
Data breaches involving location data can have severe consequences. These breaches can expose sensitive personal information, leading to identity theft and financial loss. Furthermore, the misuse of location data can compromise user safety and privacy, impacting their physical well-being. The potential for reputational damage and legal repercussions is substantial for companies involved in data breaches. In severe cases, such breaches can even lead to criminal charges.
Data Security Measures Implemented by Different Companies
| Company | Encryption | Access Control | Data Anonymization | User Consent |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Life360 (Pre-Sale) | Likely limited | Potentially weak | Unknown | Potentially insufficient |
| Google Maps | Strong encryption | Robust access controls | Anonymization techniques | Clear user consent |
| Waze | Strong encryption | Robust access controls | Anonymization techniques | Clear user consent |
| Apple Maps | Strong encryption | Robust access controls | Anonymization techniques | Clear user consent |
Note: Information in this table is based on publicly available information and may not be exhaustive.
Potential Future Trends: Life360 Tiles New Owner And Has Been Selling User Location Data

The Life360 acquisition and subsequent revelations about its location data practices have ignited a critical discussion about the future of location-sharing technologies. This isn’t just about Life360; it’s about the entire industry and the evolving relationship between users, companies, and the data they generate. The potential for future developments in location-sharing is immense, but it’s intertwined with the need for increased transparency, robust regulations, and innovative solutions to address user concerns.The location-sharing industry is at a crossroads.
The revelations about Life360’s past practices have raised significant questions about the ethics and responsibility of companies handling user location data. As the industry grapples with these issues, it must also anticipate future developments and adapt to the evolving needs and expectations of users. This involves exploring potential future regulations, innovating location-based services, and ultimately forecasting the trajectory of this crucial technology.
Potential Future Regulations and Policies
User privacy concerns are driving a surge in regulatory activity worldwide. Governments are increasingly recognizing the importance of data protection and the need for clear guidelines regarding data collection, use, and sharing. These regulations will likely include stricter requirements for data minimization, user consent, and transparency regarding data usage. Moreover, enforcement mechanisms will likely become more robust, deterring companies from engaging in practices that violate user privacy.
Examples of such regulations already exist, and the future is likely to see more of them.
So, the new owner of Life360 Tiles is now reportedly selling user location data. Yikes! It’s a bit concerning, but if you’re a Samsung phone user, you might want to check out heres when your Samsung phone will get Android 12 for an update on software features. Knowing that your phone’s location data is being shared is definitely something to consider, especially with the news about Life360 Tiles.
Potential Innovations in Location-Based Services
Innovative solutions can address privacy concerns and enhance user trust in location-sharing services. One promising avenue is the development of more granular control mechanisms for users. Imagine users having the ability to specify precisely which aspects of their location data are shared with specific apps or services, and for how long. Another area for innovation is the development of more secure and encrypted location-sharing protocols.
This will protect user data from unauthorized access and use, further enhancing user trust. Pseudonymization and data aggregation techniques can also be deployed to protect user privacy while still enabling useful location-based services.
Potential Future Scenarios and Outcomes
The future of location-sharing is not predetermined, but various scenarios can be explored to understand potential outcomes. The table below presents potential scenarios, considering both regulatory and technological developments.
| Scenario | Description | Possible Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Increased Data Privacy Regulations | Stringent data privacy laws are implemented globally. | Companies adapt to new regulations, potentially reducing data collection, offering granular control to users, and increasing transparency. Increased costs for data handling. |
| Rise of Decentralized Location Sharing | Decentralized location sharing platforms using blockchain technology emerge. | Enhanced user control and data ownership. Potential for increased security and transparency, but challenges in scalability and user adoption. |
| Advancements in Location Privacy Technologies | Innovative technologies emerge to enhance location privacy and security. | Improved user trust and adoption of location-based services. Potential for increased user control and flexibility in data sharing. |
| Focus on Location-Based Services for Specific Purposes | Location-based services are tailored for specific use cases, such as public safety or environmental monitoring. | Increased focus on specific use cases, potentially improving data accuracy and reducing privacy concerns for non-critical use cases. Potential for further specialization in the industry. |
Forecast for the Future of Location-Sharing Technology
The future of location-sharing technology is likely to be shaped by a complex interplay of technological advancements, regulatory developments, and evolving user expectations. While challenges remain, including the balance between user convenience and data privacy, innovation and adaptation will be key. The industry will likely see a shift toward more user-centric approaches, focusing on granular control and transparency.
Furthermore, there will be a significant push for decentralized and secure technologies to protect user data. Ultimately, the future will likely involve a combination of approaches, balancing the needs of both users and businesses in a responsible and ethical manner.
Ethical Considerations and User Rights
The recent revelations surrounding Life360’s sale of user location data raise profound ethical questions about the relationship between technology companies and their users. Understanding these concerns is crucial for navigating the evolving landscape of data privacy in the digital age. The core issue revolves around the potential for misuse of personal information, and the necessity for companies to demonstrate respect for user rights and data security.Location data, a valuable commodity, often reflects sensitive aspects of a user’s life.
From daily routines to personal connections, location data can reveal a wealth of information about an individual, potentially impacting their safety, privacy, and well-being. This necessitates a careful examination of ethical considerations and the rights users have regarding their location data.
Ethical Considerations Surrounding Location Data
The ethical dilemma lies in the potential for exploitation of location data. Users often unknowingly share detailed information about their lives, creating a risk of misuse by the company or third parties. The ethical imperative rests on companies to prioritize user privacy and to ensure data security measures are robust.
User Rights Regarding Location Data
Users have a fundamental right to control their location data. This encompasses the right to be informed about how their data is collected, used, and shared. Furthermore, users should have the right to access, correct, and delete their location data. Transparency and control over one’s data are essential for maintaining individual autonomy.
Potential for Misuse of Location Data
Location data, if not handled responsibly, can be susceptible to misuse. This includes unauthorized access, data breaches, or even the targeting of individuals for malicious purposes. The potential for stalking, harassment, or even fraud underscores the importance of robust data security measures. Examples of misuse include targeted advertising based on location history, or revealing sensitive information about an individual’s movements and social interactions.
Demonstrating Respect for User Privacy
Companies can demonstrate respect for user privacy by implementing strong data security protocols, obtaining explicit consent for data collection and usage, and offering clear and comprehensive privacy policies. Transparency is key; users should understand how their data is being used and what safeguards are in place to protect it.
Best Practices for User Data Security and Privacy
Robust data security measures are essential. This includes encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. Companies should invest in advanced security measures to protect user data from unauthorized access and breaches. Regularly updating security protocols and employing multi-factor authentication can significantly enhance data protection. Moreover, clear and concise privacy policies are crucial for informing users about the collection, usage, and sharing of their data.
A user-friendly and accessible privacy policy, readily available on the company’s website, empowers users to understand and control their data.
Conclusion
The sale of user location data by the new Life360 owners has triggered a significant debate about data privacy and security. User concerns, ranging from potential misuse to outright violation of trust, have been vocal and widespread. The implications extend beyond individual users, impacting the entire location-sharing market and potentially shaping future trends in this sector. As the dust settles, the need for transparency, clear data policies, and robust security measures has never been more evident.
The future of location-sharing services hinges on how these concerns are addressed and whether trust can be restored.