Chegg Google AI overviews monopoly sets the stage for a fascinating exploration of the evolving educational landscape. This overview examines the current market positions of Chegg, Google, and AI companies, delving into their services, business models, and potential synergies and conflicts. We’ll analyze Chegg’s impact on education, Google’s AI initiatives, the role of AI in learning, and the potential for a monopoly in online learning.
Beyond the immediate players, we’ll also consider alternative platforms and the overall future of online education.
The interplay between these giants raises critical questions about the future of learning. Will AI truly revolutionize education, or will it exacerbate existing inequalities? The discussion explores the potential benefits and risks, and examines how this convergence might reshape the student and educator experience. Finally, it looks at the potential for a monopoly and what regulatory or market solutions might emerge to address concerns about access and pricing.
Overview of Chegg, Google, and AI: Chegg Google Ai Overviews Monopoly
The intersection of Chegg, Google, and AI presents a fascinating interplay of established giants and rapidly evolving technologies. Chegg, a leader in online education resources, is navigating the shift towards AI-powered learning tools. Google, a tech powerhouse, is integrating AI into its vast suite of products and services. Understanding their current market positions, services, and business models is crucial to appreciating the potential opportunities and challenges ahead.This analysis explores the current landscape of these companies, examining their individual strengths and the potential for synergistic collaborations or competitive pressures arising from the integration of AI.
The evolving nature of education, information access, and the overall digital sphere necessitates a deep dive into how these companies are adapting and positioning themselves for the future.
Current Market Positions of Chegg, Google, and AI Companies
Chegg currently holds a significant market share in the online education sector, leveraging its extensive database of textbook solutions and practice questions. Google, through its search engine and suite of applications, dominates the online information and service sector. AI companies, from large players like OpenAI to numerous startups, are rapidly developing and deploying advanced AI models, impacting diverse sectors, including education and information retrieval.
Key Services and Products Offered by Each Entity
Chegg’s core offerings include online textbook rentals, practice problems, and tutoring services. Its platform facilitates student learning through a vast repository of academic content. Google’s offerings encompass search, cloud computing, advertising, and numerous applications like Gmail and Google Maps. Google’s AI is integrated into these services, enhancing search results, providing personalized recommendations, and enabling advanced features. AI companies, depending on their focus, provide various services such as natural language processing, image recognition, and machine learning algorithms.
Examples include Kami for conversational AI and image recognition software for various applications.
Comparison and Contrast of Business Models
Chegg’s business model is primarily subscription-based, leveraging its vast content library to generate revenue. Google’s model is diversified, encompassing advertising revenue, cloud services, and app store transactions. AI companies often rely on licensing agreements, partnerships, or subscription models to monetize their technology. The business models differ significantly in their revenue streams and target markets, but all are impacted by the evolving AI landscape.
Potential Synergies and Conflicts Between Chegg, Google, and AI
Potential synergies exist between these entities. For instance, Google’s AI capabilities could enhance Chegg’s learning platform by providing personalized tutoring experiences and more effective content recommendations. Chegg’s vast repository of educational content could be a valuable resource for Google’s AI development, enriching its data sets. However, potential conflicts may arise due to competitive pressures. Google’s own AI-powered educational tools could directly compete with Chegg’s offerings.
This creates a complex dynamic where collaboration and competition will shape the future of the industry.
Chegg’s Role in the Educational Landscape
Chegg has become a ubiquitous presence in the modern student’s toolkit, offering a wide array of resources designed to support learning and navigate the complexities of academic life. Its impact on the educational landscape is undeniable, both positively and negatively influencing the traditional student experience. This exploration delves into Chegg’s influence, examining its effects on student learning, its disruptive tendencies, and the nuanced perspectives of students and educators.Chegg’s services are fundamentally changing the way students approach learning.
By providing access to a vast library of study materials, practice problems, and expert-led tutoring, Chegg has democratized access to resources previously confined to the classroom or expensive supplemental courses. This accessibility, however, is intertwined with concerns about the potential for over-reliance on external support and the impact on the development of independent learning skills. It is crucial to understand the dual nature of this disruption.
Chegg’s Impact on Student Learning and Academic Support
Chegg provides a wealth of learning materials, ranging from textbooks and practice questions to expert-led tutoring sessions. This access has demonstrably improved student comprehension and performance for many. Students can revisit complex concepts at their own pace, and personalized tutoring can address individual learning gaps. Moreover, the readily available practice problems foster active learning, reinforcing understanding and improving test-taking abilities.
Chegg’s Disruptive Influence on the Traditional Educational System
Chegg’s emergence as a significant player in the educational sector has disrupted traditional educational models in several key ways. The accessibility of learning materials has diminished the perceived value of physical textbooks, prompting a shift towards digital resources. Furthermore, the availability of instant expert help has potentially altered the role of instructors in providing individualized attention. This disruption, while challenging the status quo, also presents opportunities for innovation in teaching methods and resource allocation.
Pros and Cons of Chegg’s Services for Students and Educators
- Pros for Students: Chegg’s extensive resources provide students with readily available support. This access to practice questions and solutions can accelerate learning, especially when combined with focused study strategies. The platform also offers a range of pricing options, often making resources more affordable than traditional tutoring or supplemental materials.
- Cons for Students: Over-reliance on Chegg’s resources can potentially hinder the development of critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Students may not fully internalize concepts if they are not actively engaged in the learning process. The reliance on external sources can also reduce the necessity of direct interaction with educators.
- Pros for Educators: Chegg’s resources can serve as a valuable supplement to classroom learning, offering students alternative approaches to mastering concepts. Educators can also leverage Chegg’s insights to tailor their teaching methods to better address student needs and learning styles. Educators can use Chegg for student feedback and identify areas where they are struggling, helping them to modify their teaching methods.
- Cons for Educators: Concerns exist regarding the potential for academic dishonesty if students utilize Chegg’s resources for completing assignments without proper understanding. Educators need to adapt their assessment methods to address this evolving landscape.
Comparison of Chegg’s Pricing Models to Alternative Learning Platforms
| Platform | Pricing Model | Key Features | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chegg | Subscription-based, per-resource, and bundle options | Extensive library of textbooks, practice questions, and expert tutoring | Undergraduate and graduate students |
| Khan Academy | Free access to most resources, some premium options | Comprehensive collection of educational videos and practice exercises | K-12 students, college students, and lifelong learners |
| Coursera | Subscription-based with varying pricing tiers | Online courses and specializations from top universities | Professionals seeking to upskill or retrain, students pursuing advanced degrees |
| Quizlet | Free with premium options | Flashcards, study sets, and other interactive learning tools | K-12 and college students |
This table provides a concise comparison of pricing models and features across several prominent learning platforms, offering a clearer understanding of their relative value propositions.
Google’s AI Initiatives and Potential Competition

Google’s relentless pursuit of AI innovation positions it as a formidable competitor in various sectors, including education. Their vast resources and existing infrastructure provide a potent base for challenging established players like Chegg. This exploration delves into Google’s significant AI investments, potential applications, and the implications for the educational landscape.Google’s investments in AI technology are substantial, encompassing a broad range of applications.
Their research and development efforts span natural language processing, machine learning, and computer vision, among other key areas. This extensive investment translates into a wealth of potential applications, including personalized learning experiences and intelligent tutoring systems.
Google’s AI Product Suite
Google’s AI portfolio is diverse and encompasses a range of products and services. From search algorithms to image recognition, AI underpins many of their offerings. This broad application of AI presents a potential avenue for disrupting existing educational models. Google’s AI prowess can be seen in its various tools and platforms.
- Search Engine Optimization (): Google’s search engine is heavily reliant on AI for relevance and accuracy. This implies that educational resources optimized for Google search are likely to gain visibility. This has already influenced the way educational content is produced and consumed.
- Google Workspace: Tools like Google Docs and Sheets integrate AI-powered features for improved productivity and organization. This suggests a potential to enhance collaboration and organization within the educational sphere. Students and educators can leverage these tools for streamlined research, document creation, and project management.
- Bard: This large language model (LLM) allows for complex interactions and provides insightful responses to questions. Its potential applications in education include providing personalized learning paths and facilitating access to diverse educational resources. Bard’s ability to understand and respond to complex prompts can revolutionize student interactions with educational materials.
Potential Overlap with Chegg
Several Google AI products demonstrate potential overlap with Chegg’s services. The capabilities of Bard, for example, could provide answers to study questions or summaries of complex topics, potentially impacting Chegg’s Q&A platform. Furthermore, AI-powered personalized learning platforms could potentially reduce the need for traditional tutoring services, impacting Chegg’s tutoring market. Google’s ability to create AI-driven study materials could directly compete with Chegg’s existing content offerings.
Competitive Landscape
If Google directly competes with Chegg in the education sector, the competitive landscape would likely be intense. Google’s immense resources and brand recognition would provide a significant advantage. However, Chegg’s existing user base and established network of tutors would also present a formidable obstacle. Google would need to carefully consider how to leverage its AI capabilities to create unique value propositions and target specific educational needs.
Strengths and Weaknesses
| Feature | Chegg | |
|---|---|---|
| AI Capabilities | Superior AI infrastructure and a robust research base. | Strong existing network of tutors and student-oriented content. |
| Brand Recognition | High brand recognition and widespread adoption of Google services. | Strong brand recognition in the student community, though potentially less than Google. |
| Existing Infrastructure | Significant existing infrastructure to support AI-driven services. | Existing infrastructure focused on connecting students with tutors. |
The table highlights the contrasting strengths and weaknesses of both platforms. Google’s strengths lie in its AI prowess, while Chegg’s strength lies in its established network and student trust. The crucial factor in this competition will be how effectively Google can integrate its AI capabilities into a student-friendly platform, while maintaining the trust and familiarity students already have with Chegg.
The Role of AI in Education and Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming various sectors, and education is no exception. AI’s ability to personalize learning experiences, automate administrative tasks, and provide immediate feedback is poised to revolutionize how students learn and teachers teach. This shift presents exciting opportunities for enhanced learning outcomes, but also necessitates careful consideration of the potential challenges and ethical implications.
Personalized Learning Experiences
AI algorithms can analyze individual student performance data to tailor learning paths and content delivery. This personalized approach allows students to progress at their own pace and focus on areas where they need extra support. Adaptive learning platforms utilize AI to adjust the difficulty and pace of lessons based on student responses, ensuring a more engaging and effective learning experience.
For instance, students struggling with math concepts can receive targeted practice exercises, while those excelling can be challenged with more complex problems.
While Chegg and Google’s AI overviews seem to be dominating the educational and search landscape, it’s interesting to see how creators are finding new avenues for monetization, like selling NFTs on Polygon. This is particularly relevant to how platforms like Meta Mint are enabling creators to sell their digital assets. meta mint sell nfts polygon creators monetization is a fascinating example of a new approach to digital ownership.
Ultimately, these trends are a sign of the evolving tech landscape, and it’s still early to see how these new approaches will impact the Chegg and Google AI overviews monopoly.
Automated Grading and Feedback
AI-powered tools can automate the grading of objective assessments, freeing up educators’ time to focus on more complex tasks like providing personalized feedback and fostering critical thinking. These tools can identify patterns in student errors and provide targeted suggestions for improvement. Automated essay scoring systems, for example, can quickly assess student writing, identifying strengths and weaknesses. This allows teachers to provide timely and effective feedback, enabling students to learn from their mistakes and develop their skills.
Chegg and Google’s AI overviews seem to be creating a monopoly in educational resources, but the future of gaming is also shaping up to be interesting. A recent interview about Microsoft’s Xbox Game Pass PC offering, specifically focusing on Gears Tactics, microsoft xbox game pass pc gears tactics interview , highlights the evolving landscape of gaming subscriptions. Ultimately, these developments, from educational resources to gaming platforms, all point to a larger trend of technological dominance, prompting questions about how these companies will balance accessibility with innovation in the long run.
This further emphasizes the complex nature of Chegg and Google’s potential AI monopoly.
AI-Powered Educational Tools and Platforms
A variety of AI tools and platforms are emerging to enhance learning experiences. These include interactive simulations, virtual tutors, and personalized learning platforms. For example, Khan Academy leverages AI to offer personalized learning paths and targeted practice exercises. Duolingo employs AI to create adaptive language learning experiences. These tools allow students to practice at their own pace and receive immediate feedback, fostering a more engaging and effective learning experience.
Potential Benefits and Risks of AI in Education
AI’s potential to revolutionize education is undeniable. Personalized learning experiences can lead to improved learning outcomes, and automated grading and feedback can free up educators’ time for more meaningful interactions with students. However, the integration of AI in education also raises important concerns. Ensuring equitable access to AI-powered tools and addressing potential biases in algorithms are crucial considerations.
Furthermore, the role of human interaction in education must be maintained, and AI should be viewed as a tool to augment, not replace, the teacher-student relationship.
AI Applications in Educational Settings
| AI Application | Description | Potential Benefits | Potential Risks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Personalized Learning Platforms | Adaptive learning platforms that adjust the difficulty and pace of lessons based on student performance. | Improved learning outcomes, increased student engagement, and tailored learning experiences. | Potential for bias in algorithms, limited social interaction, and high cost of implementation. |
| Automated Grading Systems | AI tools that automate the grading of objective assessments, such as multiple-choice questions and short-answer responses. | Increased efficiency for educators, timely feedback to students, and consistent grading standards. | Inability to assess subjective elements like critical thinking and creativity, potential for errors in grading, and dependence on accurate data input. |
| Virtual Tutors | AI-powered tutors that provide individualized support and guidance to students. | Accessibility to personalized support outside of classroom hours, providing additional practice and feedback. | Potential for lack of human connection, limited ability to address complex or emotional needs, and potential for bias in the tutor’s responses. |
| Intelligent Content Creation | AI tools that create educational content, such as interactive simulations and virtual labs. | Increased access to diverse and engaging learning resources, tailored to individual needs and preferences. | Potential for bias in content generation, ensuring accuracy and quality control of generated content. |
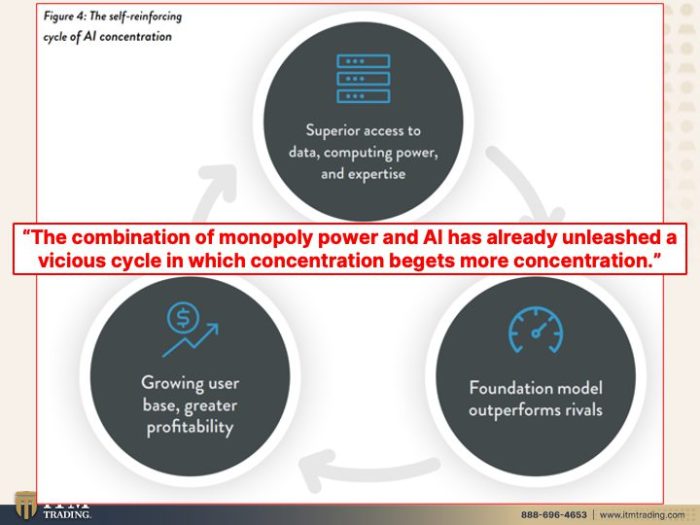
Potential for a Monopoly
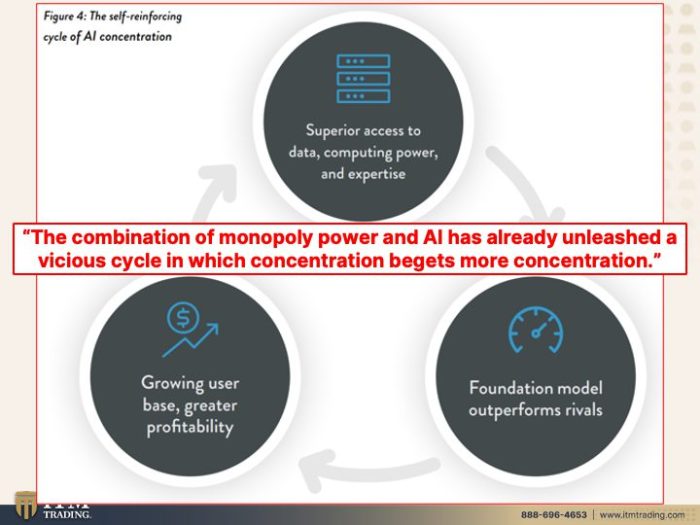
The convergence of Chegg’s robust online learning platform with Google’s AI prowess presents a compelling, yet potentially problematic, scenario. The integration of AI-powered tutoring, study materials, and personalized learning experiences could drastically alter the educational landscape, raising concerns about potential monopolistic control. This analysis delves into the conditions fostering such a monopoly, its impact on access and pricing, regulatory hurdles, and potential solutions.
Conditions for a Monopoly
The concentration of power in the hands of a few dominant players, often facilitated by technological advancements and network effects, is a well-documented factor in the emergence of monopolies. In the online learning space, several conditions could contribute to a Chegg-Google AI monopoly. These include a superior user experience, an extensive database of educational resources, and a powerful AI engine capable of tailoring learning paths for diverse learners.
Potential Implications of a Chegg-Google AI Monopoly
A Chegg-Google AI monopoly would likely lead to significant implications for educational access and pricing. Students and educators could face higher costs for services, limited choice, and a potential decline in educational innovation. The homogenization of learning experiences, driven by a single entity, might stifle creativity and diverse pedagogical approaches.
Regulatory Hurdles and Concerns
Several regulatory hurdles and concerns would arise in a scenario where Chegg and Google control a significant portion of the online learning market. Antitrust authorities would likely scrutinize the potential for anti-competitive practices, such as predatory pricing or exclusionary contracts. The potential for market manipulation, such as controlling access to critical educational resources, would be a key concern.
Furthermore, the dominance of a single entity could restrict educational choices and diversity. Concerns over data privacy and security would also arise.
Potential Solutions to Mitigate Monopoly Risk
Several strategies can mitigate the risk of a Chegg-Google AI monopoly. Firstly, promoting competition by fostering the growth of alternative platforms and educational resources could help diversify the market. Secondly, robust antitrust regulations, enforced by government agencies, are critical to ensure fair competition. Such regulations could prevent anti-competitive practices, such as exclusive deals and excessive pricing. Thirdly, the development of open educational resources and the promotion of accessible, affordable learning tools could help counteract the potential for higher costs.
Finally, fostering a culture of transparency in the development and use of AI in education is crucial to build public trust and encourage responsible innovation.
Alternative Educational Platforms and Competition
Chegg’s dominance in the online educational resource market isn’t unchallenged. Several alternative platforms are vying for students’ attention, offering diverse learning experiences and competitive features. Understanding these competitors is crucial to assessing the potential for a Chegg monopoly and the broader landscape of online education.Alternative platforms are increasingly important in the competitive educational market, offering diverse learning paths and features to complement or replace traditional methods.
These platforms often focus on specific niches or methodologies, differentiating themselves from Chegg’s broader approach. Analyzing their strengths and weaknesses allows for a more nuanced understanding of the evolving educational landscape.
Alternative Educational Platforms
Several prominent platforms offer alternative learning resources. These range from comprehensive learning management systems (LMS) to specialized subject-matter platforms, often targeting specific learning styles or subject areas. Examples include Khan Academy, Coursera, Udemy, and Quizlet. Each platform utilizes distinct strategies to attract and retain users.
Strategies Employed by Alternative Platforms
Different platforms employ various strategies. Khan Academy, for instance, emphasizes free, high-quality educational content, targeting a broad audience. Coursera and Udemy offer courses and certifications from universities and industry professionals, catering to career development needs. Quizlet, known for its flashcards and study tools, focuses on active recall and memorization. These diverse strategies highlight the variety of approaches within the online education sector.
Comparison of Features and Pricing
Chegg primarily focuses on solutions for accessing course materials and providing study aids. Alternative platforms like Khan Academy are entirely free, while Coursera and Udemy offer a mix of free and paid courses and certifications. The pricing models vary significantly. Chegg’s pricing is often tied to access to specific course materials or study guides. Alternative platforms, such as Coursera, use a tiered pricing system, often with varying subscription levels for premium access to course materials and support.
Table: Strengths and Weaknesses of Educational Platforms
| Platform | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Chegg | Extensive collection of course materials, diverse study aids, and focused on course-specific needs. | Can be expensive, limited to course-specific resources, and may not cater to broad learning styles. |
| Khan Academy | Free, comprehensive content, high-quality videos and exercises, broad range of subjects. | Lacks direct interaction with instructors, may not provide personalized learning experiences. |
| Coursera | Wide range of university-level courses, certifications, and career-oriented programs, potentially leading to professional development. | Pricing structure can be complex, and access to advanced courses or certifications may require paid subscriptions. |
| Udemy | Vast library of courses across various disciplines, often offered at lower prices than other platforms, potentially offering a wider range of subject matter. | Course quality can vary, and user reviews and ratings are crucial to identifying credible instructors and courses. |
| Quizlet | Efficient flashcards and study tools for active recall and memorization, highly effective for specific subject matter. | Limited to memorization, might not cater to more complex learning styles, and less comprehensive content than other platforms. |
The Future of Online Learning and AI
The convergence of online learning platforms and artificial intelligence (AI) is poised to revolutionize education, offering personalized learning experiences and potentially democratizing access to quality instruction. This evolution will be characterized by a dynamic interplay between technology and pedagogical approaches, ultimately shaping the future of how students learn and educators teach.
Chegg and Google’s AI overviews seem to be dominating the educational tech market, creating a sort of monopoly. While the implications of this are debated, it’s fascinating to consider the parallel universe of astronomy, where researchers are discovering repeating intergalactic radio bursts, like a cosmic chime resonating across galaxies. This fascinating phenomenon, explored in more detail at astronomy radio burst repeating intergalactic chime galaxy , highlights the incredible complexity of the universe.
Ultimately, the implications for both the educational and astronomical fields are still quite open-ended and will continue to evolve, just like the AI-driven education platforms.
Potential Trends and Developments
The coming years will witness a significant expansion of AI-powered tools in online learning environments. Adaptive learning platforms, powered by machine learning algorithms, will analyze student performance in real-time and adjust the curriculum accordingly, tailoring the learning path to individual needs and pace. Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies will enhance immersive learning experiences, creating more engaging and interactive simulations for diverse subjects.
AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants will provide 24/7 support for students, answering questions and offering personalized guidance.
Reshaping the Future of Education, Chegg google ai overviews monopoly
AI’s integration into education promises to transform the role of educators, moving them from traditional lecturing to facilitators and mentors. AI-powered tools will automate administrative tasks, allowing educators to focus on fostering student engagement and critical thinking skills. Personalized learning paths will empower students to master concepts at their own pace, leading to greater individualization and improved learning outcomes.
Furthermore, AI will unlock access to education for students in remote or underserved areas, bridging geographical gaps and fostering global learning communities.
Future Scenarios for Online Learning
One future scenario involves a hyper-personalized learning experience. AI algorithms will create unique learning journeys for each student, adapting content and pace to match individual strengths and weaknesses. Another scenario envisions a more immersive and interactive online learning environment, leveraging VR and AR technologies to simulate real-world experiences. AI-powered tutoring systems will be ubiquitous, providing instant feedback and support to students around the clock.
A third scenario foresees the development of collaborative learning platforms, facilitating online discussions and interactions between students and educators from diverse backgrounds.
Potential Future Uses of AI in Education
| AI Application | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Personalized Learning Platforms | AI algorithms analyze student performance to tailor learning content, pace, and difficulty. | Improved learning outcomes, increased engagement, reduced drop-out rates. |
| Intelligent Tutoring Systems | AI tutors provide individualized feedback, answer questions, and offer support to students 24/7. | Increased access to quality instruction, personalized learning support. |
| Automated Grading and Feedback | AI systems automate the grading of objective assessments, providing timely feedback to students. | Reduced workload for educators, faster feedback loops, improved learning efficiency. |
| Adaptive Assessment Tools | AI tools adjust assessment questions and difficulty based on student performance. | More accurate assessment of learning progress, better identification of learning gaps. |
| Virtual and Augmented Reality Simulations | AI enhances VR/AR simulations, creating more engaging and immersive learning experiences. | Improved understanding of complex concepts, enhanced engagement, greater accessibility to field trips and experiments. |
Impact on Students and Educators
The convergence of Chegg and Google AI in the educational sphere presents a complex interplay of opportunities and challenges for students and educators alike. This powerful combination could revolutionize learning, but also raises concerns about access and equitable distribution of resources. The potential for a consolidated platform to dominate the online learning landscape necessitates a careful examination of its implications.
Effects on Student Experiences
A Chegg-Google AI dominance in online learning would likely streamline the student experience in some ways. Personalized learning paths, tailored to individual needs and learning styles, are possible outcomes. AI-powered tutoring and practice exercises could provide instant feedback and targeted support, enhancing engagement and comprehension. However, the very personalization could inadvertently exacerbate existing inequalities. Students lacking access to robust internet connections or devices might be disadvantaged.
Furthermore, the potential for bias in AI algorithms used for personalized learning could disproportionately affect certain student groups.
Implications for Educators
Educators’ roles would undergo a significant transformation. The automation of certain tasks, such as grading assignments or providing basic feedback, could free up instructors to focus on more complex aspects of education, such as fostering critical thinking and collaborative learning. However, educators need ongoing professional development to adapt to these new tools and ensure the integration of AI in a way that enhances, not diminishes, their role.
Maintaining a balance between AI-assisted tools and human interaction is crucial.
Pricing Models and Implications
The pricing model implemented by a consolidated Chegg-Google AI platform will significantly influence both students and educators. A subscription-based model, with tiered access levels, could create a system where access to advanced features is restricted based on affordability. This could potentially exacerbate the digital divide. Conversely, a more affordable model could make educational resources more accessible to a wider range of students.
Furthermore, pricing structures for educators might impact their ability to utilize these platforms in their teaching. The financial implications of these choices for both student and educator needs to be carefully evaluated.
Potential for Leveling the Playing Field for Underserved Students
While a Chegg-Google AI monopoly presents potential pitfalls, there is also the possibility of using AI to level the playing field for underserved students. AI-powered tools could provide personalized support and resources, potentially bridging the gap in access to quality education. Adaptive learning platforms could address the specific learning needs of students facing challenges due to socioeconomic factors, language barriers, or disabilities.
However, this positive impact is contingent on equitable access to the technology and appropriate algorithm development that avoids exacerbating existing biases. This requires careful design and implementation, ensuring the AI tools are truly inclusive and not reinforcing existing disparities.
Last Word
In conclusion, the Chegg, Google, and AI convergence presents a complex and multifaceted picture of the future of online education. This exploration highlighted the potential for disruption and innovation, but also the inherent risks of a monopoly. The discussion has shown that the path forward will require careful consideration of the ethical, educational, and economic implications, along with potential solutions for ensuring equitable access and mitigating potential risks.
The dynamic interplay between these forces promises a compelling and transformative future, but one that requires thoughtful navigation.