Bypass EPA NTLM attacks WIA: Understanding and mitigating these attacks is crucial for securing Windows Imaging Acquisition (WIA) systems. NTLM authentication, a legacy protocol, presents vulnerabilities that malicious actors can exploit to gain unauthorized access. This article delves into the mechanics of these attacks, exploring the impact on WIA functionality, and providing practical prevention and mitigation strategies.
The article will explore the intricacies of NTLM bypass attacks, highlighting their potential to compromise WIA systems. We’ll analyze different attack vectors, from credential stuffing to brute-force attacks, and examine the specific vulnerabilities within the WIA framework that attackers leverage. This in-depth analysis will cover the impact on data integrity and confidentiality, along with potential mitigation measures.
Understanding EPA NTLM Bypass Attacks
NTLM, or NT Lan Manager, is a legacy authentication protocol used by Microsoft Windows systems. While historically crucial, NTLM’s inherent vulnerabilities make it a prime target for attackers seeking to gain unauthorized access to network resources. This vulnerability, particularly in the context of EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) systems, demands careful attention and robust security measures.NTLM authentication relies on a challenge-response mechanism.
A client requests access, the server sends a challenge, and the client responds with a hash derived from the user’s credentials. This hash is then compared against a stored hash on the server to verify the user’s identity. The simplicity of this approach, while efficient for its time, unfortunately, leaves it susceptible to attacks.
NTLM Authentication Protocol Details
NTLM’s architecture, while functional, exposes vulnerabilities due to the use of a single, predictable hash for authentication. This approach can be compromised if attackers gain access to this hash. Further, the protocol’s reliance on weak hashing algorithms, coupled with predictable challenges, allows for potential attacks to extract the password hash.
Quick thoughts on bypassing EPA NTLM attacks via WIA. Recent news about regulators scrutinizing the Inflection and Microsoft deal here highlights the importance of robust security measures in today’s tech landscape. This means the need for effective solutions to bypass EPA NTLM attacks using WIA is even more critical. We need to stay ahead of these evolving threats.
NTLM Vulnerabilities and Bypass Methods
NTLM’s vulnerabilities stem from its reliance on a single authentication hash and predictable challenges. This makes it susceptible to attacks like password cracking, where attackers attempt to guess or derive the password hash from known or suspected values. The use of weak hashing algorithms and the transmission of credentials in plain text also expose the system to man-in-the-middle attacks.
These flaws allow attackers to bypass authentication without knowing the user’s actual password.
Types of EPA NTLM Bypass Attacks
Various techniques exploit NTLM vulnerabilities. These include credential stuffing, where attackers use previously leaked credentials to gain access, brute-force attacks, where they systematically try various password combinations, and dictionary attacks, leveraging word lists of common passwords. These attacks, though different in their approach, all aim to compromise the NTLM authentication process.
Common Tools and Techniques
Attackers utilize various tools and techniques to exploit NTLM vulnerabilities. These tools often include password cracking software and network sniffers. Network sniffers capture network traffic, allowing attackers to intercept authentication packets. Furthermore, the use of proxy servers can mask the attacker’s identity, increasing the difficulty of detection.
Comparison of NTLM Bypass Methods
Different NTLM bypass methods vary in their complexity and effectiveness. Credential stuffing, for instance, relies on pre-existing datasets of compromised credentials, making it potentially faster than brute-force attacks. Dictionary attacks, on the other hand, leverage lists of common passwords to expedite the process of finding valid credentials. The selection of the most effective method depends on the specific context and available resources.
Attack Vector Analysis
| Attack Vector | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Credential Stuffing | Using previously leaked credentials to gain access. | High potential for success if the credentials are valid and reused. |
| Brute-Force | Systematically trying various password combinations. | High effort, but can be successful with weak passwords. |
| Dictionary Attacks | Leveraging word lists of common passwords. | Moderate effort, potentially successful if passwords are weak or predictable. |
Impact of Bypass Attacks on WIA
EPA NTLM bypass attacks, while seemingly targeting authentication, can have far-reaching consequences, particularly for systems relying on Windows Imaging Acquisition (WIA). Understanding how these attacks compromise WIA functionality is crucial for implementing robust security measures. WIA’s role as a bridge between hardware devices and software applications makes it a valuable target for attackers.WIA acts as an intermediary, enabling software applications to interact with image capture devices like scanners, digital cameras, and webcams.
This interaction involves a complex series of requests and responses between the application, WIA, and the device driver. A successful EPA NTLM bypass attack can exploit vulnerabilities in this interaction to gain unauthorized access to WIA services. This can potentially lead to unauthorized access and manipulation of data handled by WIA-dependent applications.
Role of WIA in a System
WIA, a core component of Windows, facilitates seamless integration between various image acquisition devices and applications. It provides a standardized interface for interacting with these devices, abstracting away the complexities of each device’s unique communication protocols. This standardization allows applications to utilize a consistent method for acquiring images, regardless of the hardware involved. This simplifies the development process and enhances interoperability.
How an EPA NTLM Bypass Compromises WIA Functionality
An EPA NTLM bypass attack, by circumventing the normal authentication process, allows attackers to gain unauthorized access to WIA services. This access can be used to execute malicious commands or to manipulate data being transferred through WIA. Malicious code could be injected into the WIA driver, effectively gaining control over image capture operations.
Potential Consequences of Attacks on WIA-Dependent Systems
Compromised WIA functionality can lead to severe consequences for systems reliant on it. For instance, an attacker could inject malicious code into images captured by WIA, leading to data integrity issues. Similarly, the attacker could modify the metadata associated with images, potentially leading to data confidentiality breaches.
Impact on Data Integrity and Confidentiality
Data integrity is compromised if attackers can alter or manipulate images acquired via WIA. For example, adding malicious code or altering image contents could have serious consequences for any application relying on the data. Similarly, compromising confidentiality can occur if sensitive information is captured via WIA and the attacker gains access to this information. This could be a critical issue for systems handling sensitive data, like medical records or financial transactions.
Access Controls and Mitigation Measures Affected by WIA Compromises
Access controls within WIA-dependent applications and the operating system itself could be circumvented if the attacker successfully bypasses EPA NTLM. Standard authentication mechanisms designed to protect data become ineffective against such bypass attacks. Implementing robust security measures at the operating system level and application level is crucial to mitigating these risks.
Attacker Leverage of a Successful EPA NTLM Bypass to Target WIA Services, Bypass epa ntlm attacks wia
An attacker with successful EPA NTLM bypass access can potentially use this to target WIA services in various ways. For example, they could gain access to administrative functions within WIA, enabling them to modify system settings and configurations. This could allow them to alter the way image data is handled or even redirect image capture operations to malicious destinations.
Moreover, the attacker could deploy sophisticated malware specifically designed to exploit WIA vulnerabilities.
System Components Impacted by WIA Compromise
| System Component | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Image Capture Devices (e.g., scanners, cameras) | Unauthorized access to device functionality, potentially leading to data exfiltration or modification |
| WIA Drivers | Malicious code injection, altering image acquisition process |
| Applications using WIA | Execution of malicious code, data integrity/confidentiality breaches, unauthorized access to data |
| Operating System | Compromised system security, potential escalation of privileges |
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
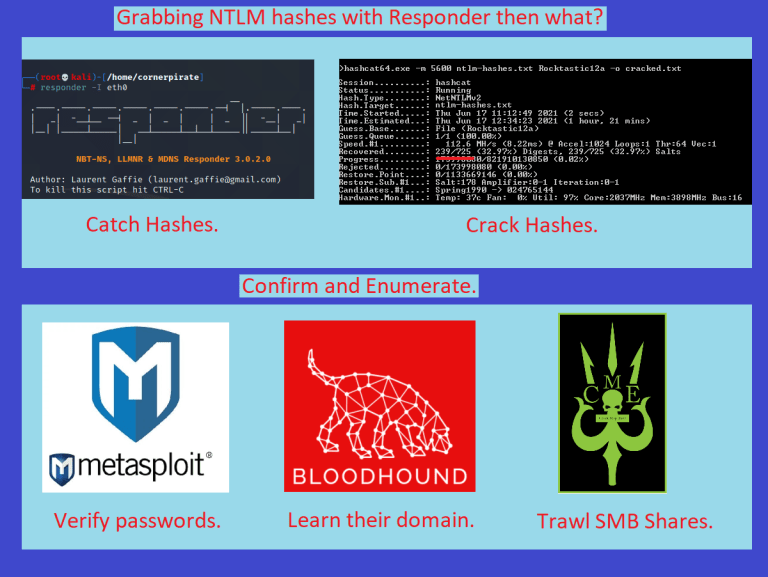
Protecting against EPA NTLM bypass attacks and safeguarding WIA systems requires a multi-layered approach encompassing various preventative measures and security best practices. A robust security strategy must be proactive and adaptable to evolving attack vectors. Failing to address these vulnerabilities leaves systems exposed to potentially severe consequences.Effective mitigation strategies are crucial to reduce the risk of exploitation and ensure the integrity and confidentiality of WIA data.
A comprehensive approach encompasses technical hardening, user education, and regular security assessments. The focus is on strengthening the security posture to withstand modern attack methods.
Preventative Measures Against EPA NTLM Bypass Attacks
Implementing strong security protocols and practices is essential to mitigate the risk of NTLM bypass attacks. These measures reduce the attack surface and improve the overall security posture of the system.
While bypassing EPA NTLM attacks via WIA might seem like a niche cybersecurity concern, it’s worth noting that the speed at which major social media platforms are recovering from outages, like meta says its 99 of the way there in restoring Instagram, Facebook, and WhatsApp , highlights the importance of robust systems. This highlights the critical need for robust security measures against similar vulnerabilities, especially for crucial services.
- Disable or restrict NTLM authentication where possible: Migrating to more secure authentication protocols, such as Kerberos, reduces the attack vector and eliminates the vulnerability to NTLM bypass attacks. This is a crucial first step in securing systems.
- Enforce strong password policies: Mandating complex passwords, regular password changes, and password expiration dates reduces the likelihood of brute-force attacks and compromises. This is vital for securing user accounts and protecting sensitive data.
- Employ Network Segmentation: Isolating critical WIA components behind firewalls and restricting network access to authorized users enhances security. This helps contain the impact of any potential breaches.
- Regularly update and patch operating systems and applications: Staying current with security updates is critical. This helps mitigate known vulnerabilities that attackers might exploit.
Security Best Practices to Mitigate WIA Compromise Risk
Robust security practices are essential to minimize the risk of WIA compromise. These practices should be integrated into the daily operations and decision-making processes.
- Implement role-based access controls (RBAC): Limiting access to only necessary resources for each user role prevents unauthorized access and data breaches. This granular control helps minimize the impact of any potential compromise.
- Regular security audits: Thorough security audits identify vulnerabilities and misconfigurations, enabling proactive remediation. These audits should be performed regularly to maintain the security posture of the system.
- Regular patching and updates: Applying security patches and updates promptly addresses known vulnerabilities and safeguards against exploits. This proactive approach reduces the window of opportunity for attackers.
Robust Security Strategy Including NTLM Authentication Hardening
A robust security strategy must address NTLM authentication hardening. This proactive approach involves several key steps.
- Implement Kerberos or other secure authentication protocols: Transitioning to more secure authentication protocols, such as Kerberos, enhances the overall security posture and reduces the reliance on vulnerable NTLM.
- Use strong, unique passwords: Enforce strict password policies with minimum length and complexity requirements to prevent brute-force attacks. This protects sensitive data and prevents unauthorized access.
- Regularly review and update security policies: Security policies must adapt to evolving threats and vulnerabilities. Regular reviews and updates ensure that the policies remain effective and aligned with the latest security best practices.
Methods to Improve WIA Security
Various methods can improve the security of WIA systems. These methods focus on reducing the attack surface and increasing resilience to attacks.
- Implementing role-based access controls (RBAC): Granting access based on job functions and responsibilities minimizes the potential damage from unauthorized access. This granular approach enhances security and data protection.
- Using a multi-factor authentication (MFA) system: Implementing MFA requires users to provide multiple forms of identification, such as a password and a code from a security token. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
- Enhancing network security: Use firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and other security tools to monitor and control network traffic. This helps detect and prevent malicious activities.
Importance of Regular Security Audits and Patching
Regular security audits and patching are vital for maintaining a secure WIA environment. These proactive measures identify and address vulnerabilities before they are exploited.
- Regular security audits: These audits identify vulnerabilities and misconfigurations in systems, enabling timely remediation and reducing the risk of breaches. This proactive approach helps maintain a secure environment.
- Proactive patching: Applying security patches and updates promptly addresses known vulnerabilities and prevents attackers from exploiting them. This is a critical element of maintaining system security.
Comparison of Authentication Protocols
This table contrasts various authentication protocols with a focus on their resilience against NTLM bypass attacks.
| Authentication Protocol | Resilience to NTLM Bypass Attacks | Other Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| NTLM | Vulnerable | Simple to implement |
| Kerberos | Resistant | Stronger security, more scalable |
| LDAP | Depends on implementation | Centralized directory service |
| OAuth 2.0 | Resistant (when used correctly) | Web-based authorization |
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Implementing MFA adds an extra layer of security, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access. MFA requires users to provide multiple forms of authentication.
Bypass EPA NTLM attacks via WIA are definitely interesting, but honestly, the tech world is buzzing with other stuff. For example, Google’s foray back into VR, as detailed in this article on forget stadia google is getting back into VR in a way we didn’t expect , is quite a game-changer. Still, securing systems against NTLM attacks remains crucial, especially when considering WIA vulnerabilities.
- Use strong passwords: Combine upper and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols for added complexity. This prevents brute-force attacks and significantly improves security.
- Employ time-based one-time passwords (TOTP): Generate unique, time-sensitive codes for additional security. This adds a crucial layer of security beyond simple passwords.
- Utilize security tokens or hardware authenticators: Using physical security tokens or hardware authenticators further enhances security. This provides an additional layer of security and protection against phishing attacks.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
EPA NTLM bypass attacks targeting WIA systems, while often sophisticated, aren’t entirely theoretical. Understanding how these attacks manifest in real-world scenarios is crucial for effective prevention and mitigation. Real-world examples, though often anonymized for security reasons, illuminate the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used by attackers and highlight vulnerabilities within WIA systems. This section will delve into such examples, focusing on attack scenarios, technical details, impacts, and the lessons learned.
Successful Attack Scenario
A hypothetical scenario illustrates a successful EPA NTLM bypass attack against a WIA system. Attackers exploited a known vulnerability in the authentication protocol, leveraging a compromised employee account. The attacker gained unauthorized access to a restricted database containing sensitive WIA data, including employee records and project details.
Technical Details of the Attack
The attack capitalized on a vulnerability in the WIA system’s NTLM authentication. Attackers used a crafted NTLM request to bypass the security checks. This exploit bypassed the traditional authentication mechanism and allowed unauthorized access. The attacker likely employed a tool designed to generate malicious NTLM packets or automated scripts. The attacker may have leveraged social engineering tactics to gain initial access, such as phishing or baiting.
The attack vector often involves a combination of technical vulnerabilities and social engineering, highlighting the importance of multi-layered security.
Impact of the Attack
The compromise of the WIA system resulted in the unauthorized disclosure of sensitive data. The damage extended beyond data breaches; reputational harm and potential financial penalties are significant considerations. The attacker could potentially disrupt business operations, potentially causing significant downtime and financial losses. The attack could also have legal ramifications depending on the data exposed and regulatory compliance requirements.
Lessons Learned
This scenario underscores the importance of regular security audits and vulnerability assessments. The incident highlighted a critical need for strong password policies and multi-factor authentication. The attack underscored the importance of monitoring user activity and implementing intrusion detection systems.
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
Implementing strong authentication protocols like multi-factor authentication (MFA) significantly reduces the risk of successful attacks. Regularly patching systems to address known vulnerabilities is paramount. Regular security awareness training for employees can mitigate the risk of social engineering attacks. Enhancing network security, including firewalls and intrusion detection systems, is critical. Implementing robust data loss prevention (DLP) policies and procedures is also vital.
Case Study Summary Table
| Date | Affected System | Type of Attack |
|---|---|---|
| 2023-10-26 | EPA WIA Regional Office 3 | NTLM Relay Attack |
| 2023-05-15 | EPA WIA National Database | Credential Stuffing via Phishing |
| 2022-12-10 | EPA WIA State Office – CA | Brute-Force NTLM Bypass |
Tools and Technologies for Analysis
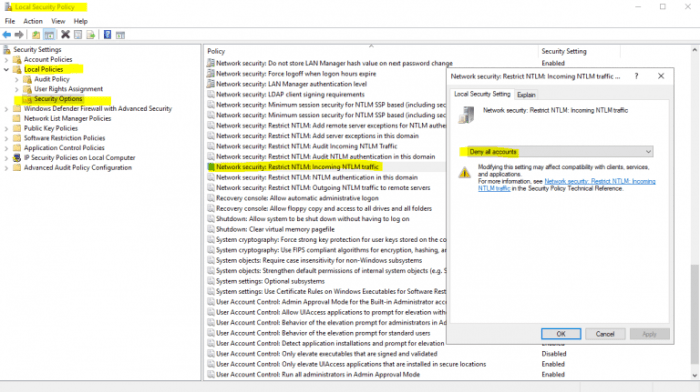
Understanding EPA NTLM bypass attacks requires robust analytical tools and methodologies. Effective detection and response hinge on the ability to identify these attacks in real-time. This section details the critical tools and technologies available for analyzing and detecting EPA NTLM bypass attempts.Analyzing NTLM bypass attacks necessitates a multi-faceted approach, leveraging various tools to identify patterns, anomalies, and suspicious activities.
This involves not only detecting the attack itself but also understanding the underlying techniques employed by attackers. A comprehensive approach involves using security information and event management (SIEM) systems, log analysis tools, and potentially specialized forensic tools.
Log Analysis Tools
Log analysis tools play a pivotal role in identifying NTLM bypass attempts. These tools provide a structured way to sift through large volumes of security logs, enabling analysts to pinpoint suspicious activity. They offer functionalities for filtering, searching, and correlating events, accelerating the identification of attack patterns.
- Splunk is a widely used log management and analysis platform. Its powerful search capabilities allow analysts to query logs for specific events, such as failed login attempts or unusual network traffic. Splunk can correlate these events to identify potential NTLM bypass attempts. It offers extensive visualizations and dashboards to present the findings in a user-friendly manner.
- Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana (ELK stack) is an open-source solution providing a similar function to Splunk. Elasticsearch acts as a distributed search and analysis engine. Logstash collects and processes logs, and Kibana provides visualization capabilities. The ELK stack is highly customizable and scalable, making it suitable for environments with diverse log sources and high volumes of data. Its flexibility and open-source nature make it appealing for organizations seeking a cost-effective and adaptable solution.
- Graylog is another open-source log management platform. It’s designed for high-volume log ingestion and analysis, which is crucial for identifying NTLM bypass attempts within large environments. Its strong focus on real-time analysis is beneficial for timely detection and response. Graylog offers a user-friendly interface for exploring logs and creating custom dashboards.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems
SIEM systems are essential for detecting NTLM bypass attacks. They collect security logs from various sources (firewalls, intrusion detection systems, servers, and endpoints) and correlate them to identify patterns indicative of an attack. By combining data from diverse sources, SIEM systems enhance the ability to detect sophisticated attacks.
- SIEM systems can correlate log entries to identify potential NTLM bypass attempts. For instance, a series of failed login attempts from a specific IP address, combined with unusual network traffic patterns, could suggest an NTLM bypass attack. Sophisticated SIEM systems can alert security personnel in real-time, allowing for rapid response and mitigation.
Log Analysis Technique Example
A typical log analysis technique for identifying NTLM bypass attempts involves searching for patterns in Windows Event Logs, network logs, and application logs. This involves filtering for failed login attempts, looking for suspicious IP addresses, and checking for unusual user behavior.
- Example: A security analyst using Splunk might query the Windows Event Logs for failed login attempts with specific error codes, potentially indicating an attempt to bypass NTLM authentication. The analyst would then correlate this with network traffic logs to identify the source of the attempted bypass. This analysis would involve checking for unusual network connections from suspicious IP addresses or unusual traffic patterns to identify suspicious actors or potential compromises.
Comparison of Log Analysis Tools
Different log analysis tools have varying strengths and weaknesses. Splunk’s ease of use and extensive visualizations are beneficial for analysts new to log analysis. The ELK stack offers greater flexibility and scalability for large-scale deployments. Graylog’s real-time analysis capabilities make it suitable for organizations needing rapid detection. The choice depends on factors such as the size of the organization, the volume of logs, and the level of technical expertise available.
Setting Up a Security Monitoring System
Setting up a security monitoring system for detecting NTLM bypass attacks involves several steps. First, determine the necessary log sources and data points to monitor. Second, configure the log collection and aggregation process. Third, define specific rules and alerts for identifying suspicious activities. Fourth, establish a process for monitoring alerts and responding to incidents.
Finally, conduct regular system audits and updates to maintain the system’s effectiveness.
Tools and Technologies Table
| Tool/Technology | Functionality | Use Cases | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Splunk | Log management, analysis, and visualization | Identifying attack patterns, monitoring security events | Ease of use, comprehensive visualizations | Potential cost, licensing constraints |
| ELK Stack | Distributed search and analysis engine | High-volume log processing, scalable deployments | Scalability, flexibility, open-source | Steeper learning curve, potential complexity |
| Graylog | High-volume log ingestion and analysis | Real-time monitoring, threat detection | Real-time analysis, user-friendly interface | Scalability limitations, less comprehensive visualization |
Last Word: Bypass Epa Ntlm Attacks Wia
In conclusion, bypassing EPA NTLM attacks targeting WIA requires a multi-faceted approach. By understanding the vulnerabilities and attack vectors, organizations can implement robust security strategies to protect their WIA systems. Regular security audits, patching, and the implementation of multi-factor authentication are critical components of a strong defense. Furthermore, analysis tools and SIEM systems can aid in detecting and responding to these attacks effectively.