When will social security reserves run out a new report estimates the date – When will social security reserves run out? A new report estimates the date, raising crucial questions about the future of this vital social program. The report delves into the intricacies of Social Security’s funding mechanism, examining historical trends and the significance of reserves in maintaining its solvency. It analyzes the methodology behind the new estimate, comparing it to previous projections and highlighting potential limitations.
The estimated depletion date is explored, considering potential implications for future benefits and different scenarios.
This analysis also investigates external economic factors, such as birth rates, life expectancy, and labor force participation, that could influence the projections. It discusses potential policy changes and their impact on the reserves. Finally, the report considers public understanding and engagement strategies, offering insights into how to effectively communicate the findings and foster public discussion about this critical issue.
Introduction to Social Security Reserves
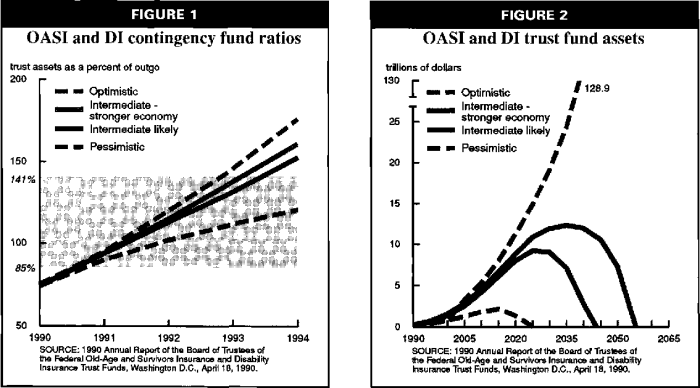
The Social Security system is a cornerstone of the American social safety net, designed to provide a crucial source of income for retirees, disabled individuals, and survivors. It operates on a pay-as-you-go system, where current workers’ contributions fund the benefits of current beneficiaries. This funding mechanism relies on a complex interplay of contributions, benefits, and economic factors, making its long-term solvency a constant subject of scrutiny.Historical trends show fluctuating reserve levels, influenced by population demographics, economic conditions, and legislative changes.
Understanding the evolution of these reserves is crucial for predicting the system’s future viability. The significance of the reserves in maintaining program solvency cannot be overstated; they act as a financial cushion, ensuring benefits can be paid even during periods of economic downturn or demographic shifts. A healthy reserve is akin to a financial safety net, allowing the system to absorb shocks and maintain its commitments.
Social Security Trust Fund Components
The Social Security Trust Fund comprises two main components: the Old-Age and Survivors Insurance (OASI) Trust Fund and the Disability Insurance (DI) Trust Fund. Each fund has its own dedicated reserves, reflecting the separate programs for retirement and disability benefits.
| Trust Fund | Description | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| OASI Trust Fund | Funds retirement and survivor benefits. | Represents the largest portion of the Social Security Trust Fund, crucial for ensuring retirement income for millions. |
| DI Trust Fund | Funds disability benefits. | Essential for providing support to individuals who become disabled and cannot work. |
Historical Trends of Social Security Reserves
The Social Security Trust Fund has historically experienced periods of growth and decline, mirroring economic fluctuations and demographic shifts. For instance, during periods of strong economic growth, workers’ contributions often exceed benefit payments, leading to a buildup of reserves. Conversely, economic downturns or shifts in the age distribution of the population can impact the balance.
Understanding these historical patterns is essential for evaluating the current state of the Trust Fund and predicting future trends.
Significance of Reserves in Maintaining Solvency
The Social Security reserves serve as a crucial buffer against potential future shortfalls. These funds allow the system to continue paying benefits even if tax revenue temporarily falls short of benefit obligations. This stability is vital for maintaining the public’s trust and confidence in the program’s long-term viability.
Understanding the New Report’s Methodology
The recent report estimating Social Security’s reserve depletion date employs a sophisticated actuarial methodology. This methodology is crucial for policymakers and the public to understand the long-term financial health of the system. Understanding the methods used, the assumptions made, and the limitations of the analysis allows for a more informed discussion about potential solutions and future projections.
Methods Employed in the New Report, When will social security reserves run out a new report estimates the date
The new report likely uses a stochastic model, incorporating various economic and demographic factors. This model simulates different scenarios and their potential impacts on Social Security’s financial position. Crucially, the model accounts for factors like future birth rates, mortality rates, wages, and average life expectancy. By incorporating a range of potential future outcomes, the model can provide a more comprehensive picture of the system’s long-term viability.
Comparison with Previous Assessments
Previous assessments of Social Security’s financial outlook often employed similar actuarial methods but might have differed in the specific assumptions used. Differences could stem from variations in economic forecasts, demographic projections, or the models themselves. For example, a change in assumed future interest rates or wage growth could significantly alter the projected depletion date. A crucial comparison will analyze the specific assumptions and data sources used in the latest report versus its predecessors.
Key Assumptions and Factors
The report’s projections are built upon several key assumptions. These include assumptions about future economic growth, inflation rates, interest rates, and the growth of wages relative to the cost of living. Demographic projections, such as future birth rates and life expectancy, also play a crucial role. A sensitivity analysis examining the impact of varying these assumptions is essential to understand the robustness of the projected depletion date.
For example, a modest increase in the assumed long-term interest rate can significantly impact the projected date of reserve depletion.
Potential Limitations of the Report’s Methodology
No model is perfect, and the Social Security reserve depletion model is no exception. A crucial limitation involves the inherent uncertainty of future economic and demographic trends. These projections are complex and rely on the accuracy of data and models. Furthermore, unforeseen events, such as significant economic downturns or unexpected shifts in demographics, could affect the accuracy of the projected depletion date.
So, a new report’s crunching the numbers on when Social Security reserves might dry up. It’s a sobering look at the future, but while we ponder that, you might find some solace in exploring online resources for books – fiction, non-fiction, whatever your heart desires. Check out how to find books online fiction nonfiction devices websites for tips on navigating the digital library and finding exactly what you’re looking for.
Regardless of how you find your next great read, the looming Social Security reserve depletion date is still a major concern.
Another important limitation is the simplification of complex social and economic realities into mathematical models. Real-world scenarios may not perfectly match the model’s assumptions.
Comparison of Forecasting Models
| Model | Description | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stochastic Model | Simulates various possible future scenarios based on probabilities. | Provides a range of potential outcomes, accounting for uncertainty. | Complexity can make it difficult to interpret results, and the choice of probability distributions can affect the results. |
| Deterministic Model | Predicts a single outcome based on fixed assumptions. | Simplicity in analysis. | Fails to account for uncertainty, potentially leading to inaccurate projections. |
This table highlights the differences between two prominent forecasting models, and illustrates how the choices made in model selection can influence the final results. Understanding these strengths and weaknesses is vital to properly assessing the new report’s findings.
Analyzing the Estimated Depletion Date
The new report paints a concerning picture of the Social Security trust fund’s future. It projects a specific date when the reserves are projected to be depleted, a critical milestone that warrants careful consideration of its implications for future beneficiaries. Understanding this projected depletion date and its potential consequences is crucial for policymakers and individuals alike.The report’s methodology, while meticulously detailed, inevitably relies on assumptions about future economic growth, inflation, and demographic trends.
These assumptions can introduce inherent uncertainties into the projections. Despite the inherent limitations, the estimated date provides a valuable framework for understanding the potential pressures on the system.
A new report estimates Social Security reserves might run out sooner than previously thought. While that’s a serious concern, it’s worth remembering that creators like those featured on igtv instagram creators youtube marques brownlee are constantly innovating and finding new ways to generate income. Ultimately, the future of Social Security funding will depend on a variety of factors, and this report is just one piece of the puzzle.
Estimated Date of Reserve Depletion
The new report estimates that the Social Security trust fund will be depleted by the year 2035. This projection is based on various economic and demographic factors, including the current trajectory of birth rates, life expectancy, and employment trends. This estimate is a significant departure from previous projections, which had placed the depletion date further into the future.
Potential Implications on Future Benefits
The projected depletion date signifies a potential reduction in the benefits paid out to future Social Security recipients. The Social Security Administration (SSA) may have to make adjustments to benefit levels or eligibility requirements to maintain the program’s solvency. This could mean that future retirees may receive smaller benefits than those currently projected. Examples of similar situations include adjustments to pension plans and government-funded healthcare programs.
Comparative Analysis with Past Projections
Comparing the current projection to past estimations reveals a concerning trend. Previous projections, while acknowledging the long-term challenges, had not anticipated such a swift depletion of reserves. This difference highlights the potential impact of unforeseen economic events and the importance of ongoing monitoring and adjustments. Comparing these estimations with similar trends in other countries and government programs would provide additional context.
Scenarios Regarding Possible Impacts on Future Recipients
Several scenarios emerge regarding the possible impact on future recipients. One scenario involves a gradual reduction in benefit levels, ensuring the program’s sustainability without immediate drastic changes. Another scenario envisions potential adjustments to eligibility requirements, such as increased retirement ages or adjusted benefit formulas.
Projected Impact on Different Age Groups
| Age Group | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Individuals under 30 | Likely to experience the most significant impact, as their retirement years would fall in the timeframe following reserve depletion. |
| Individuals between 30 and 50 | Potential impact is dependent on future legislative decisions and economic conditions. |
| Individuals over 65 | Current recipients would likely not experience any immediate changes, but future benefits may be adjusted. |
This table demonstrates a general outlook. The precise impact on specific individuals within each group will depend on a multitude of factors, including personal circumstances and economic conditions at the time of their retirement.
Potential Factors Affecting the Projection: When Will Social Security Reserves Run Out A New Report Estimates The Date
Social Security’s financial health is a complex interplay of various factors, many of which are influenced by external economic forces. Understanding these influences is crucial to accurately interpreting the projected reserve depletion date and its potential implications. While the current report provides a baseline projection, it’s essential to acknowledge the inherent uncertainties and the possibility of these factors shifting the timeline significantly.
External Economic Factors
External economic conditions significantly impact Social Security’s funding. Economic downturns, for example, can decrease tax revenues and increase the number of individuals claiming benefits, putting pressure on the system. Conversely, periods of robust economic growth can increase tax revenues and potentially alleviate the strain. Furthermore, inflation plays a critical role; if inflation outpaces wage growth, the purchasing power of benefits diminishes, leading to a greater demand on the system.
The cost of healthcare and long-term care also affects the system, as these expenses can rise considerably and directly impact the funds.
Changes in Demographic Factors
Demographic shifts can dramatically affect Social Security’s financial outlook. Changes in birth rates, life expectancy, and labor force participation rates directly impact the number of contributors versus beneficiaries. A decrease in birth rates leads to a smaller pool of workers to support the growing number of retirees. Increased life expectancy extends the period during which benefits are paid, placing a greater burden on the system.
Likewise, shifts in labor force participation rates can alter the ratio of workers to retirees, impacting the system’s ability to meet its obligations.
Government Policy Changes
Government policy decisions, including changes to tax rates, benefit formulas, or investment strategies, can significantly impact Social Security’s reserves. For example, adjustments to the payroll tax rate or modifications to benefit levels directly influence the inflow and outflow of funds. Changes in the investment strategy used for the trust fund, if made, can also influence the growth of the reserves.
Policy decisions about raising the retirement age or changing the way benefits are indexed to inflation can also significantly alter the system’s future financial health.
Impact of Various Scenarios
Predicting the precise impact of various scenarios on the reserve depletion date is challenging. However, we can compare different possibilities to illustrate the potential range of outcomes. A scenario with sustained economic growth and relatively stable birth rates, life expectancy, and labor force participation rates might delay the depletion date. Conversely, a period of prolonged economic stagnation, coupled with a decline in birth rates or an increase in life expectancy, could hasten the depletion date.
A substantial change in government policy, such as a significant increase in the retirement age, could also lead to substantial shifts in the reserve depletion timeline.
Table: External Factors and Potential Impact
| External Factor | Potential Impact on Reserves |
|---|---|
| Sustained Economic Growth | Increased tax revenues, potentially delaying depletion |
| Prolonged Economic Stagnation | Decreased tax revenues, potentially accelerating depletion |
| Rising Inflation | Reduced purchasing power of benefits, potentially accelerating depletion |
| Decreased Birth Rates | Smaller pool of workers to support retirees, potentially accelerating depletion |
| Increased Life Expectancy | Extended period of benefit payments, potentially accelerating depletion |
| Increased Labor Force Participation | Larger pool of workers to support retirees, potentially delaying depletion |
| Changes in Government Policy (e.g., increased retirement age) | Potentially delaying or accelerating depletion, depending on the specific policy change |
Implications and Alternatives for Policymakers
The Social Security report’s projections paint a clear picture of the looming challenges ahead. While the exact date of reserve depletion is a complex calculation, the potential consequences are substantial and demand proactive responses. Policymakers must now consider a range of strategies to ensure the program’s long-term viability and continued support for future generations.The report’s findings underscore the urgency of addressing the projected shortfall.
A new report suggests Social Security reserves might run dry sooner than anticipated. While the exact date is still up in the air, it’s a sobering thought. Interestingly, Accenture’s recent adoption of Cortex Xpanse, a cutting-edge solution for streamlined operations, highlights the need for innovative solutions in the face of such financial challenges. This underscores the potential strain on the system as we head toward the projected date of reserve depletion.
Delaying action could lead to significant reductions in benefits, jeopardizing the financial security of millions of retirees and those reliant on Social Security. A proactive approach, involving adjustments to the system, is crucial to maintaining the program’s integrity and value.
Potential Policy Options
Addressing the projected shortfall in Social Security reserves necessitates a multifaceted approach. Policymakers have several avenues to explore, each with its own set of implications for various stakeholder groups.
- Raising the Retirement Age: Increasing the age at which individuals can claim full retirement benefits is a frequently discussed option. This approach would lessen the strain on the program by extending the period during which funds are accumulated. However, it could negatively impact workers, especially those with limited earning potential or facing health challenges. For example, if the retirement age were raised to 70, this would lessen the burden on the system but could disproportionately affect those with fewer years of earning potential.
The long-term impact on individuals and the economy must be carefully evaluated.
- Increasing the Earnings Base: Adjusting the maximum amount of earnings subject to Social Security taxes could increase revenue for the program. However, this might disproportionately impact high-income earners, potentially leading to economic consequences for those industries. For example, increasing the ceiling on earnings could raise significant revenue, but it could also impact incentives for high-income individuals.
- Modifying Benefit Formulas: Adjusting the formulas used to calculate benefits could lead to more efficient resource allocation. For instance, adjusting formulas to reduce benefits for higher earners could reduce the burden on the program. However, this could affect the financial security of higher earners who have invested their resources in their careers. The impact on various income brackets must be fully evaluated.
- Investment Strategies: Implementing alternative investment strategies for Social Security funds could potentially generate higher returns. For instance, diversifying investments could generate greater returns and bolster the reserves. However, this would carry the risk of market fluctuations, which could have a negative impact on the program.
Impact Analysis on Stakeholder Groups
Understanding the potential impact of these policy options on different stakeholders is critical. Different groups will be affected differently, necessitating a nuanced approach to policymaking.
- Workers: Raising the retirement age could negatively affect workers, particularly those with health issues or limited earning potential. Increasing the earnings base could benefit workers with higher salaries. Modifying benefit formulas could have a varied impact, potentially affecting high-income earners more than lower-income earners. Investment strategies, if successful, would have a positive impact on the longevity of the system and benefit future workers.
- Retirees: Changes to benefit formulas could negatively affect retirees, especially those with lower incomes. Investment strategies, if successful, would enhance the sustainability of benefits for retirees. Raising the retirement age would positively affect the long-term health of the system and, therefore, benefit retirees in the future.
- Future Generations: Implementing proactive policies now can significantly enhance the sustainability of the program for future generations. A strong Social Security system provides a critical safety net and ensures financial security for future retirees.
Potential Solutions to Bolster Reserves
A comprehensive strategy for bolstering Social Security reserves requires careful consideration of various solutions. Implementing multiple strategies simultaneously may yield the best results.
- Reforming benefit calculation: Modifying formulas could reduce benefits for higher earners. This approach could lessen the burden on the program while ensuring financial security for all beneficiaries. This approach could help address the growing gap between the program’s projected costs and revenue.
- Increasing tax rates: Increasing payroll taxes, albeit controversial, could significantly boost the program’s revenue. This strategy is a direct approach to addressing the immediate financial needs of the system. However, this could lead to a decrease in worker’s disposable income and economic impact.
Policy Responses to Report Findings
| Policy Response | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Raising the retirement age | Reduces strain on reserves | Negative impact on workers with limited earning potential |
| Increasing the earnings base | Increases revenue | Disproportionate impact on high-income earners |
| Modifying benefit formulas | Potentially reduces cost | Potential negative impact on certain income groups |
| Alternative investment strategies | Potentially higher returns | Risk of market fluctuations |
Public Understanding and Engagement

The Social Security system’s future is a critical concern for millions. Accurate and accessible information is paramount to fostering informed public discourse and encouraging proactive engagement. Understanding the complexities of the system and its potential challenges is crucial for individuals to make sound financial decisions and for policymakers to develop effective strategies.
Simplifying the Report’s Findings
The report on Social Security reserves contains complex data and projections. To ensure broader public understanding, the findings need to be presented in a clear, concise, and relatable manner. This involves translating technical jargon into plain language, using visual aids like charts and graphs, and providing real-world examples that demonstrate the implications of the projections. For example, explaining how a $1000 annual decrease in benefits might affect a retiree’s lifestyle can be more impactful than simply stating the projected percentage decrease.
Using analogies to everyday financial situations can also help people grasp the concepts more easily.
Effective Communication Strategies
Engaging the public effectively requires a multifaceted approach. This includes utilizing diverse communication channels such as social media, public forums, and local community events. Social media platforms, with their wide reach and interactive features, can be invaluable tools for disseminating information, answering questions, and fostering dialogue. Public forums, town halls, and workshops can provide opportunities for direct interaction with policymakers and experts, allowing for a more personalized understanding of the issue.
Educating Individuals
Education is key to long-term understanding. Individuals need to comprehend the long-term implications of the Social Security system and how their actions today affect their future. Educational programs can explain the system’s structure, the factors influencing its sustainability, and how personal savings can complement Social Security benefits. These programs should cover the interplay between individual choices and the system’s overall health.
For example, the concept of maximizing personal retirement savings to offset potential future shortfalls can be clearly explained.
Outreach Programs and Fostering Discussion
Outreach programs should aim to foster public discussion and engagement. These programs should include interactive workshops, webinars, and online discussion forums to create opportunities for dialogue and knowledge sharing. Collaborations with community leaders and organizations can help ensure the programs resonate with various segments of the population. Encouraging feedback and input from participants is crucial for developing relevant and actionable solutions.
Communication Methods and Effectiveness
| Communication Method | Target Audience | Effectiveness | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Social Media (e.g., Facebook, Twitter, YouTube) | Millennials, Gen Z | High, due to broad reach and engagement potential | Interactive polls, infographics, live Q&A sessions |
| Local Community Events (e.g., town halls, workshops) | Older adults, those with limited internet access | High, promotes direct interaction and trust | Panel discussions, presentations, question-and-answer sessions |
| Educational Materials (e.g., pamphlets, brochures, website resources) | All segments | Moderate, for initial awareness and reference | Clear summaries, easily digestible content, downloadable resources |
| Partnerships with Financial Institutions | Individuals planning for retirement | High, due to trusted channels and relevant expertise | Integration of Social Security information into financial literacy programs, retirement planning tools |
Final Thoughts
The new report on Social Security reserves provides a comprehensive analysis of the program’s future. It highlights the potential challenges ahead and the crucial need for informed discussion and potential policy adjustments. Understanding the projected depletion date, alongside the factors that influence it, is essential for ensuring the long-term sustainability of Social Security. The report emphasizes the importance of public engagement and policy solutions to address this critical issue.





