Microsoft Windows Shadow Brokers NSA hacks patched. This significant event highlights a critical moment in cybersecurity history, revealing the extent of nation-state hacking and the subsequent efforts to secure vulnerable systems. The leak of NSA hacking tools, detailed analysis of the exploits, and Microsoft’s swift response to patch vulnerabilities all play a crucial role in understanding the intricate dynamics of cyber warfare.
This deep dive explores the technical aspects of the attacks, their impact on Windows security, and the broader implications for global cybersecurity.
The Shadow Brokers incident, a pivotal moment in modern cybersecurity, exposed a sophisticated network of vulnerabilities. The leaked tools provided a chilling insight into the capabilities of state-sponsored hacking groups. This detailed analysis of the incident, the vulnerabilities, and Microsoft’s response offers a comprehensive understanding of the challenges and solutions in this ever-evolving landscape.
Historical Context of the Leaks
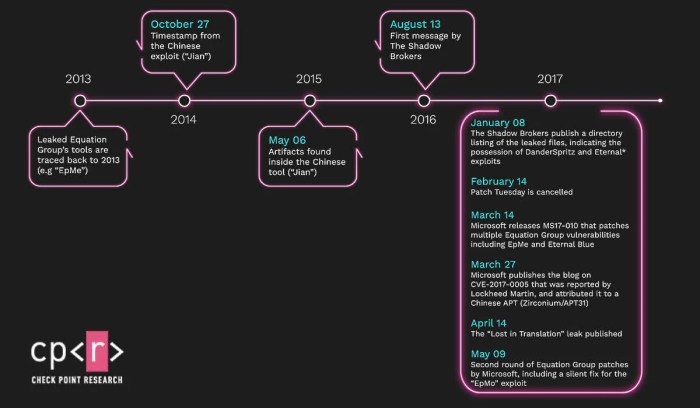
The Shadow Brokers incident, a series of leaks of hacking tools allegedly belonging to the National Security Agency (NSA), shook the cybersecurity world in 2017. These leaks exposed sophisticated hacking techniques and raised serious concerns about the potential for state-sponsored cyberattacks. The release of these tools created a ripple effect, impacting individuals, organizations, and the global cybersecurity landscape.The release of these tools represented a significant escalation in the cyber warfare landscape.
It wasn’t just about individual hackers; it demonstrated the capability of state-sponsored actors. This unprecedented disclosure brought a previously hidden realm of cyber capabilities into the open, forcing a re-evaluation of cybersecurity strategies worldwide.
Timeline of the Leaks
The Shadow Brokers’ leaks unfolded over several months, beginning with the release of a series of hacking tools. The chronological sequence provided insight into the development and evolution of these tools. Understanding this timeline highlighted the sophistication and persistent nature of the hacking techniques.
- 2017: Initial releases of hacking tools began, marking a significant escalation in the cyber warfare landscape. The tools, including exploits and malware, were gradually disseminated online. These tools were purportedly developed and used by the NSA for intelligence gathering and offensive operations. This revelation highlighted the potential for malicious actors to gain access to sensitive information and disrupt critical infrastructure.
- 2017: Subsequent releases followed, exposing further details of the NSA’s capabilities. These leaks provided a glimpse into the methods used by advanced persistent threat (APT) groups. The increasing volume of released information revealed more sophisticated exploits and malware, creating a greater risk for individuals and organizations.
Initial Release of NSA Hacking Tools
The initial release of the NSA hacking tools showcased the sophisticated capabilities of state-sponsored actors. These tools, often described as zero-day exploits, allowed for unauthorized access to computer systems.
- The tools included various exploits targeting vulnerabilities in widely used software. This demonstrated the potential for widespread impact if these vulnerabilities were exploited. The range of targets included operating systems, networking protocols, and applications.
- The release demonstrated a significant escalation in the sophistication of hacking tools available to malicious actors. The level of access granted by these tools posed a serious threat to organizations of all sizes.
Significance of the Leak in Cybersecurity
The Shadow Brokers incident highlighted the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures. The leak exposed vulnerabilities and demonstrated the capacity for state-sponsored actors to compromise systems.
So, patching up those Microsoft Windows vulnerabilities exposed by the Shadow Brokers and NSA hacks is crucial, right? It’s all about security, but it also makes you wonder about the bigger picture, like the choices we face in the Matrix. The Matrix Resurrections teaser, with its red and blue pill dilemma, the matrix resurrections teaser red blue pill , prompts us to question the nature of reality itself.
Ultimately, though, those patched Windows systems are still vital to our digital security, so it’s a good thing that’s been addressed.
- The incident emphasized the importance of proactive vulnerability management. Organizations needed to prioritize the identification and remediation of vulnerabilities in their systems. Organizations were forced to enhance their security postures to counter the risks presented by the exposed tools.
- The incident underscored the importance of incident response plans. Organizations needed to develop and practice strategies to respond to potential cyberattacks. The leak provided a valuable opportunity to identify and address weaknesses in incident response procedures.
Impact on Various Systems and Organizations
The leak had significant repercussions for various systems and organizations. The potential for misuse of the disclosed tools was a major concern.
- Organizations across various sectors, including government agencies, financial institutions, and critical infrastructure providers, were at risk. The incident highlighted the potential for a cascading effect if these tools were employed in coordinated attacks. It brought to light the importance of collaboration among organizations and governments to counter the threat.
- The release of these tools could lead to increased cyberattacks. The tools provided a blueprint for attackers, making it easier for them to compromise systems. This could potentially result in significant financial losses and damage to reputations. The potential for a cascading effect of cyberattacks underscores the need for comprehensive security measures.
Reactions and Responses from Affected Parties
The Shadow Brokers incident triggered various reactions and responses from affected parties. Organizations scrambled to assess their vulnerabilities and implement mitigation strategies.
- Affected organizations took steps to patch vulnerabilities. The incident prompted a global response in the form of software updates and security hardening efforts. The leak highlighted the urgent need for rapid patching and vulnerability management.
- The incident also spurred increased awareness and concern about state-sponsored cyberattacks. This highlighted the need for a more robust international framework for cybersecurity and accountability.
Nature of the Exploits
The Shadow Brokers’ leak of NSA exploits revealed a trove of sophisticated vulnerabilities, offering a glimpse into the inner workings of advanced persistent threat (APT) methodologies. These exploits, many of which were previously unknown, highlight the potential for widespread damage and the urgent need for robust security measures. The disclosed techniques represent a significant escalation in the sophistication of cyberattacks, demanding careful consideration of their implications.The Shadow Brokers’ leaks unveiled a diverse range of exploits targeting various software and operating systems.
These exploits demonstrate the meticulous planning and resources behind state-sponsored hacking operations. The technical details, while often complex, offer valuable insights into vulnerabilities and allow for the development of effective countermeasures.
Types of Exploits
The leaked exploits spanned a wide spectrum of attack vectors. They included vulnerabilities in network protocols, kernel-level exploits, and application-layer flaws. These exploits were often highly targeted, designed to bypass standard security measures and infiltrate systems undetected.
Technical Details of Disclosed Vulnerabilities
The technical details of the leaked vulnerabilities varied considerably. Some exploited buffer overflows, while others targeted vulnerabilities in cryptographic libraries. Specific exploits utilized intricate techniques to exploit vulnerabilities, demonstrating advanced knowledge of software architecture and system behavior. The level of sophistication in the exploits revealed an understanding of the intricacies of operating systems, making them particularly challenging to mitigate.
Examples included highly specialized memory corruption exploits targeting specific memory management functions in operating systems. These sophisticated techniques, requiring in-depth understanding of the targeted systems, often allowed attackers to gain unauthorized access, execute arbitrary code, and manipulate system behavior.
Targeted Software and Operating Systems
The leaked exploits targeted a range of software and operating systems, indicating a broad scope of potential impact. The list included various versions of Microsoft Windows, notably affecting critical system components. This breadth of target indicates the potential for widespread damage and disruption if these vulnerabilities were exploited. Exploits targeting specific versions of Windows operating systems highlight the importance of timely security updates and patching.
While patching old Microsoft Windows vulnerabilities like the Shadow Brokers NSA hacks is crucial, it’s interesting to see how tech companies are focusing on preventative health. For example, Fitbit expanding AFib notifications globally fitbit expands afib notifications globally highlights a shift towards proactive health monitoring. Ultimately, these security and health advancements, while seemingly disparate, are all part of the larger digital landscape, and remind us that robust systems are built on multiple layers of protection.
Comparison to Previously Known Vulnerabilities
The leaked exploits presented a combination of previously known vulnerabilities and novel, previously undocumented flaws. This highlights the ongoing challenge of staying ahead of evolving threats and the continuous need for security research and development. Comparison to existing vulnerabilities revealed that some of the disclosed exploits leveraged known vulnerabilities but employed them in new and sophisticated ways.
List of Vulnerabilities
The sheer number and complexity of the disclosed vulnerabilities make a comprehensive list challenging. The following table summarizes the vulnerabilities categorized by software type.
| Software Type | Specific Vulnerabilities |
|---|---|
| Microsoft Windows | Exploits targeting kernel, memory management, and cryptographic libraries. Specific exploits targeted Windows Server 2003, Windows 7, and Windows XP, among others. |
| Network Protocols | Exploits focusing on vulnerabilities in network protocols like SMB, allowing for unauthorized access and control of network resources. |
| Other Software | Vulnerabilities in various other software packages, possibly including third-party applications, were also disclosed. |
Impact on Windows Security
The Shadow Brokers’ release of NSA-acquired hacking tools had a profound and lasting impact on the security of Windows systems worldwide. This leak exposed vulnerabilities previously unknown to the public, forcing Microsoft to react swiftly and significantly adjust its security posture. The incident highlighted the vulnerability of even the most sophisticated systems to sophisticated attacks, prompting a critical reassessment of security practices.
Microsoft’s Security Strategies Post-Leak, Microsoft windows shadow brokers nsa hacks patched
The Shadow Brokers’ leak served as a stark wake-up call for Microsoft. Prior to the leak, Microsoft’s security strategy, while effective in many areas, arguably lacked a comprehensive approach to handling zero-day exploits originating from nation-state actors. The leak exposed a critical gap in the strategy, necessitating a more proactive and reactive approach. This shift in focus led to a more comprehensive strategy, emphasizing proactive vulnerability identification and a more rapid patching process.
Patching Timeline and Impact
The timeline of patching releases for the disclosed exploits varied significantly depending on the specific vulnerability. Some exploits, deemed less critical, were patched within a few weeks of their disclosure, while others, considered high-risk, were addressed more rapidly. This demonstrates the importance of prioritization and risk assessment in vulnerability management. The speed of patching releases, while commendable, also underscored the need for more robust security monitoring and threat intelligence to anticipate future exploits.
For example, the patch for EternalBlue, a critical vulnerability exploited in the WannaCry ransomware attack, was released relatively quickly, but not before significant damage had been done.
Long-Term Effects on Windows Security Posture
The Shadow Brokers’ leak significantly altered the landscape of Windows security. It forced Microsoft to accelerate its vulnerability management process and adopt a more defensive posture. The incident also demonstrated the importance of collaboration between security researchers, software vendors, and government agencies in identifying and mitigating emerging threats. This collaboration is crucial for effectively addressing future threats.
Furthermore, the leak had a ripple effect on the broader cybersecurity industry, leading to increased investment in vulnerability research and threat intelligence gathering. For example, the rise of zero-day exploit kits and the subsequent need for constant security updates have become a new reality for all users.
Comparison of Pre- and Post-Leak Security Strategies
| Aspect | Pre-Leak Strategy | Post-Leak Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Proactive Vulnerability Identification | Reactive, focused on reported vulnerabilities | Proactive, incorporating threat intelligence and zero-day exploit research |
| Patching Process | Varied, sometimes slow | Accelerated, prioritizing critical vulnerabilities |
| Threat Intelligence Gathering | Limited, relying primarily on reported exploits | Enhanced, utilizing threat intelligence and advanced analytics |
| Collaboration with Security Researchers | Limited | Increased, recognizing the crucial role of security researchers in identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities |
Wider Implications on Cybersecurity
The Shadow Brokers leak, exposing NSA hacking tools, reverberated far beyond the immediate target of Microsoft Windows. It exposed vulnerabilities in the global cybersecurity landscape, forcing a reassessment of nation-state capabilities and prompting a broader discussion about the responsible use of advanced technologies. The leak’s impact was not limited to technical improvements; it profoundly affected international relations and public trust in technology.
Broader Implications on Global Cybersecurity
The leak underscored the interconnectedness of digital systems and the potential for widespread disruption. The disclosed tools were not merely theoretical; they had been used in real-world attacks, demonstrating the potential for malicious actors to exploit vulnerabilities on a large scale. This raised concerns about the security of critical infrastructure and the ability of nations to defend against sophisticated cyberattacks.
The leaked tools exposed vulnerabilities in various aspects of cybersecurity, including network security, software development, and patching procedures. This highlighted the importance of a holistic approach to cybersecurity, emphasizing the need for strong defenses at every level.
Lessons Learned About Nation-State Hacking
The Shadow Brokers incident provided valuable insights into the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) of nation-state actors. The leak exposed the sophistication and resourcefulness of these actors, demonstrating their ability to develop and deploy highly advanced tools. Furthermore, the incident highlighted the need for proactive security measures and a greater understanding of the adversary’s capabilities. The leak prompted a shift in the focus of cybersecurity efforts, with an emphasis on threat intelligence gathering and a proactive defense posture.
So, the patched Microsoft Windows Shadow Brokers NSA hacks are finally behind us. It’s interesting to note that this security issue, along with the recent news of the official completion of the T-Mobile and Sprint merger, t mobile and sprint merger officially completed , highlights a constant struggle between the need for innovation and the threat of cyber vulnerabilities.
These are just the types of issues that keep security experts up at night. Ultimately, though, the focus remains on ensuring robust security measures for our digital world.
It demonstrated the necessity for strong collaboration between governments, private sector entities, and researchers to mitigate future threats.
Influence on the Development of New Security Tools and Practices
The Shadow Brokers leak significantly influenced the development of new security tools and practices. Security researchers and companies were spurred to develop more robust detection and prevention mechanisms to identify and counteract similar exploits. This led to the creation of advanced threat intelligence platforms and improved vulnerability scanning tools. The incident accelerated the development of machine learning-based security solutions capable of identifying malicious activity and anomalies in real time.
The leak underscored the importance of continuous security monitoring and proactive threat hunting, driving innovation in security technologies.
Impact on International Relations and Trust in Technology
The Shadow Brokers incident significantly impacted international relations. The revelation of nation-state hacking capabilities fueled distrust and suspicion among nations. The leak eroded public trust in the security of technology, raising concerns about the potential for misuse of advanced technologies by governments. This, in turn, spurred the need for international cooperation and regulatory frameworks to govern the use of advanced technologies.
The incident underscored the need for transparency and accountability in the development and deployment of powerful technologies.
Organizational Responses to the Leak
| Organization Category | Response Strategies |
|---|---|
| Government Agencies | Increased cybersecurity budgets, enhanced intelligence gathering, and strengthened international collaborations. |
| Software Vendors | Prioritized patching of vulnerabilities, enhanced security audits, and improved incident response procedures. |
| Security Researchers | Developed new detection methods, enhanced threat intelligence sharing, and collaborated to mitigate the risks associated with the leaked tools. |
| Private Sector Organizations | Implemented enhanced security measures, conducted vulnerability assessments, and prioritized incident response planning. |
The table above demonstrates the diverse reactions of various organizations to the Shadow Brokers leak. Each category reacted in ways that reflected their unique roles and responsibilities in the cybersecurity landscape. The responses highlight the interconnectedness of the cybersecurity ecosystem and the need for a coordinated approach to mitigate threats.
Vulnerability Analysis and Mitigation: Microsoft Windows Shadow Brokers Nsa Hacks Patched
The Shadow Brokers leaks revealed a trove of sophisticated NSA exploits, highlighting critical vulnerabilities in Microsoft Windows systems. Understanding these vulnerabilities and implementing effective mitigation strategies is crucial for preventing future attacks. A methodical approach to analyzing severity, developing mitigation strategies, and establishing robust patching procedures is essential for maintaining system security.Analyzing the disclosed vulnerabilities and devising a response is paramount to preventing future attacks.
This requires a layered approach to patching and vulnerability management, considering the unique characteristics of each system type.
Severity Classification Methodology
A standardized vulnerability classification system is essential for prioritizing remediation efforts. This system should consider factors like the exploit’s potential impact, the ease of exploitation, and the prevalence of the affected software. A numerical scale, for example, from 1 (low) to 10 (critical), could be used. This scale should correlate with the likelihood of a successful attack and the potential damage.
The system should be easily understandable and consistently applied across the organization.
Mitigation Strategies
Effective mitigation strategies must address the vulnerabilities revealed in the Shadow Brokers leaks. These strategies should focus on a multi-layered approach to security, encompassing both technical and procedural elements. Implementing strong access controls, regularly updating software, and educating users on security best practices are all crucial components of a comprehensive mitigation strategy. Patching alone is not sufficient; a robust security posture is required.
Vulnerability Patching Procedure
A standardized patching procedure is crucial in a corporate environment. A step-by-step guide ensures consistent application and minimizes the risk of errors.
- Vulnerability Identification: Regularly scan systems for known vulnerabilities using automated tools. This could involve using vulnerability scanners or employing security information and event management (SIEM) systems to identify exposed systems.
- Prioritization: Apply the severity classification methodology to prioritize vulnerabilities based on their potential impact and exploitability. High-severity vulnerabilities should be addressed first.
- Patch Deployment: Download appropriate patches from official vendor sources. Verify the integrity of the downloaded patches to prevent malicious code insertion. Patching should be done in a phased approach, testing the impact on systems in a controlled environment before applying to the entire network.
- System Validation: Thoroughly test patched systems to ensure functionality and stability. This involves running diagnostic tools and monitoring system performance after the patch implementation.
- Documentation: Maintain detailed records of all patching activities, including the date, time, applied patches, and any observed issues. This will be critical for auditing purposes and tracking progress.
Recommended Security Practices
To prevent similar attacks, organizations must adopt a proactive security posture.
- Regular Software Updates: Establish a policy for regularly updating software and operating systems. This is essential for addressing known vulnerabilities.
- Strong Password Policies: Enforce strong password policies and regularly audit user accounts to identify and address potential security risks.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement MFA wherever possible to enhance the security of user accounts.
- Security Awareness Training: Educate employees on phishing attacks and other social engineering tactics. Training should be regular and ongoing to keep employees informed about the latest threats.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): Deploy IDS/IPS systems to detect and block malicious activity. This is essential to identify and prevent unauthorized access and attacks.
Patching Steps for Different System Types
A structured approach to patching is vital. This table Artikels steps for patching different system types.
| System Type | Patching Steps |
|---|---|
| Servers |
|
| Workstations |
|
| Mobile Devices |
|
Case Studies of Affected Systems
The Shadow Brokers leak exposed vulnerabilities in Microsoft Windows, leaving numerous organizations susceptible to exploitation. Understanding how these attacks manifested and were addressed offers crucial insights into the real-world impact of such cyber breaches and the evolving nature of cybersecurity threats. Analyzing specific case studies provides a tangible demonstration of the potential damage and the measures taken to recover, ultimately contributing to a more robust understanding of defensive strategies.
Specific Examples of Impacted Organizations
Several organizations, ranging from government agencies to private corporations, experienced direct consequences from the exploited vulnerabilities. The leaked exploits were not limited to a specific sector or size of organization, highlighting the broad scope of potential impact. While precise details regarding specific organizations remain often limited due to privacy concerns, the general impact on various sectors is evident.
Damage and Disruption Caused
The damage and disruption caused varied depending on the specific organization and the nature of the exploit utilized. Some organizations suffered data breaches, while others experienced significant operational disruptions. In some cases, the attacks were highly targeted, resulting in financial losses and reputational damage. The effects could range from minor inconvenience to catastrophic system failures, highlighting the unpredictable nature of cyberattacks.
Organizational Responses to Attacks
Organizations reacted to the attacks in various ways, reflecting their preparedness and resources. Some immediately implemented patches and security measures, while others faced challenges in quickly adapting to the threat. The response also depended on the organization’s awareness of the vulnerabilities and their ability to implement mitigation strategies.
Recovery Efforts and Measures Taken
Organizations engaged in various recovery efforts, encompassing technical and operational strategies. These ranged from system restoration to legal and public relations activities. Some organizations might have prioritized the containment of the damage to minimize further impact, while others might have focused on rebuilding systems and restoring services. The duration and complexity of the recovery process depended on the severity of the breach and the organization’s capacity to address the situation.
Summary Table of Case Studies
| Affected System Category | Damage Description | Recovery Efforts |
|---|---|---|
| Financial Institutions | Potential for unauthorized access to sensitive customer data, leading to financial losses and reputational damage. Disruption of online banking services. | Implementation of enhanced security measures, including multi-factor authentication, improved firewall configurations, and increased security awareness training. Review and update of data encryption policies. |
| Government Agencies | Compromised sensitive data, potentially including classified information. Disruption of critical services, impacting public safety and security. | Immediate patching of vulnerable systems, emergency response protocols activation, and increased security monitoring. Assessment of the extent of the compromise and subsequent data recovery measures. |
| Healthcare Providers | Breach of patient data, potentially compromising confidential medical records and potentially violating privacy regulations. Disruption of patient care and operations. | Immediate containment measures to prevent further data exposure, compliance with data breach notification laws, and implementation of improved security protocols to protect patient information. |
Future Trends in Cyber Warfare
The Shadow Brokers incident, along with other high-profile breaches, underscores the ever-evolving nature of cyber warfare. The sophistication and frequency of attacks are increasing, driven by readily available tools and the escalating value of digital assets. Understanding these trends is crucial for anticipating and mitigating future threats.
Potential Impact of Similar Incidents
The repercussions of future breaches will likely mirror the past but on an amplified scale. Increased reliance on interconnected systems across industries will expose more critical infrastructure to potential attacks. A successful attack on a vital component of the global financial system, for example, could have far-reaching economic consequences, potentially leading to widespread financial instability. Moreover, attacks on critical infrastructure, like power grids or water systems, could result in catastrophic physical and societal disruption.
Emerging Threats and Vulnerabilities
The landscape of cyber threats is constantly evolving. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are not only employed for defense but are also being integrated into offensive strategies. Sophisticated AI-powered tools can automate attacks, making them faster, more efficient, and more difficult to detect. The increasing use of IoT (Internet of Things) devices creates a vast attack surface, with many devices lacking adequate security measures.
The potential for widespread disruption from a coordinated attack targeting a large network of IoT devices is significant. Supply chain attacks, where malicious code is introduced into legitimate software or hardware, represent another evolving threat vector.
Anticipating and Preparing for Future Attacks
Proactive measures are essential to mitigate the impact of future attacks. Robust security protocols, including multi-factor authentication, regular security audits, and intrusion detection systems, are crucial. Developing a strong incident response plan, capable of quickly identifying, containing, and recovering from breaches, is also critical. Collaboration between governments, industry, and researchers is vital for sharing threat intelligence and developing effective defenses.
Evolution of Nation-State Hacking Techniques
Nation-state actors are constantly adapting their hacking techniques. Advanced persistent threats (APTs) are becoming more sophisticated, utilizing zero-day exploits and sophisticated social engineering tactics. The blurring lines between cyber espionage and cyber warfare is a concerning trend. A nation-state could conduct an attack targeting a critical infrastructure in another nation under the guise of espionage.
Potential Impact on Individuals and Corporations
Individuals and corporations are increasingly exposed to cyber threats. Phishing scams, malware infections, and data breaches can result in significant financial losses, reputational damage, and personal harm. Data breaches can compromise sensitive personal information, leading to identity theft and financial fraud. The increasing importance of digital assets in daily life makes individuals and corporations more vulnerable. Corporations will need to prioritize cyber security investments, potentially resulting in increased operating costs.
Illustrative Example of a Vulnerability

The Shadow Brokers leaks revealed a trove of NSA exploits, exposing critical vulnerabilities in various software systems, particularly Microsoft Windows. Understanding these vulnerabilities is crucial for bolstering cybersecurity defenses. This example delves into a specific exploit, demonstrating its mechanics and potential impact.A key element of these exploits is the manipulation of system processes and memory management. This example illustrates a vulnerability that allows attackers to gain unauthorized access to a system.
Specific Vulnerability Description
This vulnerability, targeting the Windows kernel, leverages a flaw in the way the system handles memory allocation. Specifically, the vulnerability lies in a function responsible for managing memory blocks. This function fails to properly validate input data, leading to a buffer overflow condition.
Exploit Mechanics
The exploit exploits the buffer overflow vulnerability by providing carefully crafted input data. This data exceeds the allocated buffer size, overwriting adjacent memory locations. This manipulation allows attackers to inject malicious code into the system’s memory space.
- The attacker crafts a specific sequence of data, exceeding the allocated buffer size.
- This oversized data overwrites adjacent memory locations, potentially including critical system functions.
- The overwritten memory now contains the attacker’s malicious code.
- When the vulnerable function executes, it inadvertently executes the attacker’s code, granting unauthorized access.
Vulnerability Impact
A successful exploitation of this vulnerability allows an attacker to gain full control of the compromised system. This can include:
- Executing arbitrary code.
- Accessing sensitive data.
- Installing malware.
- Launching further attacks on the network.
Illustrative Example of Compromise
Imagine a company’s server hosting sensitive customer data. An attacker, exploiting this kernel vulnerability, could inject malicious code. This code might silently steal customer records or even disrupt the server’s operation, leading to significant financial and reputational damage.
Visual Representation of Exploit Process
| Step | Description | Visual Representation (Conceptual) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Attacker crafts oversized data input. | [Conceptual representation of oversized data being input into a buffer] |
| 2 | Overwritten memory now contains malicious code. | [Conceptual representation of memory being overwritten with malicious code] |
| 3 | Vulnerable function executes, executing malicious code. | [Conceptual representation of the vulnerable function triggering execution of malicious code] |
| 4 | Attacker gains control of the system. | [Conceptual representation of a malicious code gaining control of the system] |
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, the patching of Microsoft Windows vulnerabilities exposed by the Shadow Brokers incident serves as a crucial lesson in cybersecurity. The incident underscored the importance of proactive vulnerability management and the need for robust security practices. While the immediate threat has been mitigated, the lessons learned from this event remain critical for future preparedness against similar attacks. The intricate dance between attackers and defenders will continue to evolve, demanding ongoing vigilance and adaptation in the ever-changing world of cybersecurity.